New emerging large single-dish radio telescopes like Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) have heightened the need for developing both more resilient hardware and efficient algorithms than those conventional technology can provide. To process the spectral line data from the radio telescopes, the convolution-based gridding algorithm is widely adopted to solve the most compute-intensive parts of creating sky images: gridding.
HCGrid is a high performance gridding software for the spectral line data gridding of the large single-dish radio telescope. Cygrid is the state-of-the-art gridding method for single-dish radio telescope deployed in the computing environment of multiple CPU cores, and the HCGrid implementation takes reference from Cygrid (For more information, please visit https://github.com/bwinkel/cygrid or https://www.aanda.org/articles/aa/abs/2016/07/aa28475-16/aa28475-16.html).
This work was published in MNRAS, so please cite our article if you use HCGrid.
@article{wang2021hcgrid,
title={HCGrid: a convolution-based gridding framework for radio astronomy in hybrid computing environments},
author={Wang, Hao and Yu, Ce and Zhang, Bo and Xiao, Jian and Luo, Qi},
journal={Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society},
volume={501},
number={2},
pages={2734--2744},
year={2021},
publisher={Oxford University Press}
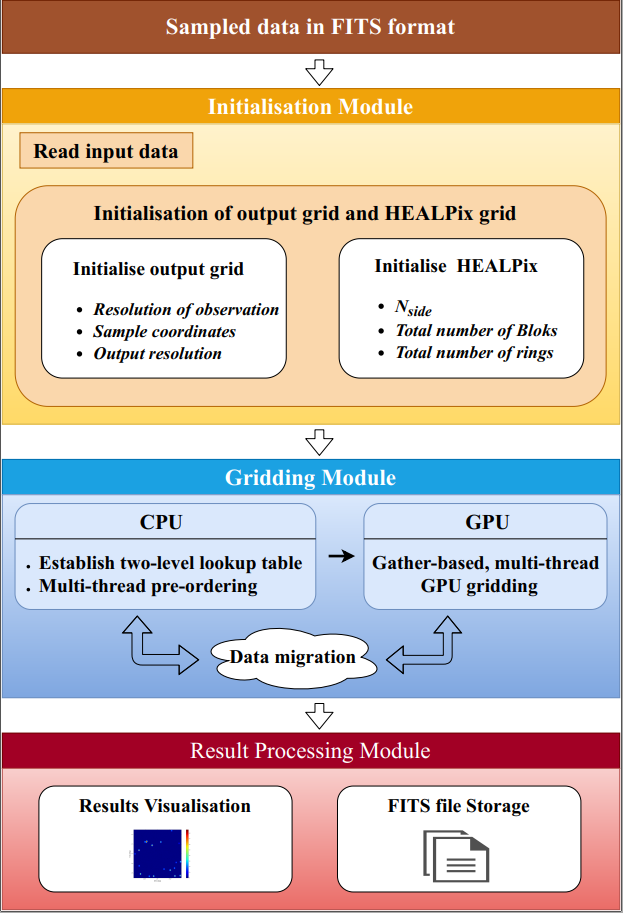
}The specific steps of gridding for single channel spectral data are shown in the following figure, including:
- Initialization module: This module mainly initializes some parameters involved in the calculation process, such as setting the size of the sampling space, output resolution and other parameters.
- Gridding module: The core functional modules of the HCGrid. The key to improving gridding performance is to increase the speed of convolution calculations. First, in order to reduce the search space of the original sampling points, we use a parallel ordering algorithm to pre-order the sampling points based on HEALPix on the CPU platform and propose an efficient two-level lookup table to speed up the acquisition of sampling points. Then, accelerating convolution by utilizing the high parallelism of GPU and through related performance optimization strategies based on CUDA architecture to further improve the gridding performance.
- Result-processing module, which visualize the gridding results, as well as exporting the final products as FITS files.
- Supports WCS projection system as target.
- Scales well in CPU-GPU heterogeneous platforms.
