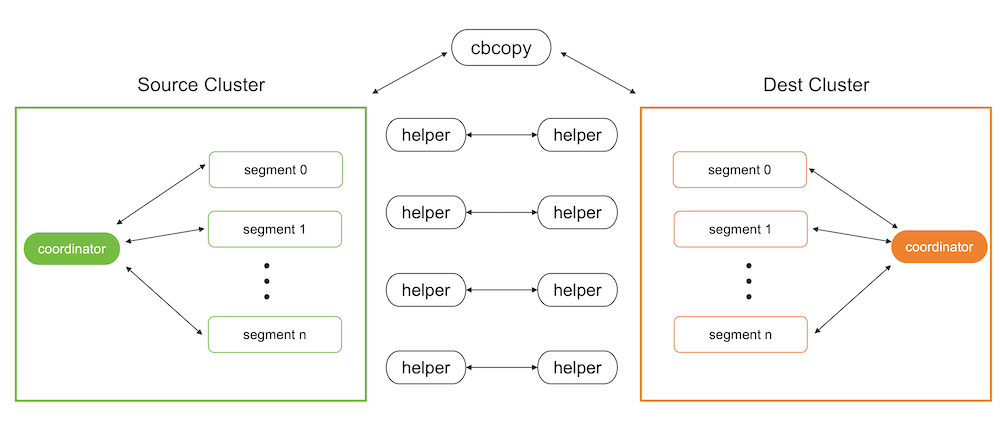
cbcopy is an efficient database migration tool designed to transfer data and metadata from Greenplum Database(GPDB) to Cloudberry Database(Cloudberrydb), while also supporting migrations between Greenplum databases and between Cloudberry databases for disaster recovery and database version upgrades.
The metadata migration feature of cbcopy is based on gpbackup. Compared to GPDB's built-in pg_dump, cbcopy's main advantage is its ability to retrieve metadata in batches. While pg_dump fetches metadata one row or a few rows at a time, cbcopy retrieves it in batches. This batch processing approach significantly enhances performance, especially when handling large volumes of metadata, making it much faster than pg_dump.
Both GPDB and CBDB support starting programs via SQL commands, and cbcopy utilizes this feature. During data migration, it uses SQL commands to start a program on the target database to receive and load data, while simultaneously using SQL commands to start a program on the source database to unload data and send it to the program on the target database.
The project requires the Go Programming language version 1.19 or higher. Follow the directions here for installation, usage and configuration instructions.
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/HashDataInc/cbcopy.gitSwitch your current working directory to the above cbcopy source directory
Build
makeThis will build the cbcopy and cbcopy_helper binaries in the source directory.
Install
make installThis will install the cbcopy and cbcopy_helper programs binaries the $GPHOME/bin directory. Note that GPDB must be sourced for this to work.
Some integration tests depend on the dummy_seclabel extension in the Database. Therefore, you need to install the dummy_seclabel extension in the Database first. This extension exists only to support testing of the SECURITY LABEL statement and is not intended for use in production. After successfully installing the dummy_seclabel extension, use the following commands to enable it.
# Configure the shared_preload_libraries parameter to include the dummy_seclabel extension
gpconfig -c shared_preload_libraries -v dummy_seclabel
# Restart the Greenplum database to apply the changes
gpstop -ra
# Verify that the dummy_seclabel extension has been successfully added to shared_preload_libraries
gpconfig -s shared_preload_libraries | grep dummy_seclabelTo run all tests except end-to-end (unit, and integration), use:
make testTo run only unit tests, use:
make unitRunning integration tests requires a database instance with the gpcloud extension installed, and the database must be configured with the --with-perl option:
make integrationTo run end to end tests (requires a running GPDB instance), use:
make end_to_endWe use goimports to maintain consistent code formatting. Before submitting any changes, please run:
make formatThis will:
- Format all Go files according to Go standard formatting rules
- Organize imports into groups (standard library, external packages, internal packages)
- Remove any unused imports
- Ensure consistent code style across the project
Before migrating data, you need to copy cbcopy_helper to the $GPHOME/bin directory on all nodes of both the source and target databases. Then you need to find a host that can connect to both the source database and the target database, and use the cbcopy command on that host to initiate the migration. By default, both metadata and data are migrated.
cbcopy relies on the "COPY ON SEGMENT" command of the database, so it has specific version requirements for the database.
