Snakemake-based pipeline for processing SHARE-seq data
- Parallelize via cloud or academic HPC cluster
(See profile/config.yaml for an example to submit via Stanford's Sherlock cluster)- Processes a Novaseq run in under 4 hours in our tests on Sherlock
- Resume cleanly after interruptions
- Demultiplex individual samples barcoded using first round cell barcode
- Merge sequencing data from multiple sequencing runs of the same experiment
- Can be run in a pre-built container
- Dockerfile provided for users to build custom containers if needed
- Raw sequencing data as one or more bcl sequencing directories
- In the future, fastq inputs will be supported
- Genome annotations:
- bowtie2 and STAR genome indexes
- gtf gene annotation
- (optional) We provide a script to automatically download, filter and build genome indices (currently hg38 support only)
cd scripts/references bash prep_genome.sh hg38
- A config yaml file (example)
- ATAC fragment file (10x compatible)
ATAC/samples/{sample}.fragments.tsv.gz
- RNA mtx file (10x compatible)
RNA/samples/{sample}.matrix.mtx.gzRNA/samples/{sample}.barcodes.tsv.gzRNA/samples/{sample}.features.tsv.gz
- Secondary outputs:
- Stats on alignment rates
ATAC/samples/alignment_stats.jsonRNA/samples/alignment_stats.json
- Stats on barcode matching rates
ATAC/samples/barcode_stats.jsonRNA/samples/barcode_stats.json
- Per-sublibrary fragment and matrix files:
ATAC/sublibraries/{sublibrary}/fragments.tsv.gzRNA/sublibraries/{sublibrary}/matrix.mtx.gz
- Stats on alignment rates
- Install required dependencies (see below)
- Adapt the example config to your input + output data locations
- At the top level your config, set:
chunk_size: 2_000_000 test_chunks: 2
- From within the
shareseq-pipelinedirectory, run:Set thesbatch -p wjg,sfgf,biochem run.sh runs/MY_CONFIG_FILE.yaml
-pargument to your partition names, and set the path to your config file appropriately. - After that runs successfully, delete the test outputs and do a full-scale run by
setting a larger chunk size and removing
test_chunksfrom the config.chunk_size: 20_000_000
- After the run has completed, generate summary plots by running the following
from within the
shareseq-pipelinedirectory:sbatch -p wjg,sfgf,biochem --mem-per-cpu=64g plot.sh runs/MY_CONFIG_FILE.yaml
- (optional) To delete the intermediate outputs after a run, run the following:
Note that this step is not needed if you remove all the
snakemake --profile=$(pwd)/profile -s prep_fastq.smk --configfile runs/MY_CONFIG_FILE.yaml --delete-temp-output --config filter_dag=false snakemake --profile=$(pwd)/profile -s shareseq.smk --configfile runs/MY_CONFIG_FILE.yaml --delete-temp-output --config filter_dag=false
--notempflags fromrun.shbefore running step 3. Snakemake will delete the intermediate outputs by default as it runs without the--notempflag.
- Install
singularityandsnakemake - Build the container image file by running:
singularity pull /YOUR/CONTAINERS/DIR/shareseq_latest.sif docker://bettybliu/shareseq:latest - Adapt the example config to your input + output data locations,
uncomment the singularity line and modify it to
singularity: "/YOUR/CONTAINERS/DIR/shareseq_latest.sif" - At the top level your config, set:
chunk_size: 2_000_000 test_chunks: 2
- From within the
shareseq-pipelinedirectory, run:Set thesbatch -p wjg,sfgf,biochem run.sh runs/MY_CONFIG_FILE.yaml
-pargument to your partition names, and set the path to your config file appropriately. - After that runs successfully, delete the test outputs and do a full-scale run by
setting a larger chunk size and removing
test_chunksfrom the config.chunk_size: 20_000_000
- After the run has completed, generate summary plots by running the following
from within the
shareseq-pipelinedirectory:sbatch -p wjg,sfgf,biochem --mem-per-cpu=64g --job-name=plot --wrap "singularity exec --cleanenv /YOUR/CONTAINERS/DIR/shareseq_latest.sif ./plot.sh runs/MY_CONFIG_FILE.yaml" - (optional) To delete the intermediate outputs after a run, run the following:
Note that this step is not needed if you remove all the
snakemake --profile=$(pwd)/profile -s prep_fastq.smk --configfile runs/MY_CONFIG_FILE.yaml --delete-temp-output --config filter_dag=false snakemake --profile=$(pwd)/profile -s shareseq.smk --configfile runs/MY_CONFIG_FILE.yaml --delete-temp-output --config filter_dag=false
--notempflags fromrun.shbefore running step 3. Snakemake will delete the intermediate outputs by default as it runs without the--notempflag.
