This GitHub repo. contains the ARM template for deploying Health Bot reference architecture.
| File/Folder | Description |
|---|---|
ARM Template |
azuredeploy.json and cert-deploy.json provision the Azure resources in the reference architecture. |
CHANGELOG.md |
List of changes to the template. |
CONTRIBUTING.md |
Guidelines for contributing to the template. |
README.md |
This README file. |
LICENSE |
The license for the template. |
-
A GitHub Account to clone and/or fork this repository.
-
An Azure Resource Group with Owner Role permission. All Azure resources will be deployed into this resource group.
-
A Health Bot instance. Refer to Create your first Healthcare Bot quickstart in the Health Bot documentation.
-
Review the ARM template
azuredeploy.jsonbefore proceeding. Update the resource configuration parameters to meet your requirements. -
(Optional) The following CLI tools are preinstalled in Azure Cloud Shell. In case you are planning to use a workstation or a VM to deploy the ARM template, install the CLI tools before proceeding. Links for downloading the tools are provided in the next section.
- Azure CLI
- GitHub CLI
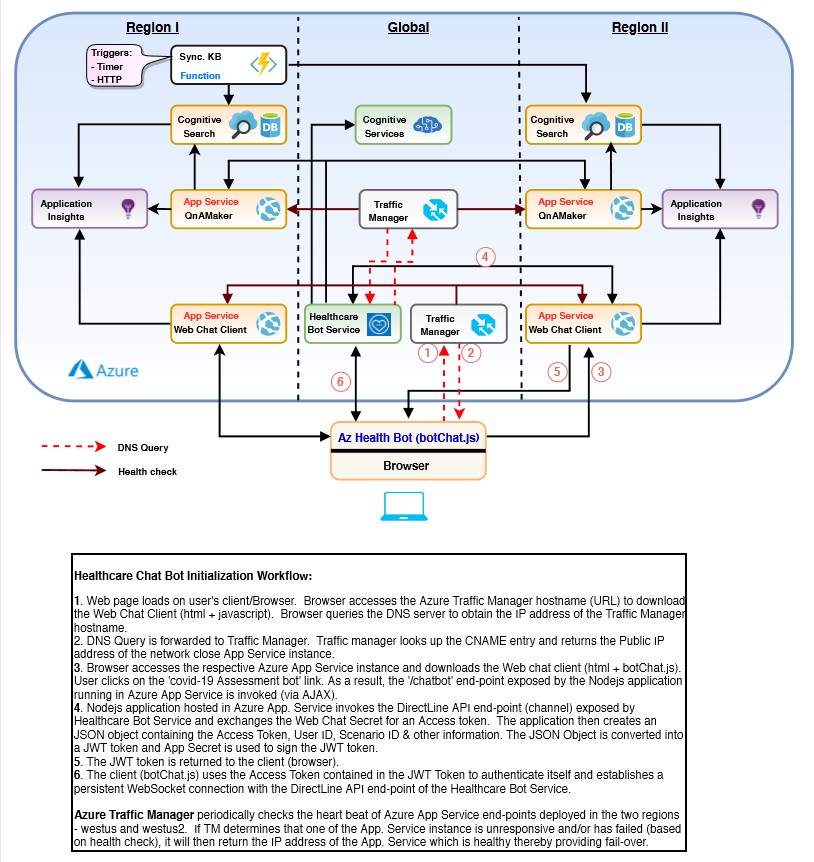
The aim of this reference architecture is multifold.
-
Help customers quickly deploy Microsoft Health Bot and Cognitive Services resources in Production region on Azure.
-
Describe the integration touch points between the Health Bot, Azure Cognitive Services and Web Chat Client application. Azure Cognitive Services includes Congitive Search, QnA Maker and other AI services.
-
Guide customers to provision the Microsoft Health Bot resources in a highly available fault tolerant configuration. Core services of the solution such as the Web Chat Client, QnA Maker runtime and Azure Cognitive Search are deployed in two separate Azure regions to provide for automatic failover.
