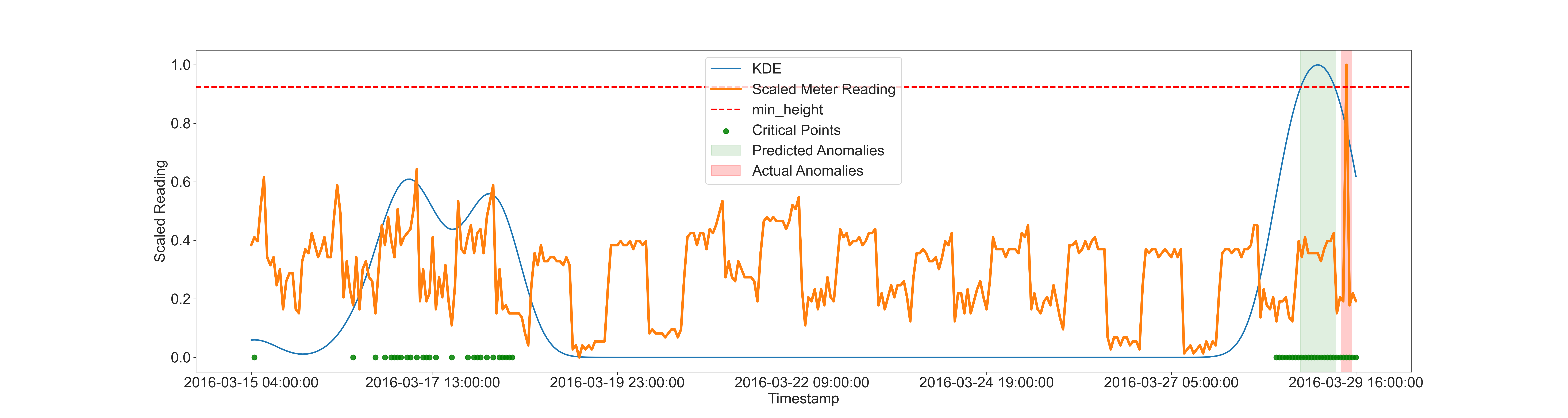
Our related paper "Generative Adversarial Network with Soft-Dynamic Time Warping and Parallel Reconstruction for Energy Time Series Anomaly Detection" (https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2402.14384) got accepted at the AI4TS Workshop @ AAAI 24.
Note: A journal extension of the paper is under development. The repository will be frequently updated.
This study uses the LEAD 1.0 dataset. This public dataset includes hourly-based electricity meter readings for commercial buildings over up to one year. The dataset consists of year-long hourly electricity meter readings with anomaly annotations from 200 buildings and is open-sourced in this GitHub repository [6]. Each building contains about 8,747 data points. Anomaly annotations are provided, marking anomalous points (timestamps) within each building's time series.
This dataset contains hourly electricity meter readings and anomaly annotations for various commercial buildings over a period of up to one year. The data is structured as follows:
building_id: Unique identifier for each building.timestamp: Hourly timestamp of the meter reading.meter_reading: Actual electricity meter reading value.anomaly: Binary indicator of whether the timestamp (reading) is considered anomalous (1) or not (0).
The dataset covers readings from 200 buildings, with each building having approximately 8,747 data points. Anomaly annotations are provided to mark specific timestamps within each building's time series where anomalous readings were detected.
Here's a small example of the dataset:
| building_id | timestamp | meter_reading | anomaly |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 01-01-2016 00:00 | 100.5 | 0 |
| 1 | 01-01-2016 01:00 | 98.2 | 0 |
| 1 | 01-01-2016 02:00 | 95.7 | 0 |
| 2 | 01-01-2016 00:00 | 200.1 | 0 |
| 2 | 01-01-2016 01:00 | 203.4 | 1 |
| 2 | 01-01-2016 02:00 | 197.8 | 0 |
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/HardikPrabhu/Energy-Time-Series-Anomaly-Detection.git- Navigate to the cloned repository.
- Install the required python packages using pip:
- First install torch with cuda support.
pip install torch==2.1.2 torchvision==0.16.2 torchaudio==2.1.2 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121- Then install other requirements.
pip install -r requirements.txt- Adjust the experiment settings:
Modify the config.json file to configure the experiment according to your requirements. This JSON config file allows you to customize various parameters and settings for your experiments.
Given below is the config file with default values.