GPDB 4.x- A minimum of GPDB version 4.3.17 or higher is required. If your version does not meet this requirement, you can upgrade to GPDB 4.3.17.GPDB 5.x- A minimum of GPDB version 5.1.0 or higher is required. If your version does not meet this requirement, you can upgrade to GPDB 5.1.0.GPDB 6.x- cbcopy is compatible with all versions of GPDB 6.x.GPDB 7.x- cbcopy is compatible with all versions of GPDB 7.x.CBDB 1.x- cbcopy is compatible with all versions of CBDB 1.x.
cbcopy supports seven migration modes.
--full- Migrate all metadata and data from the source database to the target database.--dbname- Migrate a specific database or multiple databases from the source to the target database.--schema- Migrate a specific schema or multiple schemas from the source database to the target database.--schema-mapping-file- Migrate specific schemas specified in a file from the source database to the target database.--include-table- Migrate specific tables or multiple tables from the source database to the target database.--include-table-file- Migrate specific tables specified in a file from the source database to the target database.--global-metadata-only- Migrate global objects from the source database to the target database.
cbcopy supports two data loading modes.
--append- Insert the migrated records into the table directly, regardless of the existing records.--truncate- First, clear the existing records in the table, and then insert the migrated records into the table.
If the tables you are migrating depend on certain global objects (such as tablespaces), you have two options:
-
Include the
--with-global-metadataoption (default: false) during migration, which will automatically create these global objects in the target database. -
If you choose not to use
--with-global-metadata, you must manually create these global objects in the target database before running the migration. For example:-- If your tables use custom tablespaces, create them first: CREATE TABLESPACE custom_tablespace LOCATION '/path/to/tablespace';
If neither option is taken, the creation of dependent tables in the target database will fail with errors like "tablespace 'custom_tablespace' does not exist".
If you want to change the ownership of the tables during migration without creating identical roles in the target database (by disabling the --with-global-metadata option), you need to:
- First create the target roles in the target database
- Use the
--owner-mapping-fileto specify the mapping between source and target roles
For example, if you have a mapping file with:
source_role1,target_role1
source_role2,target_role2
The migration process will execute statements like:
ALTER TABLE table_name OWNER TO target_role1;If the target role doesn't exist in the target database, these ownership change statements will fail with an error like "role 'target_role1' does not exist".
cbcopy provides three ways to handle tablespace migration:
-
Default Mode - When no tablespace options are specified, objects will be created in the same tablespace names as they were in the source database. You have two options to ensure the tablespaces exist in the target database:
- Use
--with-global-metadatato automatically create matching tablespaces - Manually create the tablespaces in the target database before migration:
CREATE TABLESPACE custom_space LOCATION '/path/to/tablespace';
- Use
-
Single Target Tablespace (
--dest-tablespace) - Migrate all source database objects into a single specified tablespace on the target database, regardless of their original tablespace locations. For example:cbcopy --dest-tablespace=new_space ...
-
Tablespace Mapping (
--tablespace-mapping-file) - Map source tablespaces to different target tablespaces using a mapping file. This is useful when you want to maintain separate tablespaces or map them to different locations. The mapping file format is:source_tablespace1,target_tablespace1 source_tablespace2,target_tablespace2
Note:
- For the default mode, either use
--with-global-metadataor ensure all required tablespaces exist in the target database before migration - If you need to migrate objects from different schemas into different tablespaces, you can either:
- Use
--tablespace-mapping-fileto specify all mappings at once - Migrate one schema at a time using
--dest-tablespacewith different target tablespaces
- Use
--copy-jobs- The maximum number of tables that concurrently copies.
During migration, we will compare the number of rows returned by COPY TO from the source database (i.e., the number of records coming out of the source database) with the number of rows returned by COPY FROM in the target database (i.e., the number of records loaded in the target database). If the two counts do not match, the migration of that table will fail.
cbcopy internally supports three copy strategies for tables.
Copy On Coordinator- If the table's statisticspg_class->reltuplesis less than--on-segment-threshold, cbcopy will enable theCopy On Coordinatorstrategy for this table, meaning that data migration between the source and target databases can only occur through the coordinator node.Copy On Segment- If the table's statisticspg_class->reltuplesis greater than--on-segment-threshold, and both the source and target databases have the same version and the same number of nodes, cbcopy will enable theCopy On Segmentstrategy for this table. This means that data migration between the source and target databases will occur in parallel across all segment nodes without data redistribution.Copy on External Table- For tables that do not meet the conditions for the above two strategies, cbcopy will enable theCopy On External Tablestrategy. This means that data migration between the source and target databases will occur in parallel across all segment nodes with data redistribution.