Readers are advised to refer to the following resources as needed.
- Azure CLI 2.2+
- Git SCM Docs
- Azure Resource Manager Documentation
- Azure Resource Manager Template Reference
- Microsoft Health Bot Documentation
- Web Chat Client GitHub Repository
- Azure Cognitive Services Documentation
- Azure QnA Maker Documentation
- Business Continuity Plan for QnA Maker Service
- Azure Cognitive Search Documentation
- Synchronize Azure Search Indexes
- Azure Function Documentation
- Unless otherwise noted explicitly, the first region listed in the locations parameter (array) will represent the primary region and the second will denote the secondary region.
- The ARM template parameter name has to be unique for each Health Bot deployment. Use an alpha numberic value for this name parameter. All Azure resources deployed by the ARM template will have names prefixed with this deployment name.
- Azure Traffic Manager is used to shift the Web Chat Client and QnA Maker API traffic across the individual Azure App Service instances deployed in the two regions. The end user (customer) is responsible for configuring the respective traffic routing algorithm in the Traffic Manager to ensure the traffic is split evenly between the App Service instances as per their requirements.
Follow the steps below to deploy the Health Bot resources on Azure.
-
Review and update template parameters in the
azuredeploy.parameters.jsonfileRefer to the table below for a description of the template parameters. Configure the values as per your requirements.
Parameter Name Type Description name string A unique name for this deployment. All provisioned resource names will be prefixed with this name. This includes the web site and traffic manager FQDN's. locations array (of strings) Specify Azure region names (max. 2) where the resources need to be provisioned. The resources can be provisioned in a max. of 2 regions. WEBCHAT_SECRET string Health Bot instance webchat_secret. Retrieve this secret value from the Health Bot Portal. Refer to the Health Bot documentation here. APP_SECRET string Health Bot instance app_secret. Obtain this secret value from the Health Bot Portal. appServicePlanSku object Use this object to specify the SKU size for the Azure App Service Plans. workerSize string Specify the number of workers in the Azure App Service Plan. qnaMakerServiceLocation string QnA Maker resource location. This should be set to westus for all commercial deployments. qnaMakerServiceSku string Specify the SKU size for the Cognitive Services account. qnaMakerSearchSku string Specify the SKU size for the Cognitive Search instances. webchatRepoUrl string Web Chat Client GitHub repository uri. Use the default value as-is. webchatRepoBranch string Web Chat Client GitHub repository branch. Use the default value ( master). If Web Chat Client v3 is desired, then set the value to webchat_v3.funcRepoUrl string GitHub repository uri for Azure Functions. The functions synchronize the knowledge bases (indexs) between the Azure Search instances deployed in two different regions. funcRepoBranch string GitHub repository branch for Azure Functions. Use the default value ( master). -
Login to Azure
Open a terminal window or login to the Azure Cloud Shell.
Refer to the commands below to login to Azure from a command prompt in a VM. You can skip this step if you are using the Azure Cloud shell.
# Login to Azure $ az login #
-
Clone this repository
Clone this GitHub repository to your local VM or cloud shell. Refer to the command snippet below.
# Create a directory to store all Git projects $ mkdir git-repos # # Switch to the 'git-repos' directory $ cd git-repos # # Clone this GitHub repository. $ git clone https://github.com/microsoft/HealthBotRefArchDeploy.git # # Switch to the Health Bot project root directory $ cd HealthBotRefArchDeploy #
-
Validate the ARM template
Follow the steps in the command snippet below to validate the ARM template.
# (Optional) Create a resource group # Substitute correct values for the following # - group-name: Name of the resource group # - region-name: Azure region for the resource group # $ az group create -n <group-name> -l <region-name> # # Validate the ARM template. Make sure there are no errors. # $ az deployment group validate --verbose --resource-group <group-name> --template-file azuredeploy.json --parameters @./azuredeploy.parameters.json #
-
Run the ARM deployment
Follow the steps in the command snippet below to run the ARM template and provision the Health Bot resources on Azure.