{
"data": {
"dataset_path": "dataset/15_builds_dataset.csv",
"train_path": "model_input/",
"only_building": 1304
},
"training": {
"batch_size": 128,
"num_epochs": 200,
"latent_dim": 100,
"w_gan_training": true,
"n_critic": 5,
"clip_value": 0.01,
"betaG": 0.5,
"betaD": 0.5,
"lrG": 0.0002,
"lrD": 0.0002
},
"preprocessing": {
"normalize": true,
"plot_segments": true,
"store_segments": true,
"window_size": 48
},
"recon": {
"use_dtw": true,
"iters": 1000,
"use_eval_mode": true
}
}dataset_path: Path to the dataset file ("dataset/15_builds_dataset.csv")train_path: Path where the training data or model inputs are stored ("model_input/")only_building: Particular building identifier or index (1304)
batch_size: Number of samples per batch during the training process (128)num_epochs: Number of training epochs (200)latent_dim: Dimensionality of the latent space in the model (100)w_gan_training: Indicates whether to use Wasserstein GAN (WGAN) training (true)n_critic: Number of critic (discriminator) iterations per generator iteration in WGAN training (5)clip_value: Clipping value for the critic's weights in WGAN training (0.01)betaGandbetaD: Beta values for the generator and discriminator, respectively (0.5)lrGandlrD: Learning rates for the generator and discriminator, respectively (0.0002)
normalize: Indicates whether to normalize the sements (transform all the readings in a segment to be in the [-1,1] range). (true)plot_segments: Specifies whether to plot the segments (true)store_segments: Indicates whether to store the segments (true)window_size: Size of the window for data preprocessing (48)
use_dtw: Indicates whether to use Soft-Dynamic Time Warping (Soft-DTW) for reconstruction (true)iters: Number of iterations used by the gradient descent algorithm in noise space for rconstruction (1000)use_eval_mode: Indicates whether to use evaluation mode of the Generator is used during reconstruction (true)
- Insert the building id of the desired building in the config file.
python config["data"]["only_building"] = 1304
-
Adjust the preprocessing settings in the config file. For example, change the
window_sizeof the subsequences. -
Run the
preprocessing.pyPython script. It will divide the building data into segments. The training segments would not contain any anomaly. The model input tensors of the training segments will be created in themodel_inputdirectory.
- First, adjust the training settings in the config file. The GAN model can be trained in two modes:
- WGAN training
- Simple training (vanilla)
- Set the
w_gan_trainingoption toFalsefor simple training andTruefor WGAN training.
python config["training"]["w_gan_training"] = True
- After adjusting the training settings in the config file, run the
training.pyscript. It will create the model files in thetrained_outdirectory. - Both the generator and the discriminator are stored separately. Only the generator would be used for reconstruction.
-
Adjust the reconstruction settings in the config file.
-
Two options are provided as reconstruction losses:
- Soft-DTW
- MSE
-
Set the
use_dtwoption toFalsefor MSE andTruefor soft-DTW loss.
python config["recon"]["use_dtw"] = True
- Run the
testing.pyscript. It will create the reconstruction data pickle files in thetest_outdirectory.
- Only the reconstruction data pickle file is required for the final step.
- Run the
anom_detect_gan.pyscript. - Note: Uncomment Line 105 and pass the list of specific buildings to be evaluated, else all the available buildings will be evaluated.
- Bayesian optimization is used to adjust the evaluation hyper-parameters.
- A results CSV is created in the working directory.
Anomaly detection process for the entire set of 200 buildings follow the same steps. Each building gets its own GAN model. The process is automated by the run.py script where the reconstruction pickle files are obtained for each building by running the preprocessing.py, training.py and testing.py scripts on loop.
- Set up the appropriate configuration in
config.json - Run
run.py(It runs 3 scripts and creates reconstruction data pickle files) - Run
anom_detect_gan.py - Run
plotting.pyto create plots for the anomaly detection
The directory "experimental" contains code for comparisons with other popular methods. We perform anomaly detection using different methodologies and also try to maintain similar evaluation and training hyper-parameters for fair comparisons.
It includes the following implementations:
-
TAnoGAN - Use gradient descent in the noise space, to get appropriate noise for reconstruction.
-
TADGAN - Train an encoder with cycle consistency, in order to map back to the noise space for reconstruction.
-
1-D CNN Autoencoder - Use the reconstruction error obtained by encoding-decoding as anomaly score.
-
DEGAN - Use the output of the discriminator (1- D(x)) directly as a score.
-
seq-LOF: Local outlier factor method by considering the subsequences as single datapoints of window size dimensions followed by our methodology to convert critical subsequences to anomalous timestamps.
