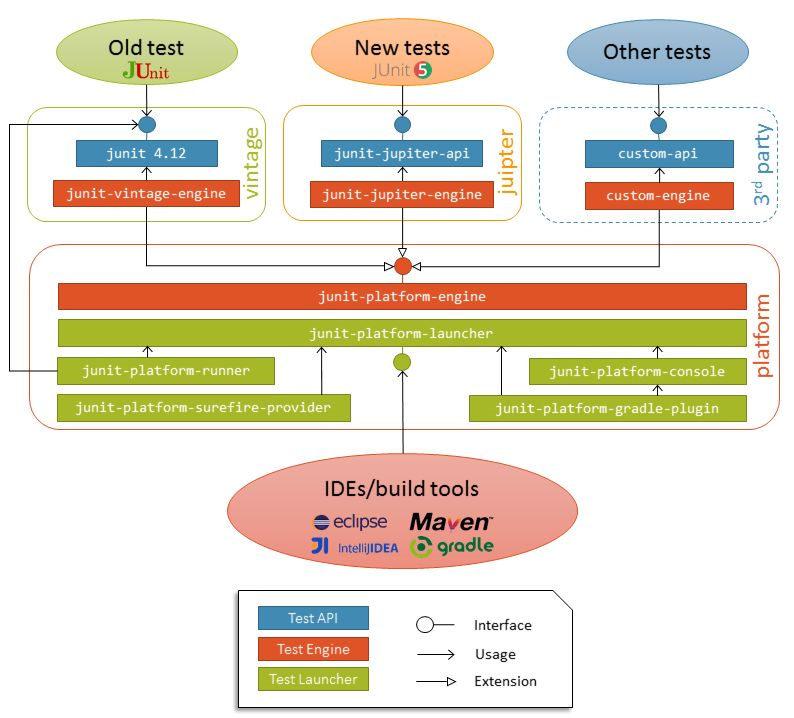
- Visibility
- Everything does not have to be public
- Custom display names
- @DisplayName: spaces, special characters, emoji 👻
- DisplayNameGenerator
- Tagging
- @Tag
- Tag expression language
- Meta-annotation support
- Create your own custom composed annotations
- Combine annotations from Spring and JUnit
- Conditional test execution
- Dependency injection for constructors and methods
- Lambda expressions and method references
- Interface default methods and testing traits
- @Nested test classes
- @RepeatedTest, @ParameterizedTest, @TestFactory
- @TestInstance lifecycle management
- Implicit / Explicit conversions
- Argument aggregation
- New extension model
- Extension: marker interface
- APIs: org.junit.jupiter.api.extension
- @ExtendWith(...)
- @RegisterExtension
- And more ...
2 + 1 or more dependencies (depending on if you want legacy and/or 3d party engines):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
<version>5.4.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Common issues:
- Mixed concerns
- Problematic dependencies
They violate the single responsibility principle. This can make it hard to:
- Access system output to apply assertions (for example outputting them to a file or report)
- Provide inputs to the code under test (when ui code is mixed with business code)
- Avoid undesired side effects (for example db access, either unavailability or slow)
Solution:
Extract and separate the code to test.
They can make testing difficult due to:
- Side effects
- Talking to remote services that aren't always present
- Inconsistent behavior
Solution:
Provide a test double for the dependency (through DI), without the harmful side effects or external dependencies. Libraries like Mockito or EasyMock make this very easy and prevent the clutter of extra classes / files.