# Deploy resources defined in the ARM template # Substitute correct values for the following # - group-name: Name of the resource group # $ az deployment group create --verbose --resource-group <group-name> --template-file azuredeploy.json --parameters @./azuredeploy.parameters.json #
NOTE: The ARM template will run for approximately 15 - 20 minutes. Be patient and treat yourself to a cookie.
-
Verify Azure Resources
Login to the Azure portal. Confirm all resources were provisioned in the resource group correctly.
NOTE: For configuring a custom domain and TLS certificates, skip the steps below and refer to the section at the end of this section (links to App Service documentation).
Follow the steps below to configure App Service Managed Certificate for the Web Chat Client and QnA Maker App Services.
-
Review and update template parameters in the
cert-deploy.parameters.jsonfileRefer to the table below for a description of the template parameters. Configure the values as per your requirements.
Parameter Name Type Description name string A unique name for this deployment. All provisioned resource names will be prefixed with this name. Specify the same deployment name as in Section A. locations array (of strings) Specify Azure region names (max. 2) where the resources need to be provisioned. The resources can be provisioned in a max. of 2 regions. Specify the same locations which were specified in Section A. tmDomainSuffix string The default DNS suffix for Azure Traffic Manager is .trafficmanager.net. -
Validate the ARM template
After making the required changes to the template parameters file, follow the steps in the command snippet below to validate the ARM template.
# Validate the ARM template. Make sure there are no errors. # Substitute correct values for # - group-name: Name of the Azure Resource Group # $ az deployment group validate --verbose --resource-group <group-name> --template-file cert-deploy.json --parameters @./cert-deploy.parameters.json #
-
Run the ARM deployment
Refer to the command snippet below to run the ARM template.
# Deploy resources defined in the ARM template # Substitute correct values for the following # - group-name: Name of the resource group # $ az deployment group create --verbose --resource-group <group-name> --template-file cert-deploy.json --parameters @./cert-deploy.parameters.json #
-
