An MDK template for Raspberry Pi Pico
-
Use RPi official RP2xxxx_DFP
-
Add Flash Programming algorithm.
- Special thanks to Aladdin-Wang. His extraordinary work makes our life much easier!
- Special thanks to fang316, whose suggestion improves how the flash programming algorithm is deployed.
-
Compiler: Arm Compiler 6.15 and above (Using non-intrusive wrapper to support pico-sdk which is written in GCC)
-
Improved BSP support
-
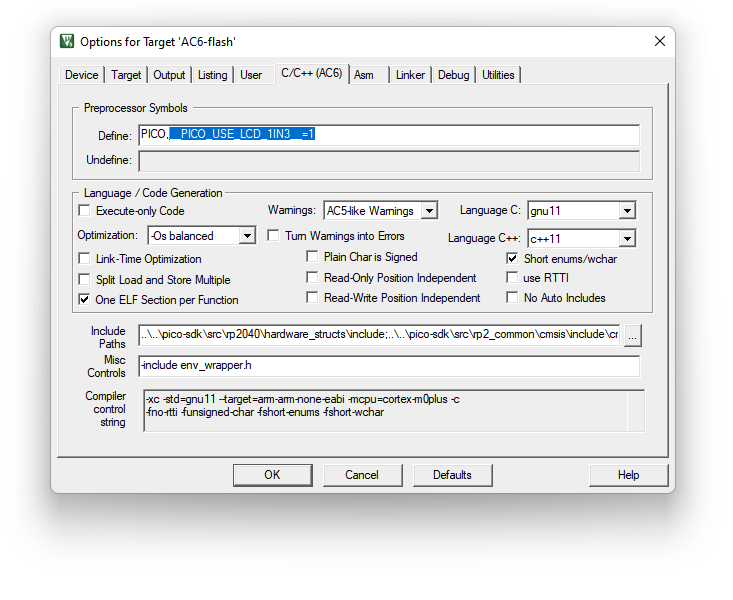
Add support for popular LCD 1.3inc module : define macro
__PICO_USE_LCD_1IN3__to enable it. -
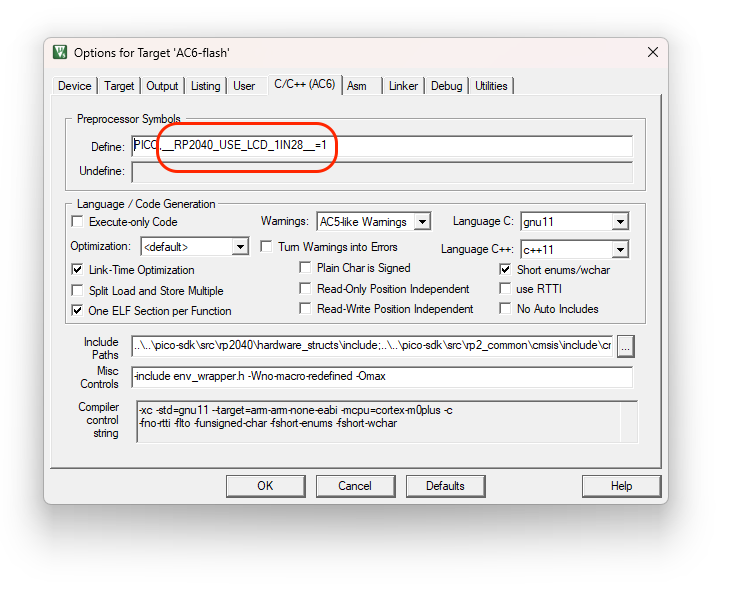
Add support for RP2040 LCD 1.28inch development kit: define macro
__RP2040_USE_LCD_1IN28__to enable it. -
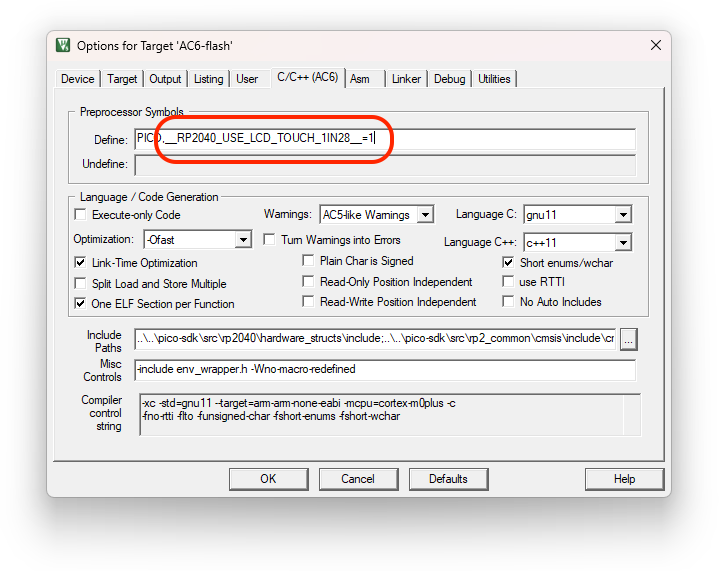
Add support for PR2040 LCD Touch 1.28inch development kit: define macro
__RP2040_USE_LCD_TOUCH_1IN28__to enable it.
-
-
Support an ultra-lightweight python VM: PikaScript (via cmsis-pack)
-
Compatible with CMSIS 5.7.0, CMSIS 6.0.0 and above
-
Ready for running Arm-2D benchmarks
-
Ready for coremark
-
Support Debug in MDK
- Using CMSIS-DAP (Validated in MDK and highly recommended)
- Support Flash Downloading
-
Add dedicated project configurations for:
-
[AC6-flash] Running code in Flash (XIP)
-
[AC6-DebugInSRAM] "no_flash" mode in the original pico-sdk.
-
I assume that you have the MDK installed on your PC. Please clone the Pico_Template with following command line:
mkdir pico-mdk
cd pico-mdk
git clone https://github.com/GorgonMeducer/Pico_Template .
git submodule update --init
Instead of using git clone, if you download a release package, then you have to download the pico-sdk manually and put them into the corresponding folder:
| submodules | URL | Directory |
|---|---|---|
