SUSTech Wireless Network and Mobile Computing Project
(c) 2024 HuaCL Zhao.K.J
- Press Reset to clear all information.
- Press Location for a single positioning (positioning after 20 RTT measurements).
- Press Track to start continuous positioning (tracking).
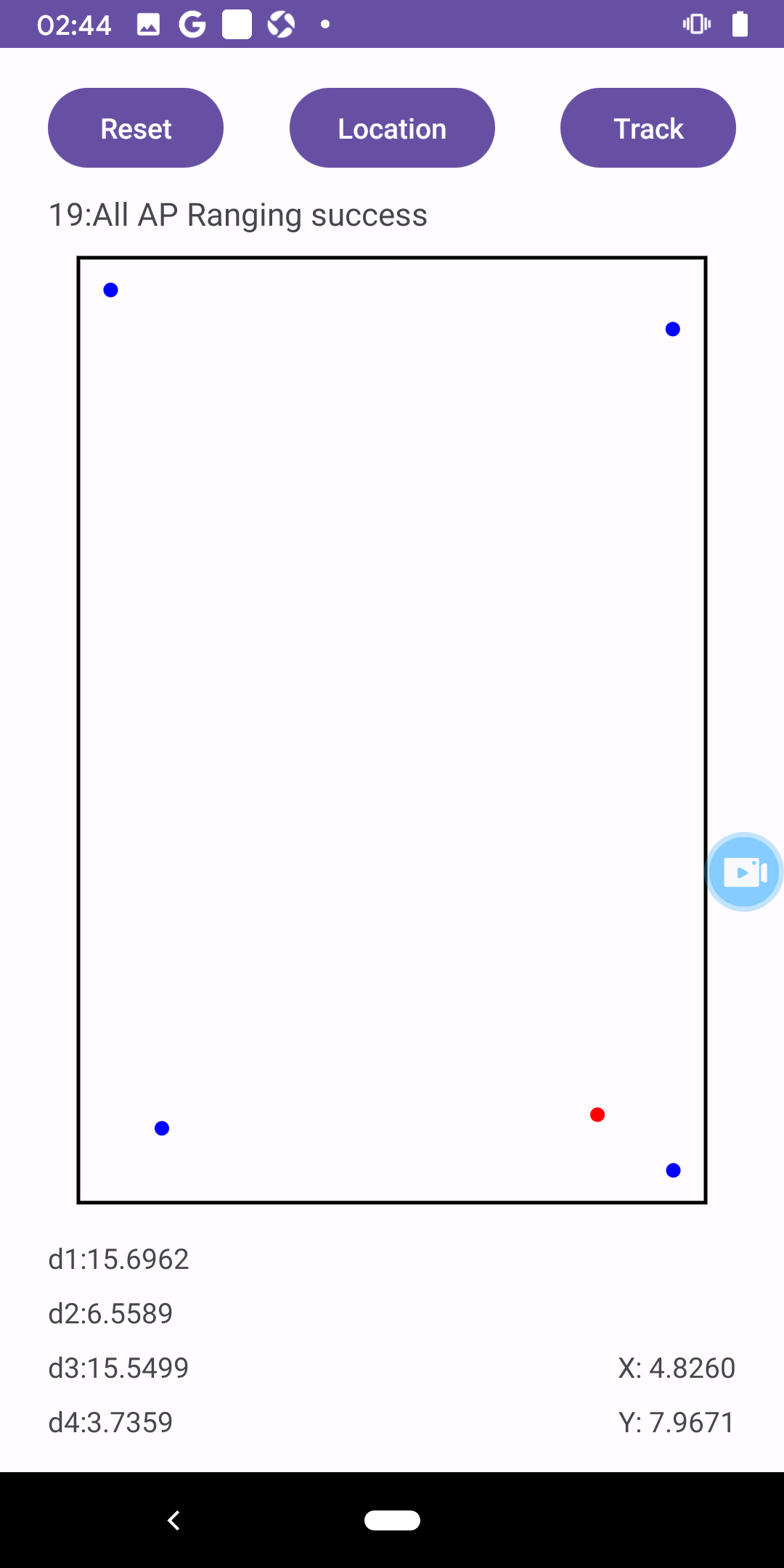
- Prompt Bar: Located in the top left corner, indicating the current measurement status.
- AP Information: Located in the bottom left corner, displaying the distance to the 4 nearest APs (after calibration).
