- 100% kotlin
- Jetpack
- Android Architecture Components
- ViewModel
- LiveData
- Manual dependency injection
- DB
- Room
- Network
- Retrofit
- Mock
- Mockk
-
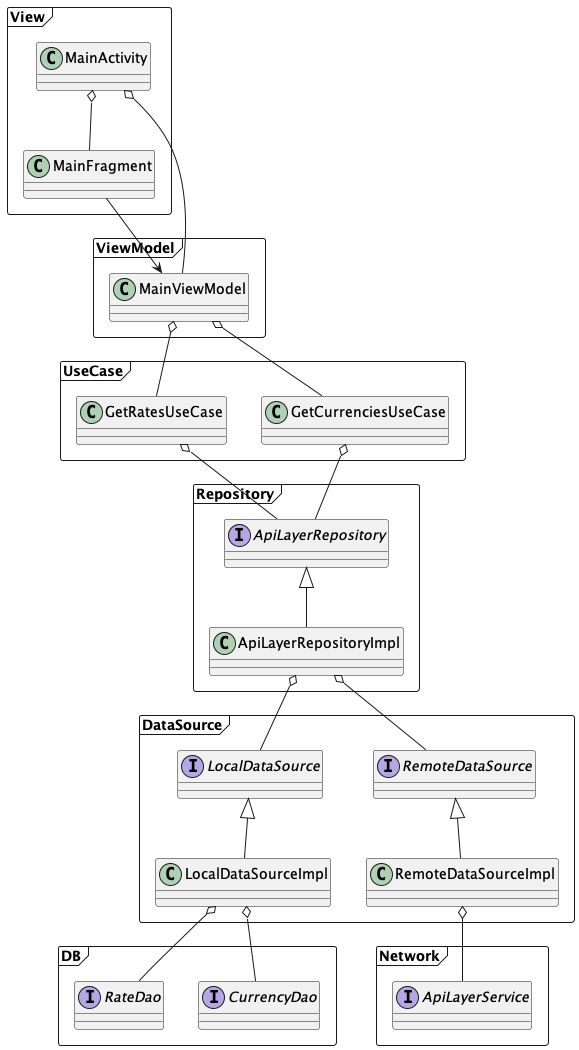
Use MVVM and clean architecture to build for
- Separation of Concerns
- UI logic resides in the View and ViewModel, while the business logic and data access are handled by Repository & Use Case. This separation makes the codebase more maintainable, testable, and easier to understand.
- Testability
- Easily tested by mocking dependencies and verifying its behavior.
- Reusability
- This modular approach allows for easier code reuse, as different components can be plugged into multiple projects without tightly coupling them to the specific implementation.
- Scalability
- The separation of layers and dependencies allows for easier addition or modification of features without affecting the entire codebase.
- Separation of Concerns
- Use
./gradlew installDebugto install App to connected device/emulator - Use
./gradlew assembleDebugto build debug apk file
Use ./gradlew test to run unit tests, due to the time limitation, only focus on core business rules in following packages
- repository
- ApiLayerRepositoryTest
- usecase
- GetCurrenciesUseCaseTest
- GetRatesUseCaseTest
- viewmodel
- MainViewModelTest
Use ./gradlew connectedAndroidTest to run unit tests, due to the time limitation, only test Room's write and read
- CurrencyDaoTest
- RateDaoTest
- Unit test for data source classes
- More instrumental tests
- Use DI tools, e.g., Hilt