| bsp | https://github.com/GorgonMeducer/RP2040_BSP | ROOT\bsp |
The project template also depends on perf_counter which is deployed with a cmsis-pack that you can find in the MDK pack installer.
The MDK project could be found in the path "ROOT\project\mdk". I assume you know how to use MDK for normal compilation.
Usually, people want to adjust the size of stack and heap, and it is very easy in this template. Please find the file "RP2040.sct" in the same MDK project directory. Find the macro STACK_0_SIZE for stack and HEAP_0_SIZE for the heap.
#define STACK_0_SIZE (1024*4)
#define STACK_1_SIZE (1024*1)
#define HEAP_0_SIZE (1024*32)
#define HEAP_1_SIZE (1024*1)
NOTE:
- Please do NOT add "u" behind those constant values.
- The STACK_1_SIZE and HEAP_1_SIZE are not in use. You can set their value to reasonable smaller ones if you do want to reduce the RAM footprint.
To take advantage of pico-sdk, this template uses bridges to retarget low level functions of stdout/stdin to _read and _write implemented by stdio.c inside pico-sdk.
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------*
* bridge the Arm Compiler's stdio and the pico-sdk's stdio *
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
__attribute__((weak))
int stdin_getchar(void)
{
/*! \note If you don't want to use pico-sdk stdio, then you can implement
*! function by yourself in other c source code. Your scanf will work
*! directly.
*! by default, we use this function to bridge the _read implemented
*! in stdio.c of pico-sdk
*/
int byte;
_read(0, (char *)&byte, 1);
return byte;
}
__attribute__((weak))
int stdout_putchar(int ch)
{
/*! \note If you don't want to use pico-sdk stdio, then you can implement
*! function by yourself in other c source code. Your printf will work
*! directly.
