Project VOICED: Depth Completion from Inertial Odometry and Vision
Tensorflow implementation of Unsupervised Depth Completion from Visual Inertial Odometry
Published in RA-L January 2020 and ICRA 2020
Model have been tested on Ubuntu 16.04 using Python 3.5, Tensorflow 1.14
Authors: Alex Wong, Xiaohan Fei, Stephanie Tsuei
If you use this work, please cite our paper:
@article{wong2020unsupervised,
title={Unsupervised Depth Completion From Visual Inertial Odometry},
author={Wong, Alex and Fei, Xiaohan and Tsuei, Stephanie and Soatto, Stefano},
journal={IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters},
volume={5},
number={2},
pages={1899--1906},
year={2020},
publisher={IEEE}
}
Table of Contents
- About sparse-to-dense depth completion
- About VOICED
- Setting up
- Training VOICED
- Downloading pretrained models
- Evaluating VOICED
- Related projects
- License and disclaimer
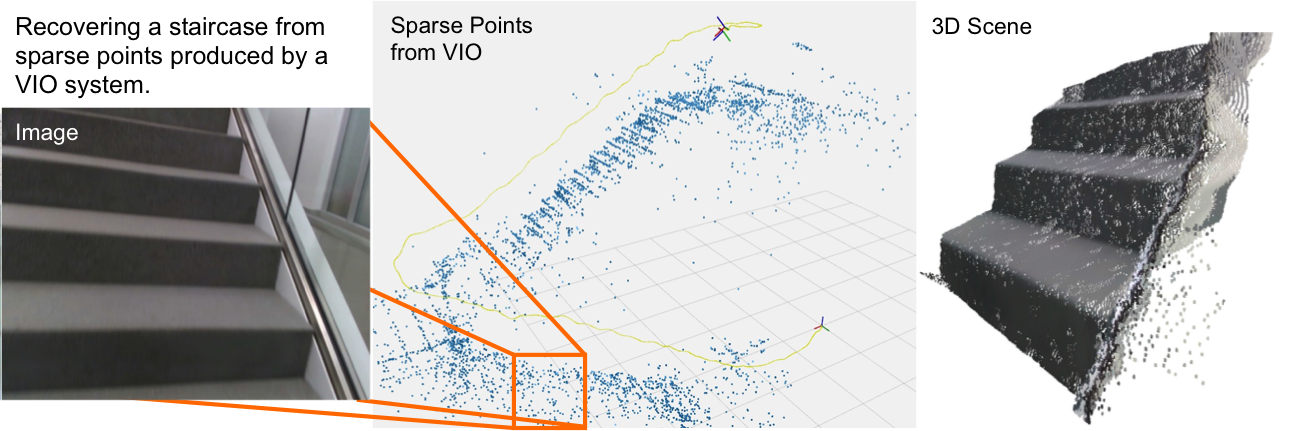
In the sparse-to-dense depth completion problem, we seek to infer the dense depth map of a 3-D scene using an RGB image and its associated sparse depth measurements in the form of a sparse depth map, obtained either from computational methods such as SfM (Strcuture-from-Motion) or active sensors such as lidar or structured light sensors.
| Input RGB image from the VOID dataset | Densified depth map -- colored and back-projected to 3-D |
|---|---|
 |
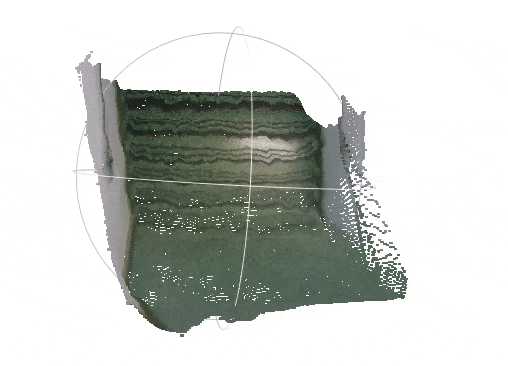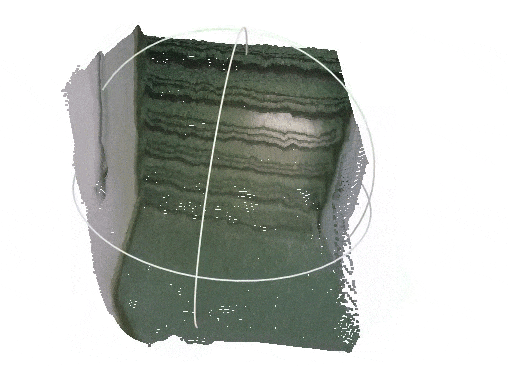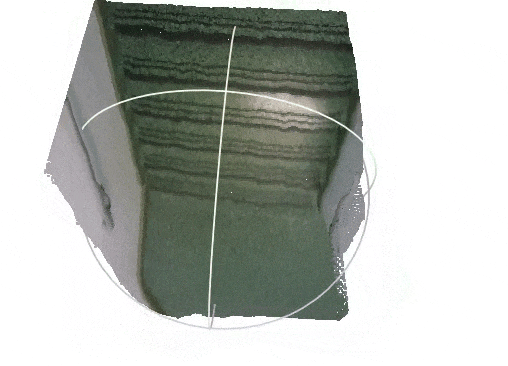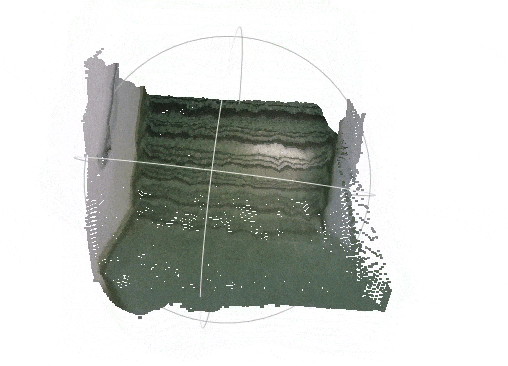 |
| Input RGB image from the KITTI dataset | Densified depth map -- colored and back-projected to 3-D |
|---|---|
 |
 |
To follow the literature and benchmarks for this task, you may visit: Awesome State of Depth Completion
VOICED is an unsupervised depth completion method that is built on top of XIVO. Unlike previous methods, we build a scaffolding of the scene using the sparse depth measurements (~5% density for outdoors driving scenarios like KITTI and ~0.5% to ~0.05% for indoors scenes like VOID) and refines the scaffolding using a light-weight network.