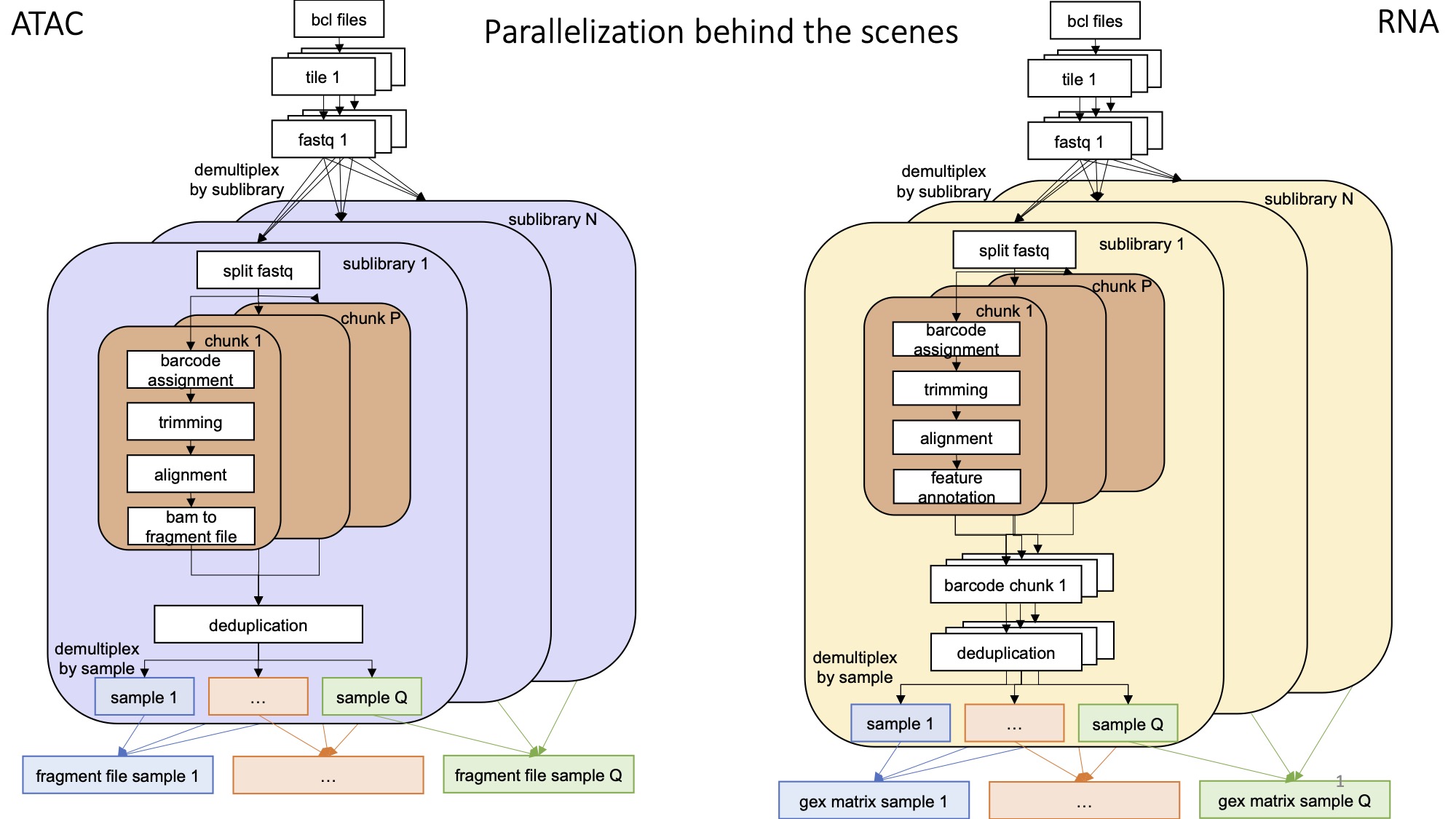
The pipeline runs in two steps:
prep_fastq.smkcounts the number of reads, and runs bcl2fastq as neededshareseq.smkruns the actual analysis