*! by default, we use this function to bridge the _write implemented
*! in stdio.c of pico-sdk
*/
return _write(1, (char *)&ch, 1);
}
Those bridge functions are decorated as "weak", hence if you want to retarget printf/scanf directly to a place where you can "see through" and/or you have total control, please implement those bridge functions (without delete the weak version) in one of your c source code, for example, sending chars to USART or storing them to a memory block directly.
NOTE: I try to provide you the freedom of choice, and I don't need you to digging deep inside scripts to gain such freedom.
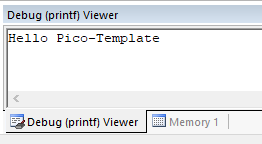
When using configurationAC6-DebugInSRAM-printf, all printf output is retargeted to 'Debug (printf) Viewer' inside MDK (as shown below) with the help from EventRecorder.
Pico-debug is an open-source project which turns one Cortex-M0+ core in RP2040 into a CMSIS-DAP adapter. It means that without an extra one, you can debug a Pico in MDK with just one USB connector. In order to do so, please download the latest uf2 file first.
Pico-Template provides a dedicated project configuration for downloading and debugging code in SRAM. This is the most convenient one and it delivers the best development experience among the three configurations. To use it, please follow the steps below:
- Boot the Pico with the BOOTSEL button pressed.
- Drag and drop pico-debug-gimmecache.uf2 to RPI-RP2 mass-storage driver in the explorer. It immediately reboots as a CMSIS-DAP adapter. Pico-debug loads as a RAM only
.uf2image, meaning that it is never written to flash and doesn't replace existing user code. - Compile and Debug
- Enjoy...
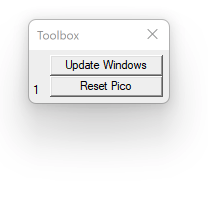
**NOTE: **
1. In this mode, the "RESET" doesn't really work as we expect. If you do want to RESET, please press the "Reset Pico " button shown below:
2. If you cannot find this Toolbox, please start your debug session and go to menu "View"->"Toolbox Window".
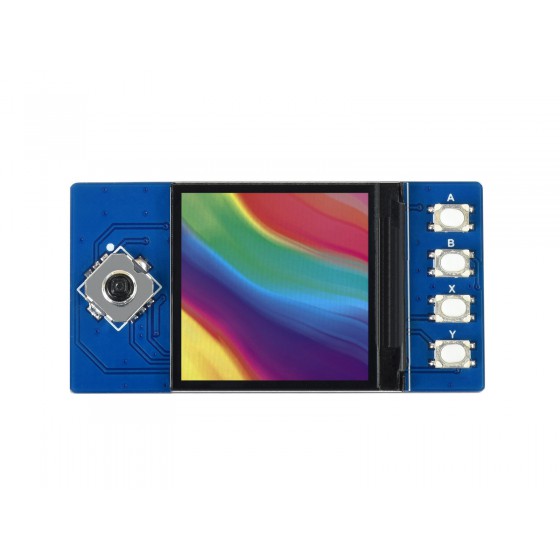
To make it easier for people to turn Pico into a 'game pad', I've picked a popular 1.3inc LCD module and added a tailored driver into this Pico template.
In brief, it is an
1.3inch LCD Display Module For Raspberry Pi Pico, 65K RGB Colors, 240×240 Pixels, SPI Interface
To enable the built in support, please set the macro __PICO_USE_LCD_1IN3__ to 1 in MDK project configuration as shown below:
After that, you can
- Use the API
GLCD_DrawBitmap()to flush a display buffer to the 1.3 inch LCD fully or partially (with specified location and size).
extern
void GLCD_DrawBitmap( int_fast16_t x, int_fast16_t y,
int_fast16_t width, int_fast16_t height,
uint16_t *frame_ptr);NOTE: an alternative API, i.e. Disp0_DrawBitmap, is ready for working with Arm-2D.