This paradigm allows us to achieve the state-of-the-art on the unsupervised depth completion task while reducing parameters by as much as 80% compared to prior-arts. As an added bonus, our approach does not require top of the line GPUs (e.g. Tesla V100, Titan V) and can be deployed on much cheaper hardware.
We will create a virtual environment with the necessary dependencies
virtualenv -p /usr/bin/python3 voiced-py3env
source voiced-py3env/bin/activate
pip install opencv-python scipy scikit-learn Pillow matplotlib gdown
pip install numpy==1.16.4 gast==0.2.2
pip install tensorflow-gpu==1.14
For datasets, we will use KITTI for outdoors and VOID for indoors
mkdir data
bash bash/setup_dataset_kitti.sh
bash bash/setup_dataset_void.sh
The bash script downloads the VOID dataset using gdown. However, gdown intermittently fails. As a workaround, you may download them via:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1GGov8MaBKCEcJEXxY8qrh8Ldt2mErtWs
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1c3PxnOE0N8tgkvTgPbnUZXS6ekv7pd80
https://drive.google.com/open?id=14PdJggr2PVJ6uArm9IWlhSHO2y3Q658v
which will give you three files void_150.zip, void_500.zip, void_1500.zip.
Assuming you are in the root of the repository, to construct the same dataset structure as the setup script above:
mkdir void_release
unzip -o void_150.zip -d void_release/
unzip -o void_500.zip -d void_release/
unzip -o void_1500.zip -d void_release/
bash bash/setup_dataset_void.sh unpack-only
For more detailed instructions on downloading and using VOID and obtaining the raw rosbags, you may visit the VOID dataset webpage.
To train VOICED on the KITTI dataset, you may run
sh bash/train_voiced_kitti.sh
To train VOICED on the VOID datasets, you may run
sh bash/train_voiced_void.sh
To monitor your training progress, you may use Tensorboard
tensorboard --logdir trained_models/<model_name>
To use our KITTI and VOID models, you can download
gdown https://drive.google.com/uc?id=18jr9l1YvxDUzqAa_S-LYTdfi6zN1OEE9
unzip pretrained_models.zip
Note: gdown fails intermittently and complains about permission. If that happens, you may also download the models via:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=18jr9l1YvxDUzqAa_S-LYTdfi6zN1OEE9
We note that the VOID dataset has been improved (size increased from ~40K to ~47K frames) since this work was published in RA-L and ICRA 2020. We thank the individuals who reached out and gave their feedback. Hence, to reflect the changes, we retrained our model on VOID. We achieve slightly better performance than the reported numbers in the paper.
| Model | MAE | RMSE | iMAE | iRMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG11 from paper | 85.05 | 169.79 | 48.92 | 104.02 |
| VGG11 retrained | 82.27 | 141.99 | 49.23 | 99.67 |
To achieve the results, we trained for 20 epochs and use a starting learning rate of 5 x 10-5 up to the 12th epoch, then 2.5 x 10-5 for 4 epochs, and 1.2 x 10-5 for the remaining 4 epochs. The weight for smoothness (wsm) is changed to 0.15. This is reflected in the train_voiced_void.sh bash script.
To evaluate the pretrained VOICED on the KITTI dataset, you may run
sh bash/evaluate_voiced_kitti.sh
To evaluate the pretrained VOICED on the VOID dataset, you may run
sh bash/evaluate_voiced_void.sh
You may replace the restore_path and output_path arguments to evaluate your own checkpoints
You may also find the following projects useful:
- VOID: from Unsupervised Depth Completion from Visual Inertial Odometry. A dataset, developed by the authors, containing indoor and outdoor scenes with non-trivial 6 degrees of freedom. The dataset is published along with this work in the Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L) 2020 and the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2020.
- XIVO: The Visual-Inertial Odometry system developed at UCLA Vision Lab. This work is built on top of XIVO. The VOID dataset used by this work also leverages XIVO to obtain sparse points and camera poses.
- GeoSup: Geo-Supervised Visual Depth Prediction. A single image depth prediction method developed by the authors, published in the Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L) 2019 and the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2019. This work was awarded Best Paper in Robot Vision at ICRA 2019.
This software is property of the UC Regents, and is provided free of charge for research purposes only. It comes with no warranties, expressed or implied, according to these terms and conditions. For commercial use, please contact UCLA TDG.