After cbcopy completes its execution, it generates several files in the $USER/gpAdminLogs directory:
-
Log File
cbcopy_$timestamp.log- Contains all execution logs, including:- Debug messages
- Error messages
- Operation details
-
Migration Result Files
cbcopy_succeed_$timestamp- Lists all successfully migrated tablescbcopy_failed_$timestamp- Lists all tables that failed to migrate
These files are useful for:
- Monitoring the migration process
- Troubleshooting any issues
- Planning retry attempts for failed migrations
When a migration fails partially (some tables succeed while others fail), cbcopy generates two files:
cbcopy_succeed_$timestamp- Lists all successfully migrated tablescbcopy_failed_$timestamp- Lists all tables that failed to migrate
For retry attempts, you can skip previously successful tables by using the success file:
cbcopy --exclude-table-file=cbcopy_succeed_$timestamp ...This approach helps you:
- Save time by not re-migrating successful tables
- Reduce the risk of data inconsistency
- Focus only on resolving failed migrations
# Migrate specific schemas
cbcopy --with-global-metadata --source-host=127.0.0.1 \
--source-port=45432 --source-user=gpadmin \
--dest-host=127.0.0.1 --dest-port=55432 \
--dest-user=cbdb --schema=source_db.source_schema \
--dest-schema=target_db.target_schema \
--truncateFor more detailed examples, you can refer to our test files:
cbcopy utility for migrating data from Greenplum Database (GPDB) to Cloudberry Database (CBDB)
Usage:
cbcopy [flags]
Flags:
--append Append destination table if it exists
--compression Transfer the compression data, instead of the plain data
--copy-jobs int The maximum number of tables that concurrently copies, valid values are between 1 and 512 (default 4)
--data-only Only copy data, do not copy metadata
--data-port-range string The range of listening port number to choose for receiving data on dest cluster (default "1024-65535")
--dbname strings The database(s) to be copied, separated by commas
--debug Print debug log messages
--dest-dbname strings The database(s) in destination cluster to copy to, separated by commas
--dest-host string The host of destination cluster (default "127.0.0.1")
--dest-port int The port of destination cluster (default 5432)
--dest-schema strings The schema(s) in destination database to copy to, separated by commas
--dest-table strings The renamed dest table(s) for include-table, separated by commas
--dest-table-file string The renamed dest table(s) for include-table-file, The line format is "dbname.schema.table"
--dest-tablespace string Create all database objects in the specified tablespace on destination database
--dest-user string The user of destination cluster (default "gpadmin")
--exclude-table strings Copy all tables except the specified table(s), separated by commas
--exclude-table-file string Copy all tables except the specified table(s) listed in the file, The line format is "dbname.schema.table"
--full Copy full data cluster
--global-metadata-only Only copy global metadata, do not copy data
--help Print help info and exit
--include-table strings Copy only the specified table(s), separated by commas, in the format database.schema.table
--include-table-file string Copy only the specified table(s) listed in the file, The line format is "dbname.schema.table"
--metadata-jobs int The maximum number of metadata restore tasks, valid values are between 1 and 512 (default 2)
--metadata-only Only copy metadata, do not copy data
--on-segment-threshold int Copy between Coordinators directly, if the table has smaller or same number of rows (default 1000000)
--owner-mapping-file string Object owner mapping file, The line format is "source_role_name,dest_role_name"
--quiet Suppress non-warning, non-error log messages
--schema strings The schema(s) to be copied, separated by commas, in the format database.schema
--schema-mapping-file string Schema mapping file, The line format is "source_dbname.source_schema,dest_dbname.dest_schema"
--source-host string The host of source cluster (default "127.0.0.1")
--source-port int The port of source cluster (default 5432)
--source-user string The user of source cluster (default "gpadmin")
--tablespace-mapping-file string Tablespace mapping file, The line format is "source_tablespace_name,dest_tablespace_name"
--truncate Truncate destination table if it exists prior to copying data
--validate Perform data validation when copy is complete (default true)
--verbose Print verbose log messages
--version Print version number and exit
--with-global-metadata Copy global metadata objects (default: false)