UdaConnect - Microservices
Overview
Background
Conferences and conventions are hotspots for making connections. Professionals in attendance often share the same interests and can make valuable business and personal connections with one another. At the same time, these events draw a large crowd and it's often hard to make these connections in the midst of all of these events' excitement and energy. To help attendees make connections, we are building the infrastructure for a service that can inform attendees if they have attended the same booths and presentations at an event.
Getting started
The existing application has been refactored into microservices however most of the previous stes are still valid on this new version
How to run
First check the preriquisites and then follow the install/deploy steps
Prerequisites
We will be installing the tools that we'll need to use for getting our environment set up properly.
- Set up
kubectl - Install VirtualBox with at least version 6.0
- Install Vagrant with at least version 2.0
1. Initial Setup
In this project's root, run vagrant up.
$ vagrant upThen access via ssh
$ vagrant sshInside the virtual machine execute the following command and copy it result:
$ cat /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yamlExit the virtual machine and paste it into the ~/.kube/config file if the ~/.kube folder doesn't exists please create it.
$ nano ~/.kube/config2. Deploy to kubernetes
kubectl apply -f deployment/db-configmap.yaml- Set up environment variables for the podskubectl apply -f deployment/db-secret.yaml- Set up secrets for the podskubectl apply -f deployment/postgres.yaml- Set up a Postgres database running PostGISkubectl apply -f deployment/kafka-configmap.yaml- Set up the kafka configmapskubectl apply -f deployment/zookeeper.yaml- Set up the zookeeper servicekubectl apply -f deployment/kafka.yaml- Set up the kafka clusterkubectl apply -f deployment- Deploys the application containers and services
3. Seeding the database
Please execute the following command:
$ kubectl get po And copy the postgress pod name, then paste it to replace the <POD_NAME> placeholder with that name
$ sh scripts/run_db_command.sh <POD_NAME>4. Check if it works
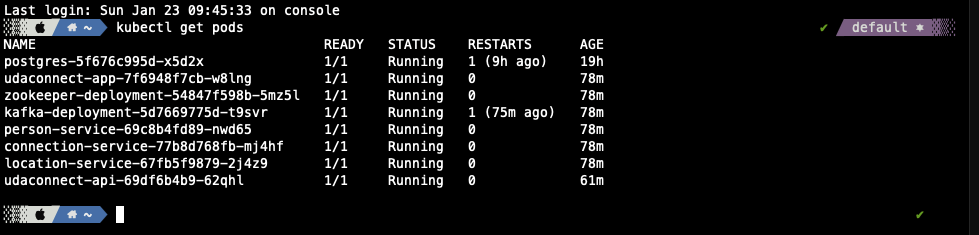
Once the project is up and running, you should be able to see 8 deployments and 8 services in Kubernetes:
kubectl get pods and kubectl get services - should both return udaconnect-app, udaconnect-api, zookeeper-deployment, kafka-deployment, connection-service, person-service, location-service and postgres
These pages should also load on your web browser:
http://localhost:30001/- OpenAPI Documentationhttp://localhost:30001/api/- Base path for APIhttp://localhost:30000/- Frontend ReactJS Application
Alternative you could use the included postman collection to test the created services: