A Webpack development server in a plugin.
Be sure to browse our recipes and peruse the FAQ after reading the documentation below.

Please consider donating if you find this project useful.
webpack-plugin-serve is an evergreen 🌲 module.
This module requires an Active LTS Node version (v8.0.0+ or v10.0.0+). The client scripts in this module require browsers which support async/await. Users may also choose to compile the client script via an appropriately configured Babel webpack loader for use in older browsers.
In many ways, webpack-plugin-serve stands out from the alternatives. Feature parity with existing solutions is a high priority. If a feature you've come to expect in an alternative isn't directly available, it's likely easy to implement via middleware. Feel free to open an issue for direction.
For those interested in direct comparisons, please see the Feature Grid for a breakdown of feature comparisons between webpack-plugin-serve and the alternatives.
Using npm:
npm install webpack-nano webpack-plugin-serve --save-devNote: We recommend using webpack-nano, a very tiny, very clean webpack CLI.
Create a webpack.config.js file:
const { WebpackPluginServe: Serve } = require('webpack-plugin-serve');
const options = { ... };
module.exports = {
// an example entry definition
entry: [
'app.js',
'webpack-plugin-serve/client' // ← important: this is required, where the magic happens in the browser
]
...
plugins: [
new Serve(options)
],
watch: true // ← important: webpack and the server will continue to run in watch mode
};Note: For more information and examples on configuring the entry property, please see the Configuring Entry Points recipe.
And run webpack:
$ npx wpType: Object
Default: null
Sets options specifically for the client script. In most situations this option doesn't need to be modified.
Type: String
If set, allows for overriding the WebSocket address, which corresponds to the server address by default. Values for this option should be in a valid {host}:{port} format. e.g. localhost:433.
Type: Boolean
If true, instructs the client to attempt to reconnect all WebSockets when their connects are interrupted, usually as a result of the server being stopped and/or restarted. Note: This can be very spammy in the browser console, as there is no way to suppress error messages from the browser when a WebSocket fails to connect.
Type: Boolean
If true, instructs the client not to log anything to the console.
Type: Boolean
Default: false
If true, enables compression middleware which serves files with GZip compression.
Type: Boolean | Object
Default: false
If true, enables History API Fallback via connect-history-api-fallback. Users may also pass an options Object to this property. Please see connect-history-api-fallback for details.
This setting can be handy when using the HTML5 History API; index.html page will likely have to be served in place of any 404 responses from the server, specially when developing Single Page Applications.
Note: The Accept header is explicitly stripped from the /wps WebSocket path when using historyFallback, due to an issue with how Firefox and the middleware interact.
Type: boolean
Default: true
If true, will enable Hot Module Replacement which exchanges, adds, or removes modules from a bundle dynamically while the application still running, without the need of a full page reload.
Note: If the build process generates errors, the client (browser) will not be notified of new changes and no HMR will be performed. Errors must be resolved before HMR can proceed.
Type: String | Promise
Default: :: for IPv6, 127.0.0.1 for IPv4
Sets the host the server should listen from. Users may choose to set this to a Promise, or a Function which returns a Promise for situations in which the server needs to wait for a host to resolve.
Note: The default URI is http://[::]:{port}. For more info, please read the FAQ.
Type: boolean | http2 options | secure http2 options
If set, this option will instruct the server to enable HTTP2. Properties for this option should correspond to HTTP2 options or HTTP2 SSL options.
Type: Object
Default: null
If set, this option will instruct the server to enable SSL via HTTPS. Properties for this option should correspond to HTTPS options.
Type: boolean
Default: false
If true, will instruct the client to perform a full page reload after each build.
Note: This option overrides any value set for the hmr option property.
Type: String
Default: { level: 'info' }
Valid level Values: 'trace' | 'debug' | 'info' | 'warn' | 'error'
Sets a level for which messages should appear in the console. For example: if warn is set, every message at the warn and error levels will be visible. This module doesn't produce much log output, so you probably won't have to fiddle with this.
A timestamp: true property/value may also be used to preface each log line with an HH:mm:ss format timestamp.
Type: Function
Default: (app, builtins) => {}
Allows users to implement custom middleware, and manipulate the order in which built-in middleware is executed. This method may also return a Promise to pause further middleware evaluation until the Promise resolves. This property should only be set by users with solid knowledge of Express/Koa style middleware and those which understand the consequences of manipulating the order of built-in middleware.