- Position Information: Located in the bottom right corner, displaying the current position.
- Schematic Plan:
- Black frame represents the room.
- Blue dots represent APs.
- Red dot represents the location.
- Android API Level 28+
- Android Support Repository
- Android phones supporting WifiRttManager
For more information, see:
https://developer.android.com/reference/android/net/wifi/rtt/WifiRttManager
This app uses the Gradle build system. To build this project, use the "gradlew build" command or use "Import Project" in Android Studio.
The code is available at Github: https://github.com/HUA428571/FTM_Localization
You need to appropriately set the room and AP positions before running the program (these settings can be found in \app\src\main\res\values\location.xml).
In this activity, we uses Wi-Fi Round-Trip Time (RTT) for indoor positioning. It calculates the device's position by measuring the distance to nearby Wi-Fi Access Points (APs). The application includes Wi-Fi RTT capability detection, AP scanning, position calculation, and user interface interaction. Key features include dynamically loading AP and room configuration from XML resources, processing Wi-Fi RTT ranging results, and displaying this information on the user interface.
Key Functions
-
startScanAP(): This function initiates a Wi-Fi scan to find nearby APs. It checks for location permissions and uses theWifiManager'sstartScan()method. The scan results are stored in thescanResultslist. -
startFTMRanging_Track()andstartFTMRanging_MultiRequest(): These functions initiate RTT ranging. They buildRangingRequestobjects and start ranging requests throughWifiRttManager. They handle both single and multiple ranging requests. -
getCoordinates()andgetCoordinates_Track(): These functions calculate the device's position using the least squares method. They compute the average distances from the device to each AP using ranging results and use these distances along with the APs' location information to estimate the device's coordinates. -
RttRangingResultCallbackandRttRangingResultCallback_MultiClasses: These inner classes handle the results of Wi-Fi RTT ranging. They override theonRangingFailureandonRangingResultsmethods to handle cases of ranging failure and success. -
importAPLocation(): This function imports AP location and calibration data from XML resource files, allowing the application to adjust parameters dynamically based on the configuration file.
These functionalities work together to enable the application to effectively use Wi-Fi RTT technology for indoor positioning, providing real-time location information to users.
Requesting location information is a prerequisite for conducting AP scanning and subsequent operations.
This code defines a custom View class named LocationView in an Android application. It is designed to display the positioning points and Access Points (APs) in an indoor environment. The key components and their functionalities are as follows:
-
Paint Objects: Utilizes
Paintobjects for drawing. There are separate paint objects for general drawing (paint), drawing APs (apPaint), and drawing the location point (locationPaint). -
Room and AP Positions: Stores the dimensions of the room (
roomLength,roomWidth) and the positions of APs (apPositionsarray). -
Location Coordinates: Maintains the current location coordinates (
x,y). These are initialized to an off-screen position. -
Scaling and Offsets: Calculates the scale factor and offsets (
offsetX,offsetY) to proportionally fit the room within the device's screen, keeping the drawing centered. -
Initialization: In the constructor (
LocationView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)), it callsinitLocationView()to initialize the paint objects. -
Setting Methods: Includes methods to set the room size (
setRoomSize(float length, float width)), AP positions (setApPositions(float[][] positions)), and location (setLocation(float positionX, float positionY)). These methods also callinvalidate()to trigger a redraw of the view. -
Drawing Logic: Overrides the
onDraw(Canvas canvas)method to draw the room outline, APs, and the current location. The drawing accounts for the calculated scale and offsets.
This code defines a class TFLiteModel to integrate a TensorFlow Lite (TFLite) model for machine learning inference in an Android application. The class encapsulates the model loading and inference process. Key components and their functionalities are:
-
TensorFlow Lite Interpreter:
Interpreter tfliteis an instance of the TFLite Interpreter, responsible for running the machine learning model. -
Model Loading: The
loadModelFilemethod loads a TFLite model from the app's assets. It opens a file descriptor fordense_model.tfliteand maps it into memory. -
Constructor: The constructor (
public TFLiteModel(Context context)) initializes theInterpreterwith the loaded model. -
Normalization: Mean (
mean) and standard deviation (std) arrays are defined for normalizing the input data to the model. -
Inference Method (
runInference): This method takes input data, normalizes it, runs the model inference, and returns the output. The normalization is performed by subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard deviation.