NBIOT -> Azure IoT HuB cloud-gw
The code provided in this sample is not production ready and was built for demonstration and illustration purposes. Hence, the code has sample quality. We have done some basic and scalability testing but no in depth validation.
Architecture
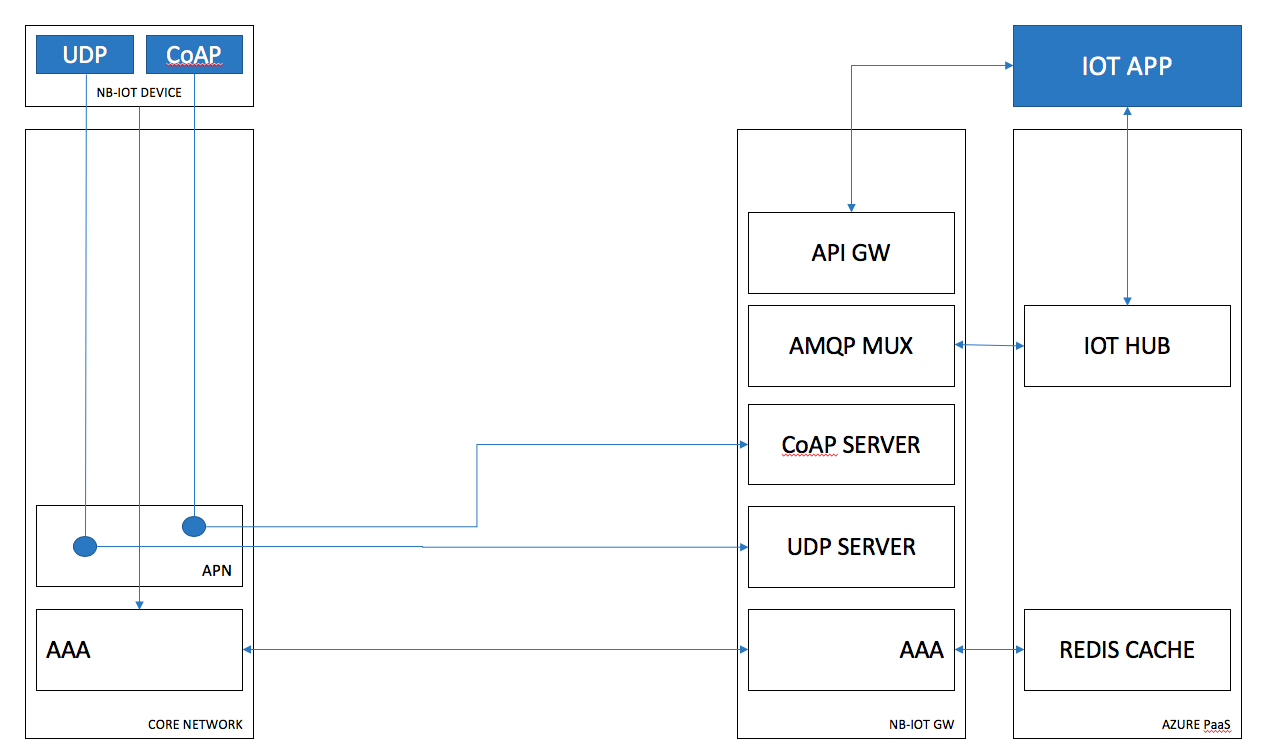 This App provides an interface for NB-IoT devices to interact with Azure IoT Hub, while it still not supporting UDP and able to terminate VPNs.
The device communication can be done on IPv4 or IPv6, all the other communication will be over IPv4.
This App provides an interface for NB-IoT devices to interact with Azure IoT Hub, while it still not supporting UDP and able to terminate VPNs.
The device communication can be done on IPv4 or IPv6, all the other communication will be over IPv4.