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new WebpackPluginServe({
middleware: (app, builtins) =>
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.body = 'Hello world';
await next();
})
})
]
};Currently supported built-in middleware that are available on the builtins parameter:
compress → forwards to koa-compress
four0four → handles requests that result in a 404 status
headers → applies specified custom headers to each request
historyFallback → forwards to connect-history-api-fallback
proxy → forwards to http-proxy-middleware
static → forwards to koa-static
websocket → Custom middleware that provides WebSocket support
Type: boolean | Object
Default: false
If true, opens the default browser to the set host and port. Users may also choose to pass an Object containing options for the opn module, which is used for this feature.
Type: Number | Promise
Default: 55555
Sets the port on which the server should listen. Users may choose to set this to a Promise, or a Function which returns a Promise for situations in which the server needs to wait for a port to resolve.
Type: boolean | String
Default: true
If truthy, the module will add a ProgressPlugin instance to the webpack compiler, and display a progress indicator on the page within the browser.
If a value of 'minimal' is set, the progress indicator will render as a small, colored bar at the top of the window. This can be useful when the default fancy progress indicator interferes with elements in the page.
Type: String | Array(String) | Object
Default: compiler.context
Sets the directory(s) from which static files will be served from the root of the application. Bundles will be served from the output config setting. For specifying options for static file directories, please see middleware > static. For a in-depth example, check out the Static HTML File recipe.
The static option supports glob patterns when an Object is passed with a glob property. This is useful for targeting only specific directories in a complex tree. Users may also provide an options property which supports globby options. For example:
static: {
glob: [path.join(__dirname, 'dist/**/public')],
options: { onlyDirectories: true }
}Type: boolean
Default: true
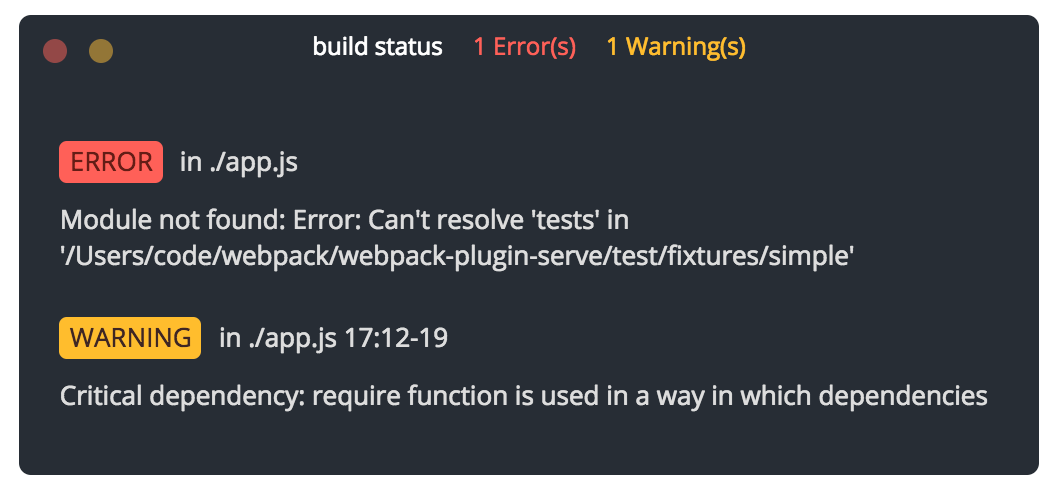
By default, webpack-plugin-serve will display a status overlay when a build results in errors and/or warnings. To disable this feature, set status: false in the options.
When the minimize button (yellow dot) is clicked, the overlay will shrink to a single small box in the lower right corner of the page and display a status beacon using the same green, red, and yellow colors for build success, errors, and warnings, respectively.
Type: boolean
Default: false
If true, instructs the server to halt middleware processing until the current build is done.
Proxying with webpack-plugin-serve is supported via the middleware option. But while this plugin module doesn't contain any fancy options processing for proxying, it does include access to the http-proxy-middleware module by default, and the rest should look familiar to users of http-proxy-middleware.
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
...,
plugins: [
new WebpackPluginServe({
middleware: (app, builtins) => {
app.use(builtins.proxy('/api', { target: 'http://10.10.10.1:1337' }));
}
})
]
};Note: The app.use(...) call here is slightly different than what Express users are used to seeing with http-proxy-middleware. This is due to subtle differences in how the module interacts with Koa, which is used under the hood in this plugin.
To get type definitions for this project:
npm install -D @types/webpack-plugin-serve