Verify TLS/SSL and Custom domain configurations for App Services
Login to the Azure Portal. Go to the App Service and click on Custom domains and TLS/SSL settings blades. Verify the custom domain, TLS/SSL certificate and bindings have been configured properly.
For configuring custom domains and TLS certificates with the App Services, refer to the articles below.
- Add an SSL certificate in Azure App Service
- Secure a custom DNS name with SSL binding in Azure App Service
The following steps have to be completed manually once the ARM template is deployed and all required resources have been provisioned on Azure.
-
Generate the QnA Maker Knowledge Base for COVID-19 FAQs in the Health Bot Service Portal
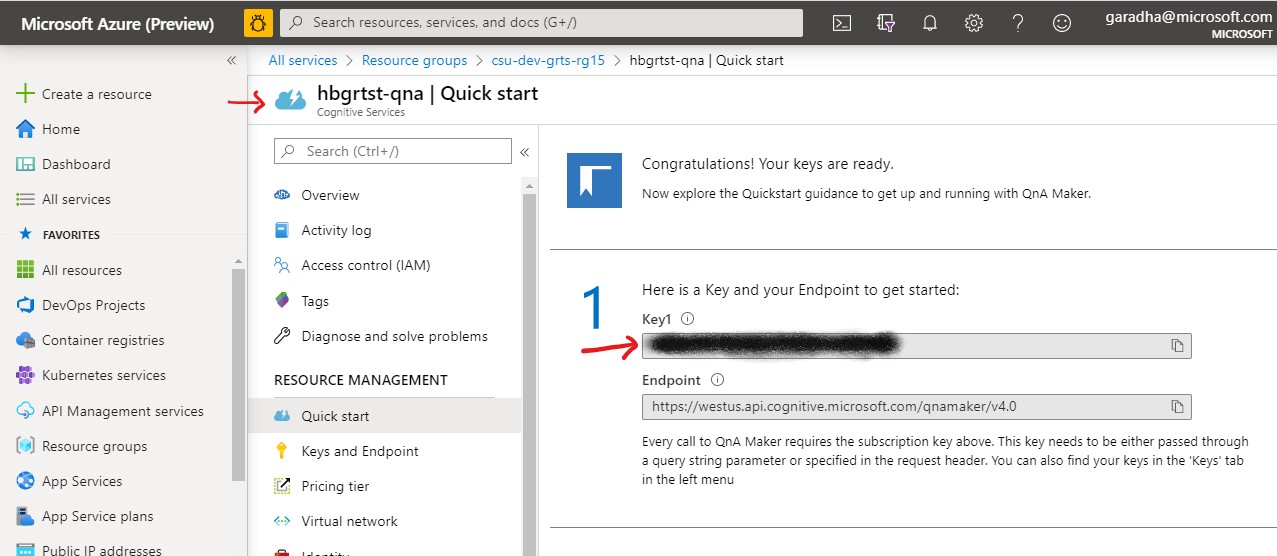
Login to Azure Portal and retrieve the QnA Maker Subscription Key by accessing the Cognitive Service. The Cognitive Service resource should have a name that ends with -qna. See screenshot below.
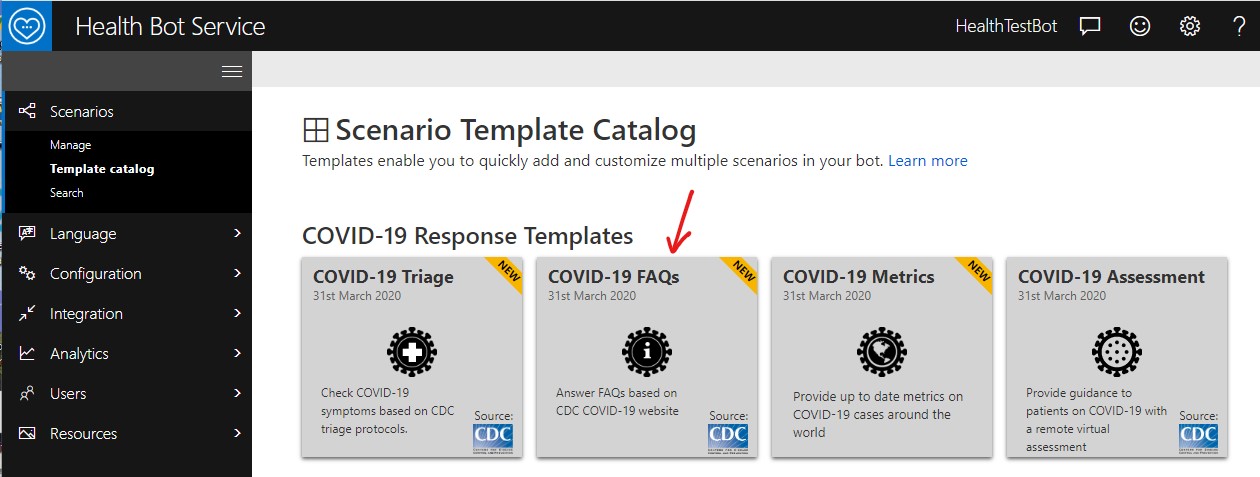
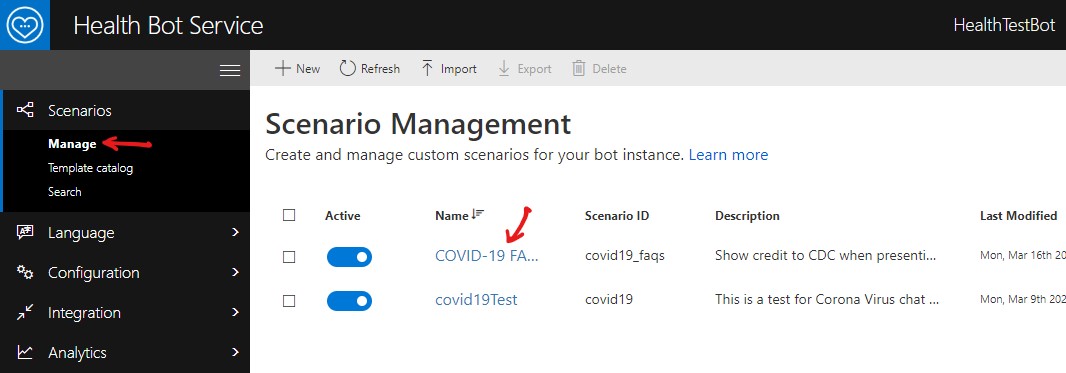
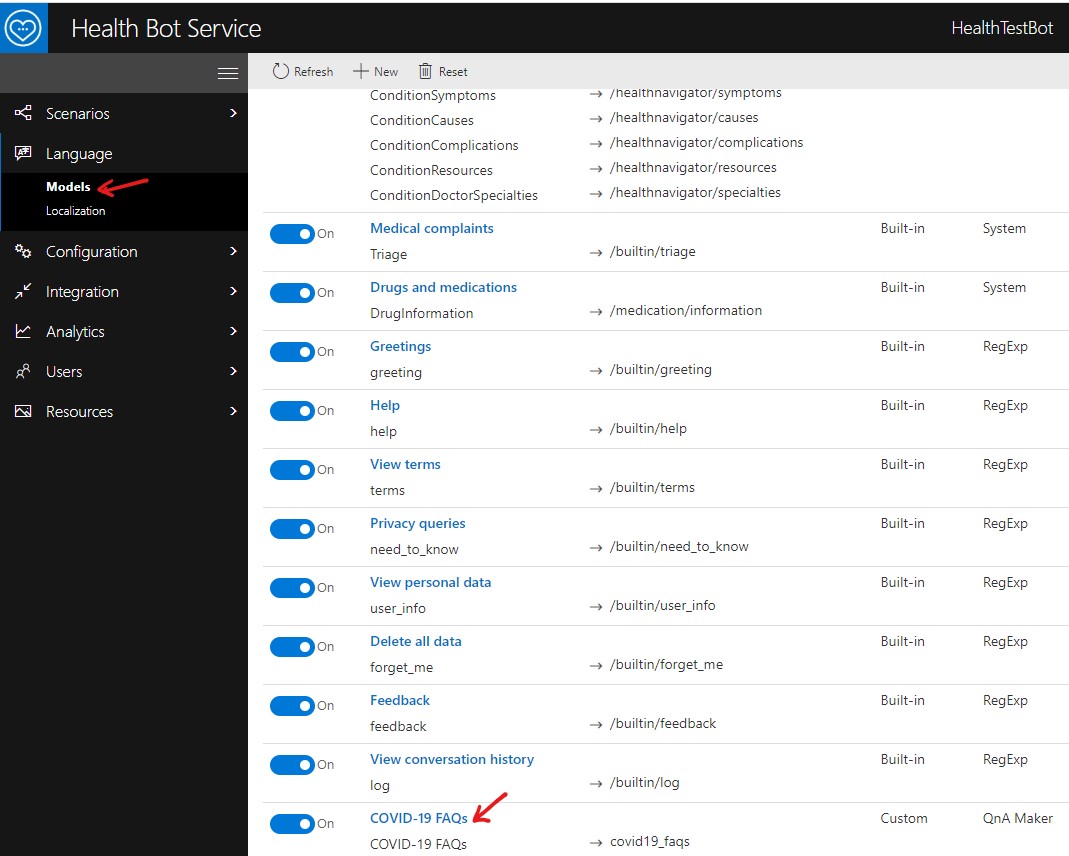
Login to Health Bot Service Portal, access the Scenario Template Catalog and create a QnA Model using COVID-19 FAQs template. See screenshots below.
