tf-explain implements interpretability methods as Tensorflow 2.0 callbacks to ease neural network's understanding.
See Introducing tf-explain, Interpretability for Tensorflow 2.0
Documentation: https://tf-explain.readthedocs.io
tf-explain is available on PyPi as an alpha release. To install it:
virtualenv venv -p python3.6
pip install tf-explaintf-explain is compatible with Tensorflow 2. It is not declared as a dependency to let you choose between full and standalone-CPU versions. Additionally to the previous install, run:
# For CPU or GPU
pip install tensorflow==2.1.0tf-explain offers 2 ways to apply interpretability methods. The full list of methods is the Available Methods section.
The best option is probably to load a trained model and apply the methods on it.
# Load pretrained model or your own
model = tf.keras.applications.vgg16.VGG16(weights="imagenet", include_top=True)
# Load a sample image (or multiple ones)
img = tf.keras.preprocessing.image.load_img(IMAGE_PATH, target_size=(224, 224))
img = tf.keras.preprocessing.image.img_to_array(img)
data = ([img], None)
# Start explainer
explainer = GradCAM()
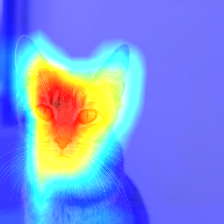
grid = explainer.explain(data, model, class_index=281) # 281 is the tabby cat index in ImageNet
explainer.save(grid, ".", "grad_cam.png")If you want to follow your model during the training, you can also use it as a Keras Callback, and see the results directly in TensorBoard.
from tf_explain.callbacks.grad_cam import GradCAMCallback
model = [...]
callbacks = [
GradCAMCallback(
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
class_index=0,
output_dir=output_dir,
)
]
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=2, epochs=2, callbacks=callbacks)- Activations Visualization
- Vanilla Gradients
- Gradients*Inputs
- Occlusion Sensitivity
- Grad CAM (Class Activation Maps)
- SmoothGrad
- Integrated Gradients
Visualize how a given input comes out of a specific activation layer
from tf_explain.callbacks.activations_visualization import ActivationsVisualizationCallback
model = [...]
callbacks = [
ActivationsVisualizationCallback(
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
layers_name=["activation_1"],
output_dir=output_dir,
),
]
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=2, epochs=2, callbacks=callbacks)Visualize gradients importance on input image
from tf_explain.callbacks.vanilla_gradients import VanillaGradientsCallback
model = [...]
callbacks = [
VanillaGradientsCallback(
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
class_index=0,
output_dir=output_dir,
),
]
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=2, epochs=2, callbacks=callbacks)Variant of Vanilla Gradients ponderating gradients with input values
from tf_explain.callbacks.gradients_inputs import GradientsInputsCallback
model = [...]
callbacks = [
GradientsInputsCallback(
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
class_index=0,
output_dir=output_dir,
),
]
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=2, epochs=2, callbacks=callbacks)Visualize how parts of the image affects neural network's confidence by occluding parts iteratively
from tf_explain.callbacks.occlusion_sensitivity import OcclusionSensitivityCallback
model = [...]
callbacks = [
OcclusionSensitivityCallback(
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
class_index=0,
patch_size=4,
output_dir=output_dir,
),
]
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=2, epochs=2, callbacks=callbacks)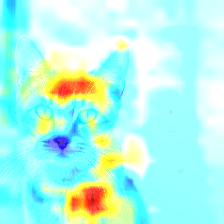
Occlusion Sensitivity for Tabby class (stripes differentiate tabby cat from other ImageNet cat classes)
Visualize how parts of the image affects neural network's output by looking into the activation maps
From Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-based Localization
from tf_explain.callbacks.grad_cam import GradCAMCallback
model = [...]
callbacks = [
GradCAMCallback(
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
class_index=0,
output_dir=output_dir,
)
]
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=2, epochs=2, callbacks=callbacks)Visualize stabilized gradients on the inputs towards the decision
From SmoothGrad: removing noise by adding noise
from tf_explain.callbacks.smoothgrad import SmoothGradCallback
model = [...]
callbacks = [
SmoothGradCallback(
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
class_index=0,
num_samples=20,
noise=1.,
output_dir=output_dir,
)
]
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=2, epochs=2, callbacks=callbacks)Visualize an average of the gradients along the construction of the input towards the decision
From Axiomatic Attribution for Deep Networks
from tf_explain.callbacks.integrated_gradients import IntegratedGradientsCallback
model = [...]
callbacks = [
IntegratedGradientsCallback(
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
class_index=0,
n_steps=20,
output_dir=output_dir,
)
]
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=2, epochs=2, callbacks=callbacks)- Subclassing API Support
- Additional Methods
- Auto-generated API Documentation & Documentation Testing
To contribute to the project, please read the dedicated section.