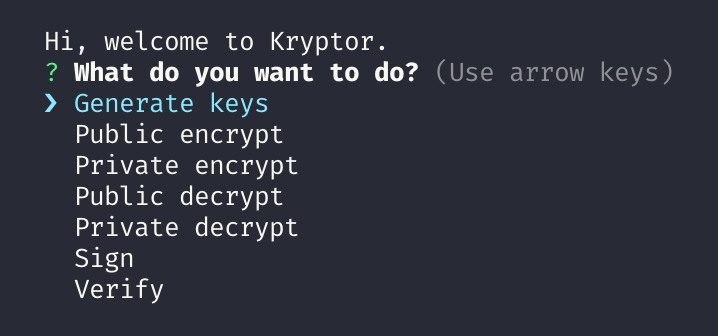
A CLI to generate RSA key (private and public), public encrypt, private decrypt, private encrypt, public decrypt, sign & verify.
These instructions will help you to get this project on your own machine and run the 7 available commands.
The only thing you must have is NodeJs 10.14+.
Check the NodeJs documentation to know how to install it: https://nodejs.org
To get the project run the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/GillianPerard/kryptor.gitThen run the npm command to install all dependencies:
npm ciNow normally, everything should be ready to use.
Go to the project folder then go to src folder.
There you can run the following commands.
To display the documentation:
node kryptor -h
# or
node kryptor --helpTo generate private and public keys into the desired folder with the desired key size (private.pem and public.pem):
Command:
generate | g <keySize> [Required] Key size in bits
Options:
-e, --export <destFolder> [Required] Destination folder
-h, --help Output usage information
# Example: node krypto generate 2048 -e .To encrypt a text with a public key (encoding: base64):
Command:
public-encrypt | pcet
Options:
-p, --publicKey <path> [Required] Path of the public key
-f, --fileToEncrypt <path> [Required] Path of the file to encrypt
-e, --export <path> [Required] Path of the encrypted file
-h, --help Output usage information
# Example: node krypto public-encrypt -p public.pem -f file.txt -e file.encTo decrypt an encrypted text with a private key which matches with a public key (from encoding: base64):
Command:
private-decrypt | pedt
Options:
-p, --privateKey <path> [Required] Path of the private key
-f, --fileToDecrypt <path> [Required] Path of the file to decrypt
-e, --export <path> [Required] Path of the decrypted file
-h, --help Output usage information
# Example: node krypto private-decrypt -p private.pem -f file.enc -e file.txtTo encrypt a text with a private key (encoding: base64):
Command:
private-encrypt | peet
Options:
-p, --privateKey <path> [Required] Path of the private key
-f, --fileToEncrypt <path> [Required] Path of the file to encrypt
-e, --export <path> [Required] Path of the encrypted file
-h, --help Output usage information
# Example: node krypto private-encrypt -p private.pem -f file.txt -e file.encTo decrypt an encrypted text with a public key which matches with the private key (from encoding: base64):
Command:
public-decrypt | pcdt
Options:
-p, --publicKey <path> [Required] Path of the public key
-f, --fileToDecrypt <path> [Required] Path of the file to decrypt
-e, --export <path> [Required] Path of the decrypted file
-h, --help Output usage information
# Example: node krypto public-decrypt -p public.pem -f file.enc -e file.txtTo create a signature for a given file.
Command:
sign | s
Options:
-p, --privateKey <path> [Required] Path of the private key
-f, --fileToSign <path> [Required] Path of the file to sign
-e, --export <path> [Required] Path of the signature
-h, --help Output usage information
# Example: node krypto sign -p private.pem -f file.txt -s file.signTo verify that a file is not forged thanks to the signature file.
Command:
verify | v
Options:
-p, --publicKey <path> [Required] Path of the public key
-f, --fileToVerify <path> [Required] Path of the file to verify
-s, --signature <path> [Required] Path of the signature
-h, --help Output usage information
# Example: node krypto verify -p public.pem -f file.txt -s file.sign
# Returns: 'Verified OK' or 'Verified Failure'Instead of use the CLI if you don't know how to or just because you think it's boring to remember you all options; you can use Kryptor thanks to the easy-kryptor.js file.
Run the one of the following commands to start the program and follow the instructions:
npm startnode easy-kryptorExample:
For the moment there is only one test that checks all command from kryptor.js.
To run it, use the following command from the root directory:
npm testGillian Pérard - Creator - GillianPerard
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details