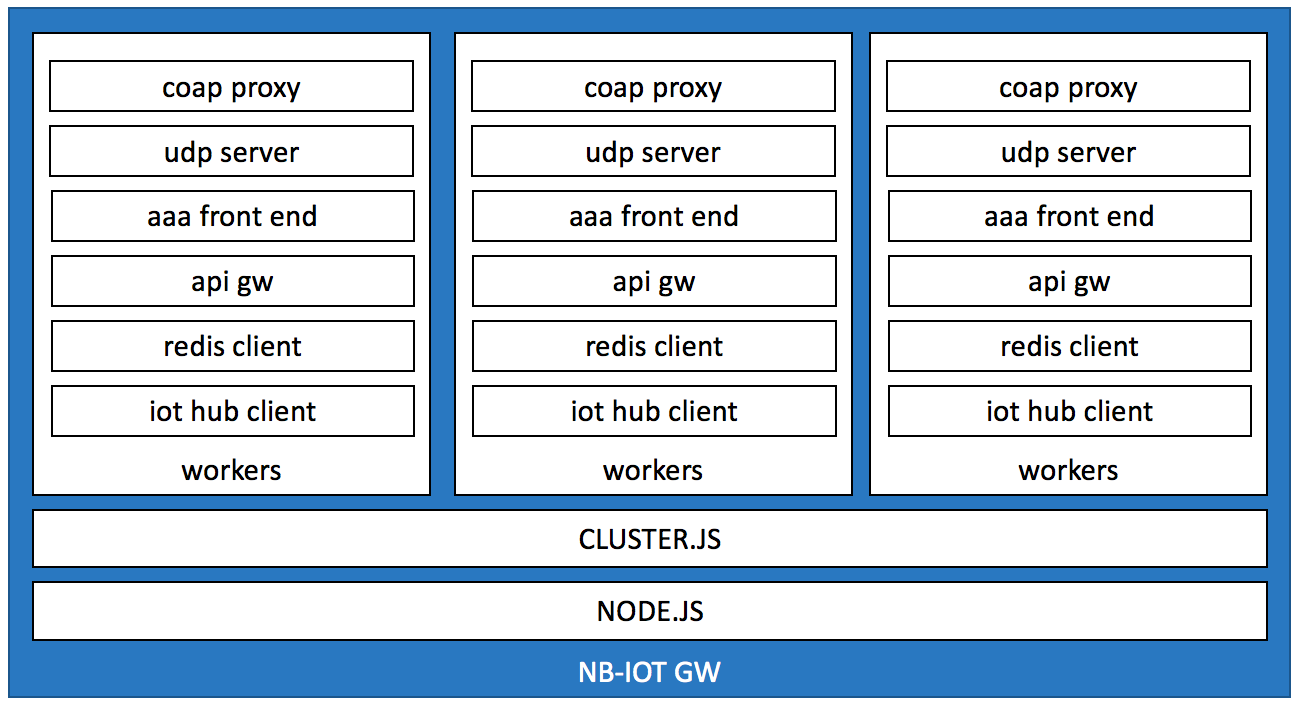
The GW can be deployed in a kubernetes cluster (yaml for AKS in this repo), as a docker application (docker pull lucarv/nbiot-gateway) or on any machine with node installed.
The gateway is a cluster with as many worker nodes as there are CPUs in the host machine. It can be executed stand-alone just typing npm start or npm run-script debug at the command prompt.
It can be run as a docker container by typing
(sudo) docker run -it --name nig --network host -v [some path in the host disk]:/usr/src/app/data -p1815:1815/UDP -p41234:41234/UDP -p41235:41235/UDP -p5683:5683/UDP lucarv/nbiot_iothub_gateway
Note that the gateway needs to run outside docker bridge adapter to get hold of the devices IP addresses
The application needs a configuration file called config.json as follows:
{
"connectionString": <get the iothubowner CS from your Iot Hub in Azure>,
"ipVersion": "udp4" (or ipv6),
"redis": {
"key": <get the that from your Redis Cache in Azure>,
"url": <get the that from your Redis Cache in Azure>
},
"ports": {
"radius": "1815",
"udp_raw_d2c": "41234",
"udp_raw_c2d": "41235",
"coap": "5683"
}
}
(Note that the ports above can be changed according to your IP Network planning)
The GW uses The following ports:
- UDP port 1815 for RADIUS
- UDP port 41234 for D2C messages
- UDP port 41235 for C2D messages
- UDP port 5683 for CoAP
- TCP port 8080 for API calls
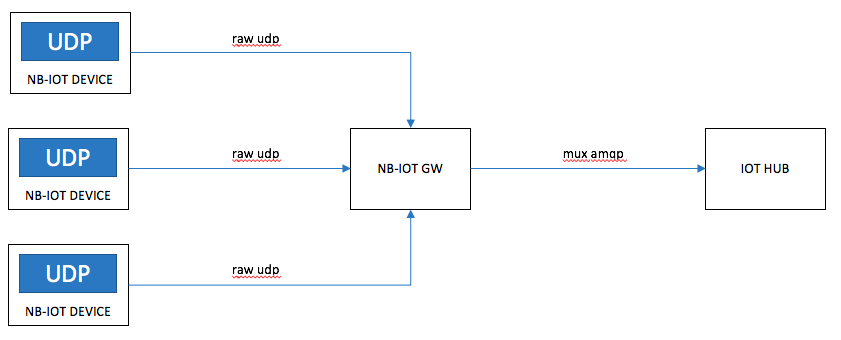
Use Case 1:
An UDP device sends a raw datagram to the GW that forwards to IoT Hub over AMQP.