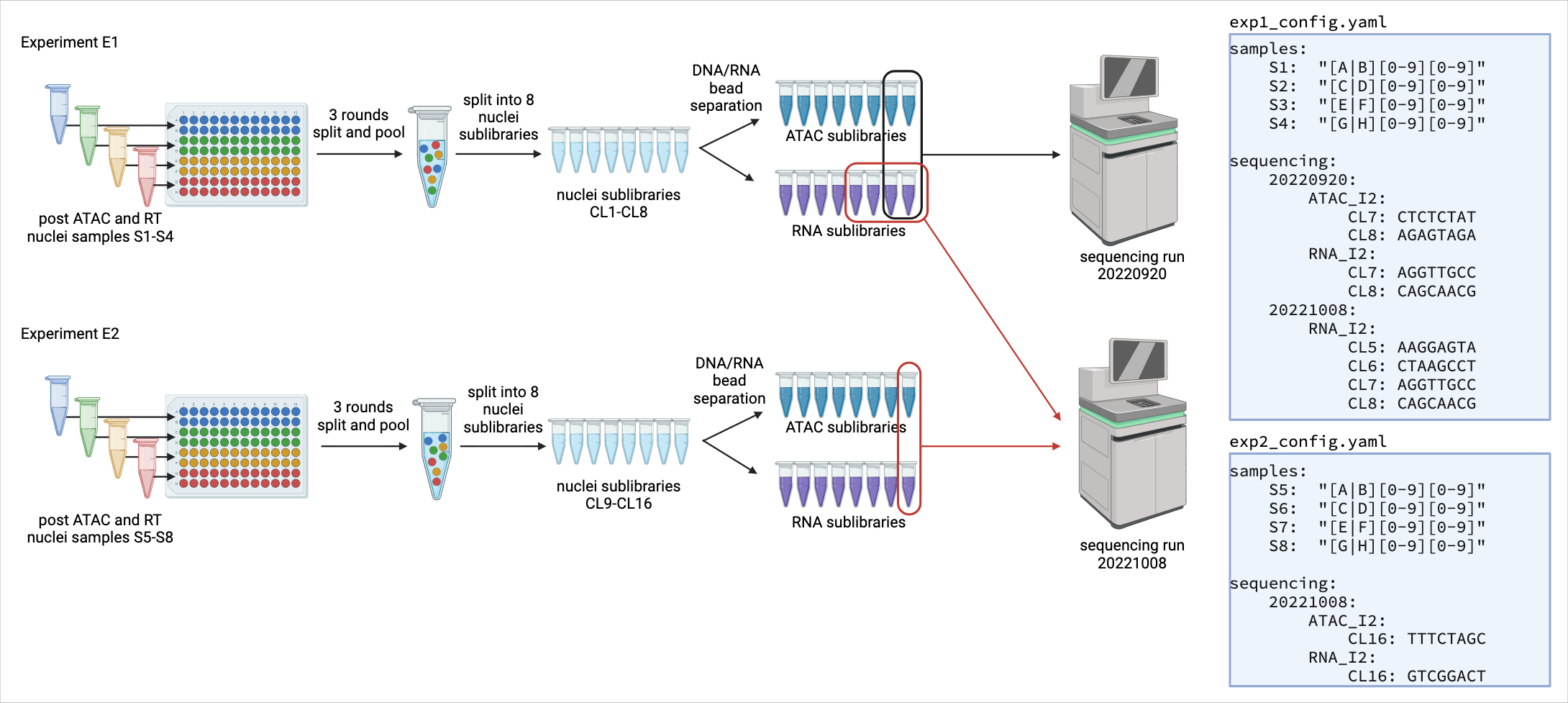
Model of experiment:
- experiments consist of a run where a group of cells were physically present together and barcoded in the same set of plates.