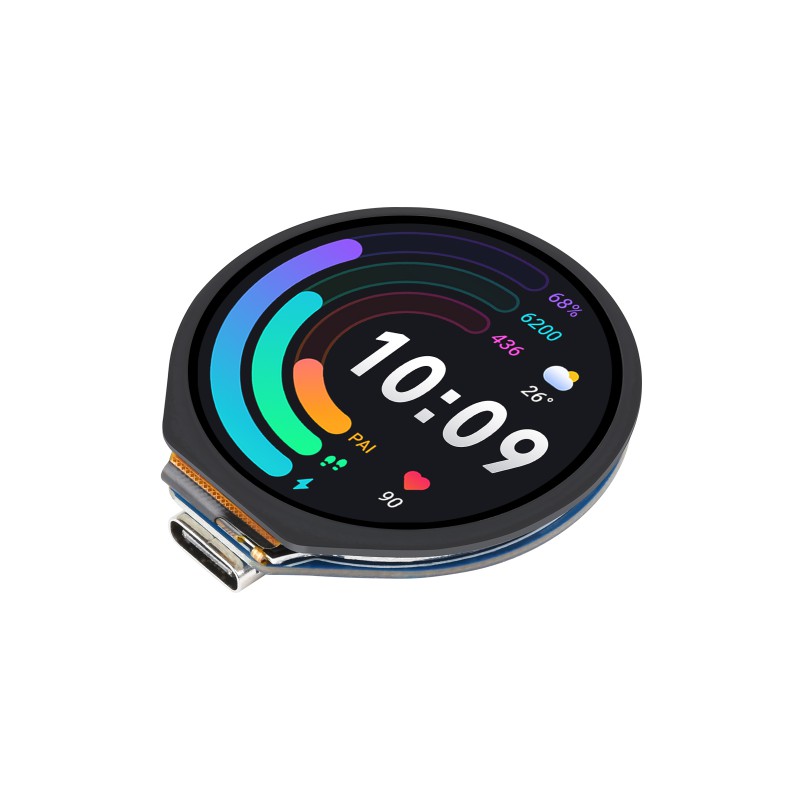
To make it easier for people to create watch faces, I've picked a popular LCD 1.28inch development kit and added a tailored driver into this Pico template.
In brief, it is an
RP2040 MCU Board, With 1.28inch Round LCD, accelerometer and gyroscope Sensor

To enable the built in support, please set the macro __RP2040_USE_LCD_1IN28__ to 1 in MDK project configuration as shown below:
To make it easier for people to create watch faces, I've picked a popular PR2040 LCD Touch 1.28inch development kit and added a tailored driver into this Pico template.
In brief, it is an
RP2040 MCU Board, With 1.28inch Round Touch LCD, accelerometer and gyroscope Sensor
To enable the built in support, please set the macro __RP2040_USE_LCD_TOUCH_1IN28__ to 1 in MDK project configuration as shown below:
PikaScript is an ultra-lightweight Python engine with zero dependencies and zero-configuration, that can run with 4KB of RAM and 32KB of flash (such as STM32G030C8 and STM32F103C8).
Pico-Template supports PikaScript via cmsis-pack which you can find in the root directory. After the installation, please following the official guidance to enable the support.
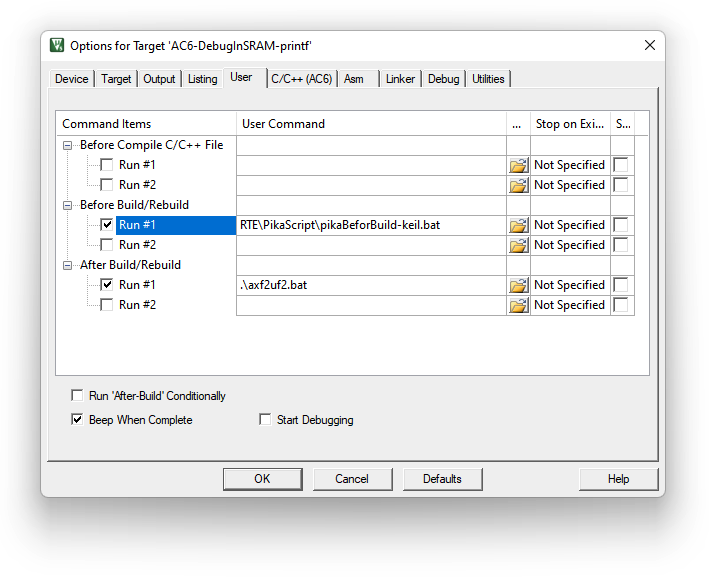
NOTE: The first time compilation after selecting the Before Build/Rebuild might takes a longer time than you thought.