The message can be anything you want and in the device simulator included in this repo you can type whatever you like at the command prompt.
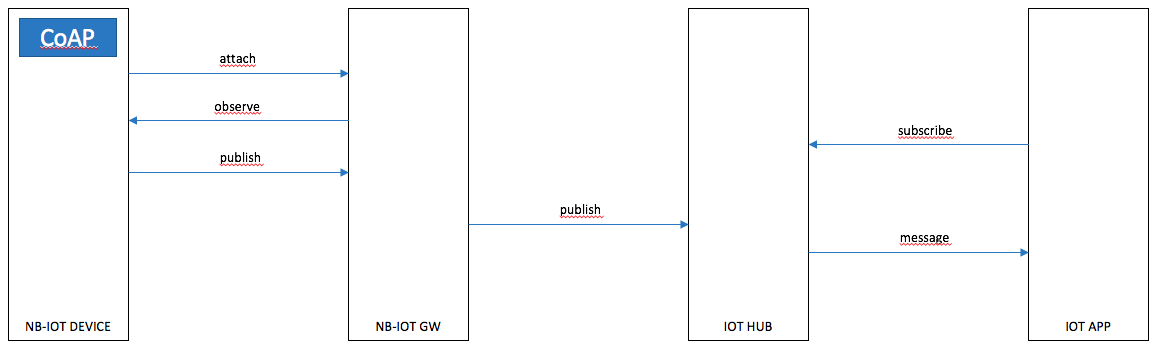
Use Case 2:
An CoAP device attaches to the network and has its messages forwarded to all applications that are observing CoAP devices.
Note that this example will let applications observe all CoAP devices that can be observed using the app connection string. To make sure that an app only receive messages from devices it observes, an intermediary filtering needs to be created.
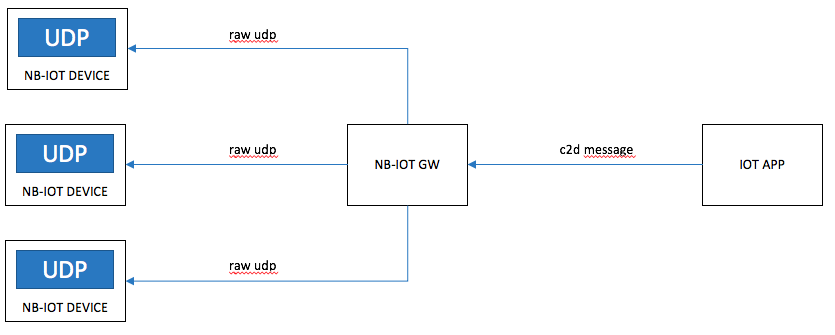
Use Case 3:
An application requests to send a message to a device as a raw datagram via the GW.
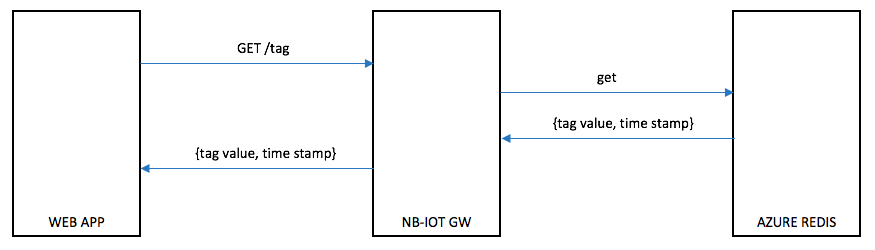
Use Case 4:
An application requests the last reported tag from a device using a REST API.
- Provision your devices on your IoT Hub.
- Start the GW (npm start). Edit the environment variables to point at the correct IoT Hub.
- Get the AAA Simulator.
- Get an NBIOT device simulator.
NOTE
Both the GW and the IoT Hub are payload agnostic, and it is up to the application layer to parse the messages.
TO DO
- Extensive error handling
- DTLS Support
- Resource discovery
- Proxy caching
- Multicast
- C2D to CoAP device
- Proper API management