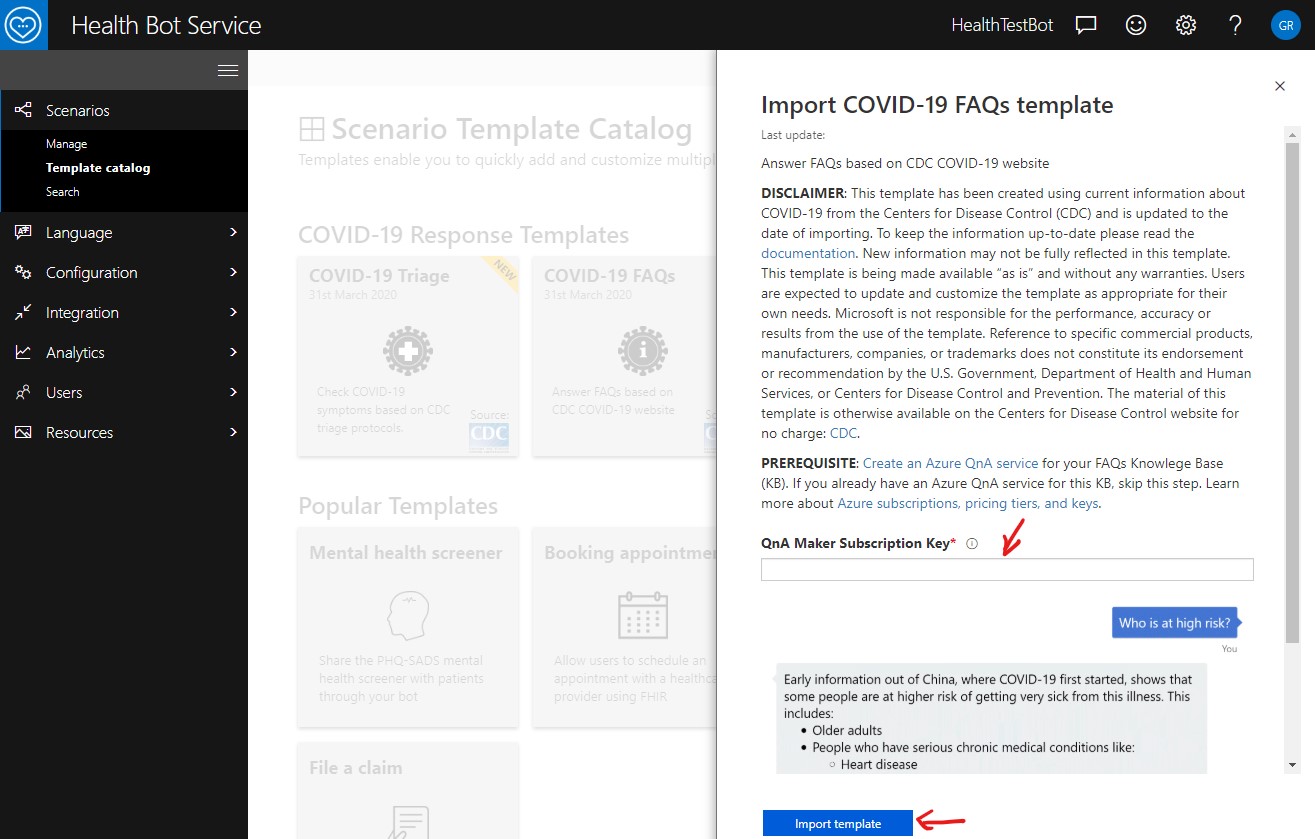
Specify the QnA Maker Subscription Key which you retrieved in the previous step. Then click on Import template.