- cfitsio-3.47 or later
- wcslib-5.16 or later
- HDF5
- boost library
- CUDA Toolkit
All of these packages can be found in "Dependencies" directory or get from follow address:
- cfitsio: https://heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov/fitsio/
- wcslib: https://www.atnf.csiro.au/people/Mark.Calabretta/WCS/
- HDF5: https://www.hdfgroup.org/downloads/hdf5
- boost: https://www.boost.org/
- CUDA: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive
- Change the direction to "HCGrid" folder
- Update the library file paths in the Makefile according to the paths of installed dependencies, e.g. CUDA, fits, wcslib, etc.
- make
- Defined and create a target grid map according to specific scenario, in Creat_target_file.py, such as:
# define target FITS/WCS header
header = {
'NAXIS': 3,
'NAXIS1': dnaxis1,
'NAXIS2': dnaxis2,
'NAXIS3': 1,
'CTYPE1': 'RA---SIN',
'CTYPE2': 'DEC--SIN',
'CUNIT1': 'deg',
'CUNIT2': 'deg',
'CDELT1': -pixsize,
'CDELT2': pixsize,
'CRPIX1': dnaxis1 / 2.,
'CRPIX2': dnaxis2 / 2.,
'CRVAL1': mapcenter[0],
'CRVAL2': mapcenter[1],
}- Set the related kernel parameters in HCGrid.cpp
/*Set kernel*/
kernel_type = GAUSS1D;
kernelsize_fwhm = 300./3600.;
kernelsize_sigma = 0.2;
kernel_params[0] = kernelsize_sigma;
sphere_radius = 3.*kernelsize_sigma;
hpx_max_resolution=kernelsize_sigma/2;
_prepare_grid_kernel(
kernel_type,
kernel_params,
sphere_radius,
hpx_max_resolution
);- make
In the terminal window, after successful compilation, you can do the following thing:
- Type "./HCGrid -h" to get the detail parameter guide.
- ./HCGrid [options]. The options include the following parameter:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| fits_path | Absolute path of FITS file |
| input_file | Name of unsorted input FITS file |
| target_file | Name of target FITS file |
| output_file | Name of output FITS file |
| sorted_file | Name of sorted input FITS file |
| fits_id | ID of FITS file |
| beam_size | Beam size of FITS file |
| register_num | total number of registers for each thread block of the GPU |
| sp_num | the number of SPs in each SM of the GPU. |
| ord_arg | Select the pre_order function |
| block_num | The number of thread in each block |
| coarsening_factor | The value of coarsening factor |
- Create the target map:
$ python Creat_target_file.py -p /home/summit/Project/HCGrid/data/ -t target -n 1 -b 300Note: You need to set the relevant parameters of target_map according to the coverage sky area and beam width of the sampled data. For details, please refer to "Creat_target_file.py " file.
- Do the gridding:
$ ./HCGrid --fits_path /home/summit/Project/HCGrid/data/ --input_file input --target_file target --output_file output --fits_id 1 --beam_size 300 --register_num 64 --sp_num 64 --order_arg 1or
$ ./HCGrid --fits_path /home/summit/HCGrid/data/ --input_file input --target_file target --output_file output --fits_id 1 --beam_size 300 --order_arg 1 --block_num 64The former further specifies the relevant hardware parameters, please refer to our article for details.
Notice:
- fits_path represents the absolute path to all FITS / HDF5 files (including input files, target map files, and output files).
- The parameter "block_num" represents the number of thread in each block. Changing the value of it will also change the number of block in the grid to realize the reasonable thread organization configuration. The best value of block_num has relationship with the register of GPU. For example, For Tesla K40, the total number of registers available per block is 64K. And the compilation report shows that the kernel of HCGrid calls a total of 184 registers, because the kernel does not use shared memory to store parameters, so it is expected that each thread block can execute about 64K/184
$\approx$ 356 threads concurrently. So, the better value of block_num should close to 356. 3. Parameter "coarsening_factor" represents the value of coarsening factor$\gamma$ . When applying thread coarsening strategy in practice, the factor$\gamma$ should be reasonable setting according to the resolution of the output grid. Through experiments, we found that a large$\gamma$ would reduce the accuracy of gridding, so we suggested that the selection range of$\gamma$ should be$\gamma=1,2,3$ .
HCGrid is being further improved, if you have any question or ideas, please don't skimp on your suggestions and welcome make a pull request. Moreover, you can contact us through the follow address.