GART is a graph extension that includes an interface to an RDBMS and a dynamic graph store for online graph computation. It is designed to bridge the gap between relational OLTP and graph-based OLAP.
Please to refer GART documentation for more details.
gart-demo.mp4
We would like to be able to use graph data flexibly without re-altering the existing relational database system. Moreover, users do not need to be aware of the storage of graph data and the synchronization of data between relational data and graph data for freshness. To fulfill this requirement, we build GART, an in-memory system for real-time online graph computation.
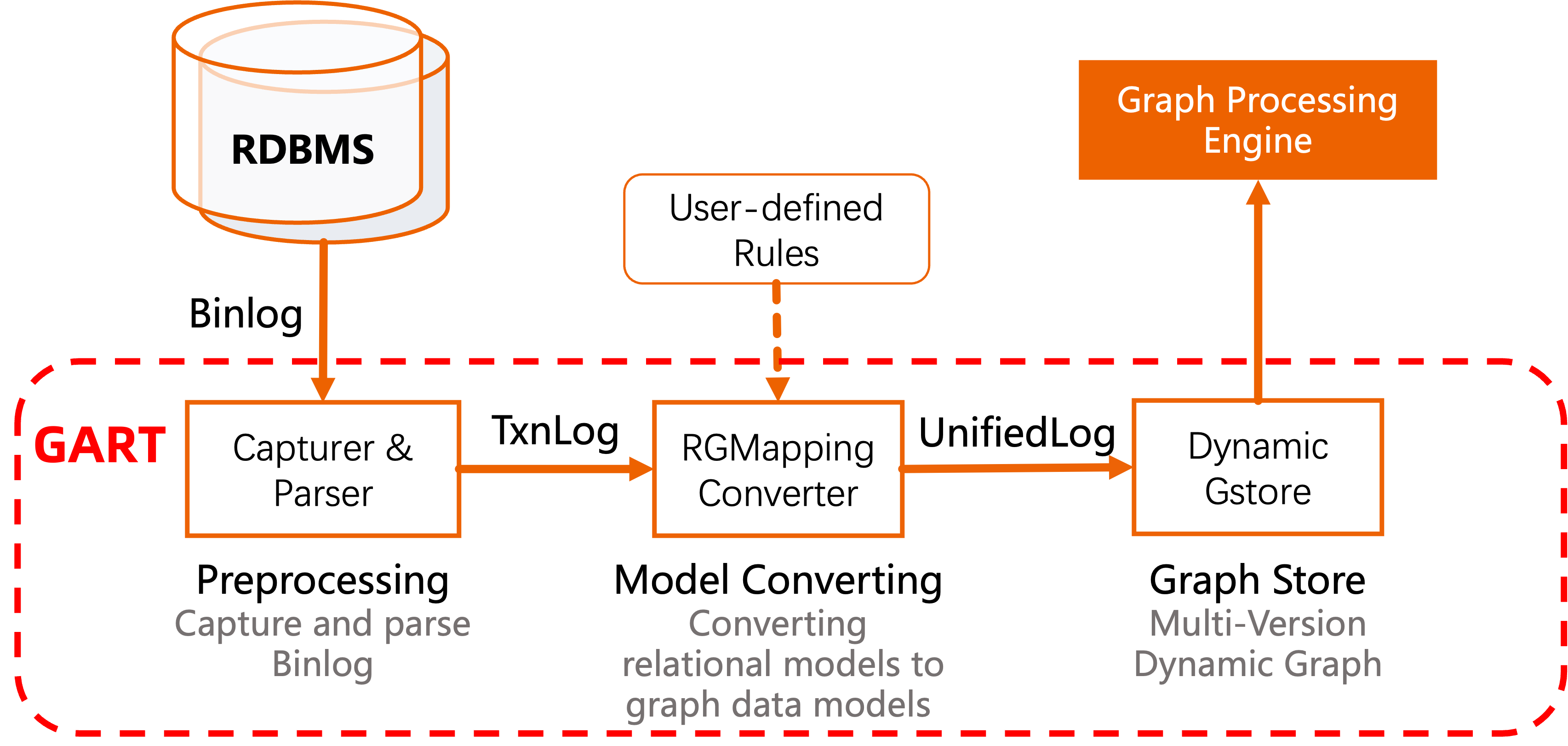
GART uses transactional logs (e.g., binlog) to capture data changes, then recovers data changes into fresh graph data in real time. GART integrates graph computation engines (e.g. GraphScope, NetworkX) to support efficient graph computation processing. The workflow of GART is shown below.
-
1. Preprocess (Capture & Parser): GART captures data changes from data sources by logs (e.g., Binlogs in SQL systems). Then, it parsers these logs into a recognized format, called as TxnLog. Currently, we use Debezium (for MySQL, PostgreSQL, ...) as the log capture.
The sample format of an inserted tuple of TxnLog is as follows (Debezium style, only necessary information):
{ "before": null, "after": { "org_id": "0", "org_type": "company", "org_name": "Kam_Air", "org_url": "http://dbpedia.org/resource/Kam_Air" }, "source": { "ts_ms": 1689159703811, "db": "ldbc", "table": "organisation" }, "op": "c" }This sample records the log that inserts a tuple of
organisation. -
2. Model Convert (RGMapping Converter): This step is an important step for GART. The conversion between different data models for online graph computation requires more semantic information. For example, it needs the mapping between relational tables and vertex/edge types, and the mapping between relational attributes and vertex/edge properties. The GART administrator (such as DBA) can define the rules of relation-graph mapping (RGMapping) once by the interfaces provided by GART. GART will convert relational data changes into graph data changes in the unified logs (UnifiedLog) automatically.
-
3. Graph Store (Dynamic GStore): GART applies the graph data changes on the graph store. The graph store is dynamic, which means the writes from GART and the reads from the graph analysis processing can be executed on the store concurrently.
Compared to current solutions that provide graph interfaces on relational data, GART has three main features:
To adapt to rich workload flexibility, GART proposes transparent data model conversion by graph extraction interfaces, which define rules of relational-graph mapping.
We provide a sample definition file called rgmapping-ldbc.yaml.
To ensure the performance of graph computation, GART proposes an efficient dynamic graph storage with good locality that stems from key insights into online graph computation, including:
- an efficient and mutable compressed sparse row (CSR) representation to guarantee the locality of scanning edges;
- a coarse-grained MVCC to reduce the temporal and spatial overhead of versioning;
- a flexible property storage to efficiently run various graph computation workloads.
Please refer to our paper for specific technical implementation details.
GART acts as a service to synchronize database changes to the graph store. When pulled up as a service on its own, users can try out the full power of GART and different graph computation engines on the graph store. At the same time, GART also provides a front-end, used as a database plug-in, currently supported as PostgreSQL extension. Users can invoke GART's functions in the database client, such as RGMapping definitions, graph computation on the graph store, etc.
Please to refer our documentation.
GART is released under Apache License 2.0. Please note that third-party libraries may not have the same license as GART.
[USENIX ATC' 23] Bridging the Gap between Relational OLTP and Graph-based OLAP. Sijie Shen, Zihang Yao, Lin Shi, Lei Wang, Longbin Lai, Qian Tao, Li Su, Rong Chen, Wenyuan Yu, Haibo Chen, Binyu Zang, Jingren Zhou. USENIX Annual Technical Conference, Boston, MA, USA, July 2023.