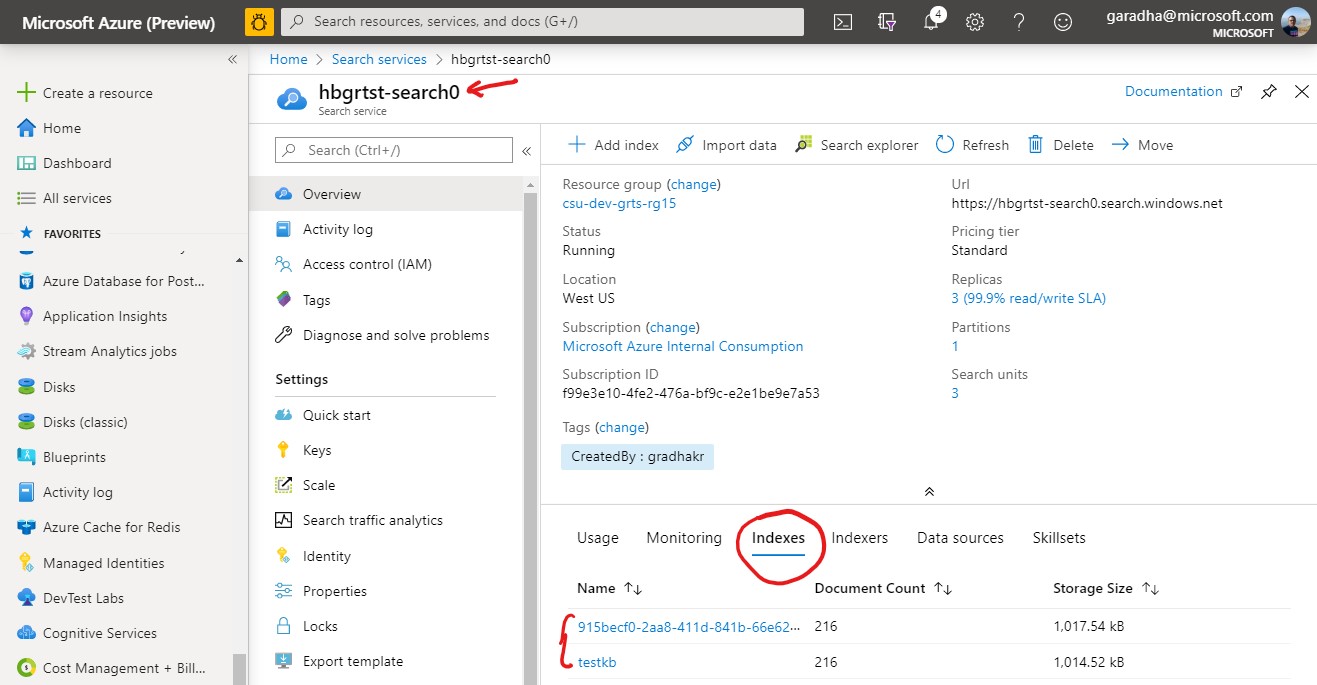
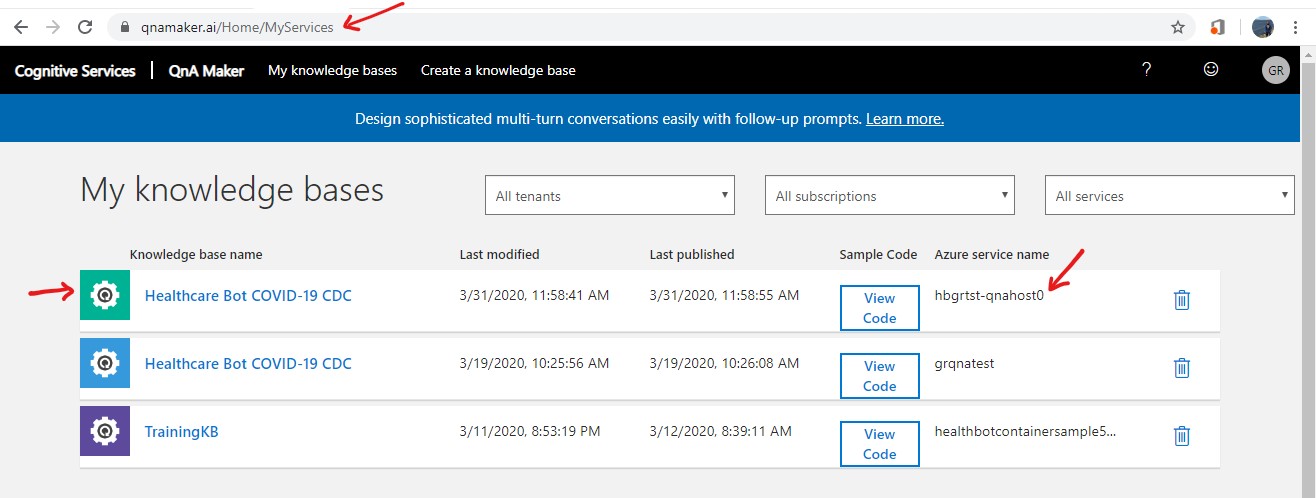
Exit out of the Scenario Editor. The previous step creates the following resources which can be viewed by accessing the respective portals. See below.
Health Bot Service Portal
Azure Portal
QnA Maker Portal
Review the above resources.
-
Back up the QnA Maker runtime in primary region and restore it in the secondary region
The ARM template deploys one Cognitive Services resource and two QnA Maker App Service instances, one in each region. The template deploys the QnA Maker runtime only in the App Service instance deployed in the primary region. As a consequence, the QnA Maker runtime has to be deployed in the secondary region. The quickest and easiest way is to take a back up of the QnA Maker App Service instance in the primary region and restore it in the secondary region.
Refer to Back up an app to take a back up of the QnA Maker App Service in the primary region. The QnA Maker App Service in the primary region would have a name ending with -qnahost0.
Refer to Restore a backup to restore the back up from primary into the secondary region. The QnA Maker App Service in the secondary region would have a name ending with -qnahost1.
-
Reconfigure the QnA Maker runtime in secondary region
Update QnA Maker App Service application settings in secondary region.
In Azure Portal, access the QnA Maker App Service instance in secondary region. The name for this resource should end with -qnahost1. Access the Configuration blade of the App Service and update application settings values listed in the table below.