shareseq.smkshould be run once per split-and-pool experiment
- samples are distinct biosamples or biological/technical replicates
- samples are distinguished by being placed in distinct sets of wells during the first round of split+pool barcoding.
- Each experiment may have one or more samples
- sublibraries are subsets of cells split after the final round of split+pool but prior to reversing crosslinking.
- If the same cell barcode is found in multiple sublibraries, the reads are assumed to have arisen from distinct cells.
- Each experiment may have one or more sublibraries
- Each sublibrary contains cells uniformly distributed from all the samples.
- sublibraries can be pooled for sequencing, but each can be demultiplexed based on unique sequencing adapters (one adapter for ATAC and one adapter for RNA)
- sequencing runs can contain the ATAC and/or RNA reads for one or more sublibraries
prep_fastq.smkshould be run once per sequencing run
In simple cases, you will have one experiment and one sequencing run. In this case a single config file is sufficient for both prep_fastq.smk and shareseq.smk.
In complex cases where experiments are pooled onto different sets of sequencing runs, you may need to make one config file per sequencing run for prep_fastq.smk and one config file per experiment for shareseq.smk. The figure below illustrates an example where separate config files are created for shareseq.smk.
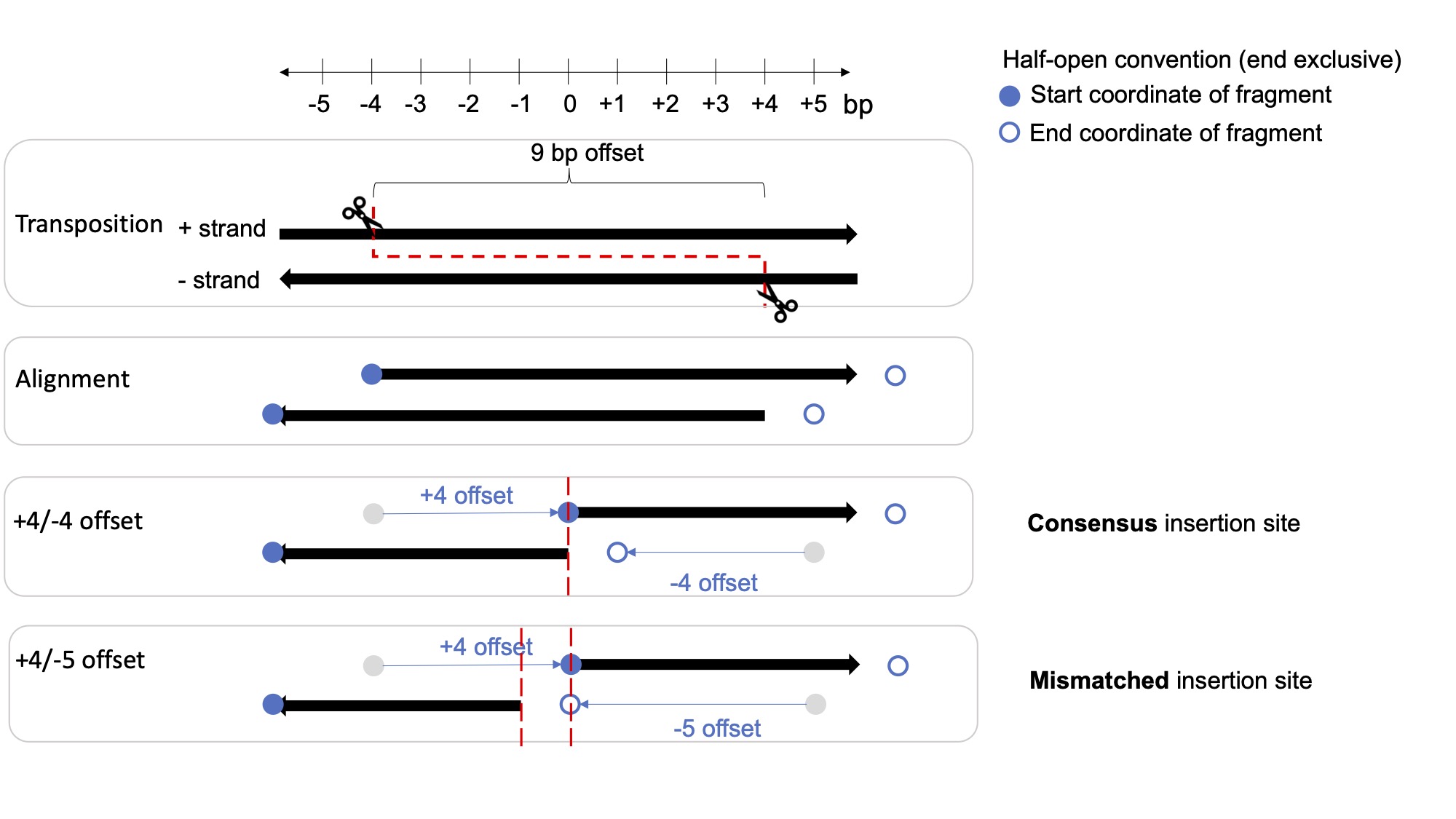