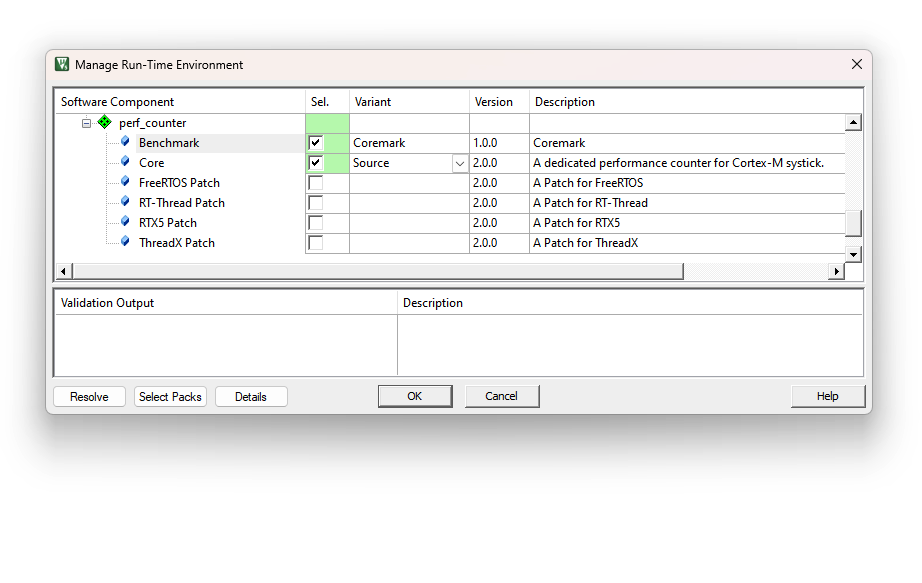
With the help from perf_counter v2.0.0 , we can now run coremark on Pico-Template with just one click in RTE as shown below:
A code in main() will run the coremark after that:
int main(void)
{
system_init();
printf("Hello Pico-Template\r\n");
...
#if defined( __PERF_COUNTER_COREMARK__ ) && __PERF_COUNTER_COREMARK__
printf("\r\nRun Coremark 1.0...\r\n");
coremark_main();
#endif
...
while (true) {
breath_led();
...
}
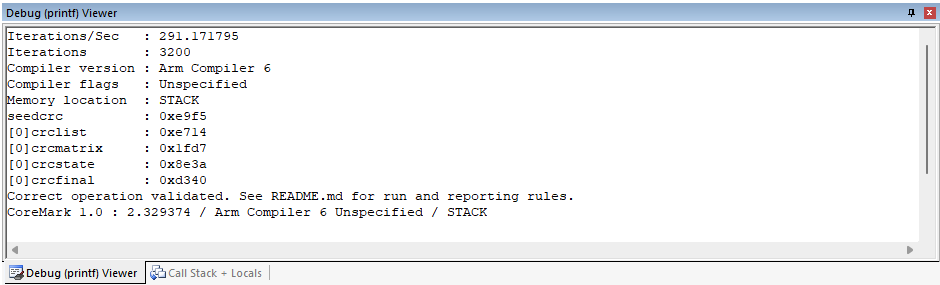
}By default, you can observe the test result in Debug (printf) View as shown below:
NOTE: The coremark has to run at least 10 secs to generate a valid result. Fail to do so, you can change the macro ITERATIONS defined in core_portme.h to a bigger value and try again.