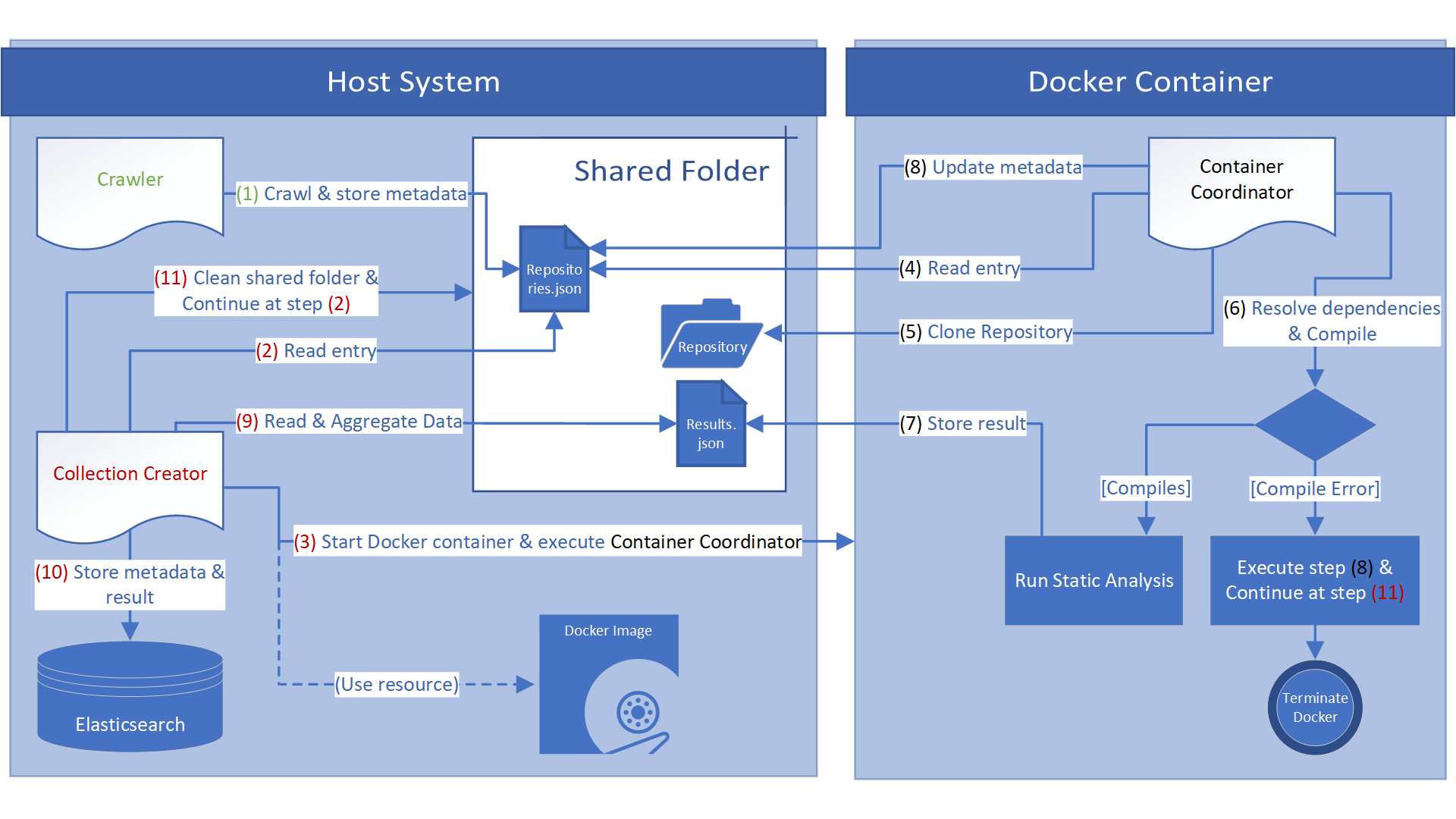
Researchers are heavily committed towards improving and developing new static analysis tools and algorithms. Hence, it creates the necessity to evaluate their validity and performance. The best way to compare and test the effectiveness of such tools or algorithms, is to let them analyse the same code base, also called benchmark suite, and compare their results. Thus for the systematic evaluation of such tools benchmark suites are required that are representative of real world applications that are up-to-date. Yet current benchmark suites only exist for few research areas and are often insufficiently maintained. This repository introduces a benchmark system that develops a knowledge database by collecting information of C/C++ open-source repositories using static code analysis. The focus is especially on the automation of the overall benchmark system's process.
All components of the benchmark system are implemented in Java. It facilitates the collection of repository metadata and code statistics through static analysis in an automatic manner. All information collected throughout the benchmark system's process, i.e. static analysis results, are stored into a database. These information serve as a starting point for creating current, targeted benchmark suites, and thus helps to evaluate static analysis tools and algorithms. It does so by automatically crawling for suitable open-source repositories published on GitHub. Subsequently, each repository is automatically downloaded, software dependencies are resolved with Conan and the source code is compiled with the CMake build system. Each successful compilation is followed by the extraction of the repository's LLVM IR code and static analysis of it using the static analysis framework PhASAR. Finally, all collected data is stored into an Elasticsearch database.
Tests show that more than 40% of 176 crawled repositories are successfully built by the proposed benchmark system. Consequently, the benchmark system collected metadata of 176 repositories and code statistics of 616 executables, 32 libraries and 90 archives. (Results from Dec. 2019)
Elasticsearch 7.4.0
Docker
$ wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -$ sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https$ echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.list\$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install elasticsearch$ sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io$ docker build -t conan-cmake:clang .$ sudo systemctl start elasticsearch.service3. Go to the Program folder and run the Crawler
$ java -jar Crawler.jar4. Go to the Program folder and run the Collection Creator
$ sudo java -jar CreateCollection.jar$ sudo java -jar CreateCollection.jar [NUMBER]