In ATAC-seq experiments, Tn5 transposase forms a homodimer with a 9-bp gap between the two Tn5 molecules, resulting in two insertions 9-bp apart on different DNA strands per accessible site. When sequencing the DNA fragments using paired-end sequencing, the start and end positions need to be adjusted based on the insertion offset of Tn5 to reflect the true center of the accessible site at the midpoint of the Tn5 dimer.
To account for the Tn5 offset, previous ATAC-seq studies used a +4/-5 offset approach where plus-stranded insertions are adjusted by +4 bp, and minus-stranded insertions by -5 bp. However, this actually results in a 1bp mismatch of the adjusted insertion sites between the two fragments sharing a single transposition event. This mismatch does not affect most downstream ATAC analysis that bins insertions on the hundreds of bp scale, but it does affect bp-sensitive analysis like TF footprinting and motif analysis.
In this SHAREseq preprocessing pipeline, we have adopted the +4/-4 offset instead, which results in a consensus insertion site.
Read more:
- UCSC reference and UCSC blog on bed format and the half-open convention
- 10x reference describing the bed format correctly but using an incorrect +4/-5 offset
- bcl2fastq
- bgzip
- bowtie2 version >=2.4.2 (flag --sam-append-comment)
- fastp
- featureCounts (subread)
- pysam
- python3
- STAR
- samtools
- snakemake
- tabix
- umi_tools
- zstd
Builtin unix tools:
- awk
- gcc
- grep
- gzip
- sort
- split
- poppler
- R
- Seurat
- ggplot2
- patchwork
- ggrastr
- gridExtra
- dplyr
- rjson
- BPCells