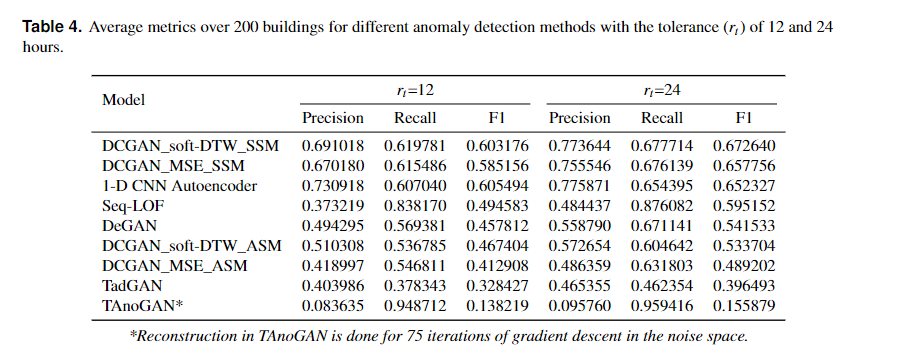
Our model with different configurations and other baseline models are tested on a large dataset of 200 buildings. The average metrics are shown in the table below.
- DCGAN-soft-DTW_SSM:
{
"data": {
"dataset_path": "dataset/200_buildings_dataset.csv",
"train_path": "model_input/",
"only_building": 1304
},
"training": {
"batch_size": 128,
"num_epochs": 200,
"latent_dim": 100,
"w_gan_training": true,
"n_critic": 5,
"clip_value": 0.01,
"betaG": 0.5,
"betaD": 0.5,
"lrG": 0.0002,
"lrD": 0.0002
},
"preprocessing": {
"normalize": true,
"plot_segments": true,
"store_segments": true,
"window_size": 48
},
"recon": {
"use_dtw": true,
"iters": 1000,
"use_eval_mode": true
}
}- DCGAN_MSE_SSM:
{
"data": {
"dataset_path": "dataset/200_buildings_dataset.csv",
"train_path": "model_input/",
"only_building": 1304
},
"training": {
"batch_size": 128,
"num_epochs": 200,
"latent_dim": 100,
"w_gan_training": true,
"n_critic": 5,
"clip_value": 0.01,
"betaG": 0.5,
"betaD": 0.5,
"lrG": 0.0002,
"lrD": 0.0002
},
"preprocessing": {
"normalize": true,
"plot_segments": true,
"store_segments": true,
"window_size": 48
},
"recon": {
"use_dtw": false,
"iters": 1000,
"use_eval_mode": true
}
}- DCGAN-soft-DTW_ASM:
{
"data": {
"dataset_path": "dataset/200_buildings_dataset.csv",
"train_path": "model_input/",
"only_building": 1304
},
"training": {
"batch_size": 128,
"num_epochs": 200,
"latent_dim": 100,
"w_gan_training": true,
"n_critic": 5,
"clip_value": 0.01,
"betaG": 0.5,
"betaD": 0.5,
"lrG": 0.0002,
"lrD": 0.0002
},
"preprocessing": {
"normalize": true,
"plot_segments": true,
"store_segments": true,
"window_size": 48
},
"recon": {
"use_dtw": true,
"iters": 1000,
"use_eval_mode": false
}
}- DCGAN-MSE_ASM:
{
"data": {
"dataset_path": "dataset/200_buildings_dataset.csv",
"train_path": "model_input/",
"only_building": 1304
},
"training": {
"batch_size": 128,
"num_epochs": 200,
"latent_dim": 100,
"w_gan_training": true,
"n_critic": 5,
"clip_value": 0.01,
"betaG": 0.5,
"betaD": 0.5,
"lrG": 0.0002,
"lrD": 0.0002
},
"preprocessing": {
"normalize": true,
"plot_segments": true,
"store_segments": true,
"window_size": 48
},
"recon": {
"use_dtw": false,
"iters": 1000,
"use_eval_mode": false
}
}[1] 1D-DCGAN : https://github.com/LixiangHan/GANs-for-1D-Signal
[2] soft-dtw loss cuda : https://github.com/Maghoumi/pytorch-softdtw-cuda
[3] TAnoGAN : https://github.com/mdabashar/TAnoGAN
[4] MADGAN : https://github.com/Guillem96/madgan-pytorch
[5] TADGAN : https://github.com/arunppsg/TadGAN
[6] LEAD Dataset : https://github.com/samy101/lead-dataset
[7] DEGAN : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2210.02449.pdf