Parameter Name Description AzureSearchName Specify the name of the Cognitive Search resource. Name of this resource should end with -search1. AzureSearchAdminKey Specify the value of Cognitive Search Admin key (Primary admin key). You can retrieve this key by accessing the Keys blade of the Cognitive Search instance. UserAppInsightsAppId Application Insights App ID UserAppInsightsKey Application Insights Instrumentation Key UserAppInsightsName Application Insights resource name NOTE: Remember to specify the names of the resources and application insights keys deployed in the secondary region.
Click Save and this will restart the QnA Maker App Service in the secondary region.
-
Synchronize the Azure Search Indexes in the primary and secondary regions
Finally, invoke the Azure Function to copy the search indexes from the Cognitive Search instance in primary to secondary.
The Azure Function name ends with -qnakb-sync and is deployed in primary region. This Function is configured with both an HTTP and Timer trigger.
To initiate the synchronization process manually, issue a HTTP
GETAPI call to the Function's HTTP endpoint (below) from a web browser or a terminal window (usingcurlcommand).http://[name]-qnakb-sync.azurewebsites.net/api/httpcogsearchkbsync
Substitute the deployment name in the
nameplaceholder above.NOTE: The source code for the Azure Search synchronization function is available on GitHub. The synchronization code can also be run as a standalone program. The source code for the standalone program is also available on GitHub.
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.