This tutorial will guide you through building a functional CI/CD pipeline with Github Actions. You will create a workflow that automatically runs unit tests on all pull requests, and deploys the latest version of the master branch to a Kubernetes cluster.
For an introduction to the core concepts behind GitHub Actions, I recommend reading this article to learn the basic vocabulary used in this tutorial.
To complete this tutorial, you will need the following:
- A Github account. No paid plan is necessary.
- Basic knowledge of git and Github: how to commit changes to branches and open pull requests.
- A DockerHub account. Alternatively, you can use any public container registry for this tutorial.
- A working Kubernetes cluster. You must have the
kubectlcommand-line tool configured with administrator-level previleges on your cluster. For example, a fresh Google Kubernetes Engine cluster will work perfectly. This tutorial will work on most cloud-providers.
The first thing you should do is fork this repository. As you advance through the steps below, you can add your work to your fork.
Once forked, clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/github-actions-tutorial.git
cd github-actions-tutorialThis repository contains code for a simple HTTP server. Here is a quick tour of the files already in place. Feel free to take a deeper look at the code if you are interested.
The go.mod, main.go files and foobar/ directory implement a rudimentary
HTTP server, complete with unit tests. The server has two endpoints: /foobar,
which responds with a FooBar sequence, and /healthz, which reports on the
server's health.
A Dockerfile provides a recipe for compiling the Go code into a container image.
The manifests/ directory contains Kubernetes resource specifications and a
Kustomize configuration file.
The foobar package contains unit tests. A good practice is to run unit tests
on all pull requests and on every commit to the master branch.
Create a .github/workflows/workflow.yml file in your repository for your
GitHub Actions workflow. In the file, start with a name:
name: main-worklfowUse the on field to trigger your workflow whenever a commit is pushed to the
master branch or a pull request is made:
on:
push:
branches:
- master
pull_request:
branches:
- masterA workflow is composed of independent jobs. Create a job called run-tests
that will run the application's unit tests:
jobs:
# Run all unit tests.
run-tests:Every job requires an operating system to run on. For this tutorial, you will be
using Ubuntu. Fill in the runs-on field of the job:
jobs:
# Run all unit tests.
run-tests:
runs-on: ubuntu-latestJobs contain a list of steps, which are executed consecutively. Often, the
first step is to clone your repository to use the source code it contains. To do
this, use an action provided by Github, called actions/checkout. To use
this action, fill in the uses field of the first step:
jobs:
# Run all unit tests.
run-tests:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
# Check out the pull request's source code.
- name: Check out source code
uses: actions/checkout@v3Next, you need to have Go installed to run your unit tests. There is already an
action that sets up everything for you, called actions/setup-go. This action
takes a go-version parameter, to know which version of Go to install.
Provide parameters to an action by filling in the with field:
steps:
# Check out the pull request's source code.
- name: Check out source code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
# Install Go.
- name: Set up Go
uses: actions/setup-go@v3
with:
go-version: "^1.14" # The Go version to download and use.In the code above, ^1.14 means 1.14.x, where x can be anything. Each
1.14.x release of Go is compatible with your code, so this is not an issue.
That being said, it would be nice to know exactly which version of Go
you are using here. Print the version in the next step. There is no existing
action that does this, so use the run field to execute the go version
command:
# Install Go.
- name: Set up Go
uses: actions/setup-go@v3
with:
go-version: "^1.14" # The Go version to download and use.
- name: Print Go version
run: go versionThe run field allows you to run any shell command. Use it again in the job's
final step to run your application's unit tests:
# Run unit tests.
- name: Run unit tests
run: go test -v ./...At this point, you should have the following code for your workflow:
name: main-worklfow
env: {}
on:
push:
branches:
- master
pull_request:
branches:
- master
jobs:
# Run all unit tests.
run-tests:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
# Check out the pull request's source code.
- name: Check out source code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
# Install Go.
- name: Set up Go
uses: actions/setup-go@v3
with:
go-version: "^1.14" # The Go version to download and use.
- name: Print Go version
run: go version
# Run unit tests.
- name: Run unit tests
run: go test -v ./...Commit these changes and push them to the master branch:
git checkout master
git pull
git add .github/workflows/workflow.yml
git commit -m 'Add run-tests job to workflow'
git pushWhen you pushed your commit to Github, it automatically triggered the workflow. On your repository's page, go to the Actions tab. You should see the run in question.
If it is still running, it will have a yellow dot next to your commit message. Once it has finished, depending on the result it will have either a red cross or a green tick. For this first run, the unit tests should pass and the workflow should complete successfully.
Your workflow not only triggers when commits are pushed to master, but also when
developers make pull requests. Check out a new branch called awesome-feature:
git checkout -b awesome-featureEdit the foobar/foobar.go file to introduce a breaking change. For instance,
replace a 5 with a 7. Then, commit and push the change to Github:
git add foobar/foobar.go
git commit -m 'Introduce breaking change'
git push -u origin awesome-featureGo to your repository's webpage and create a pull request
for the new branch. Make sure to merge into the master branch of your
repository, and not into padok-team's. Once the pull request is created, the
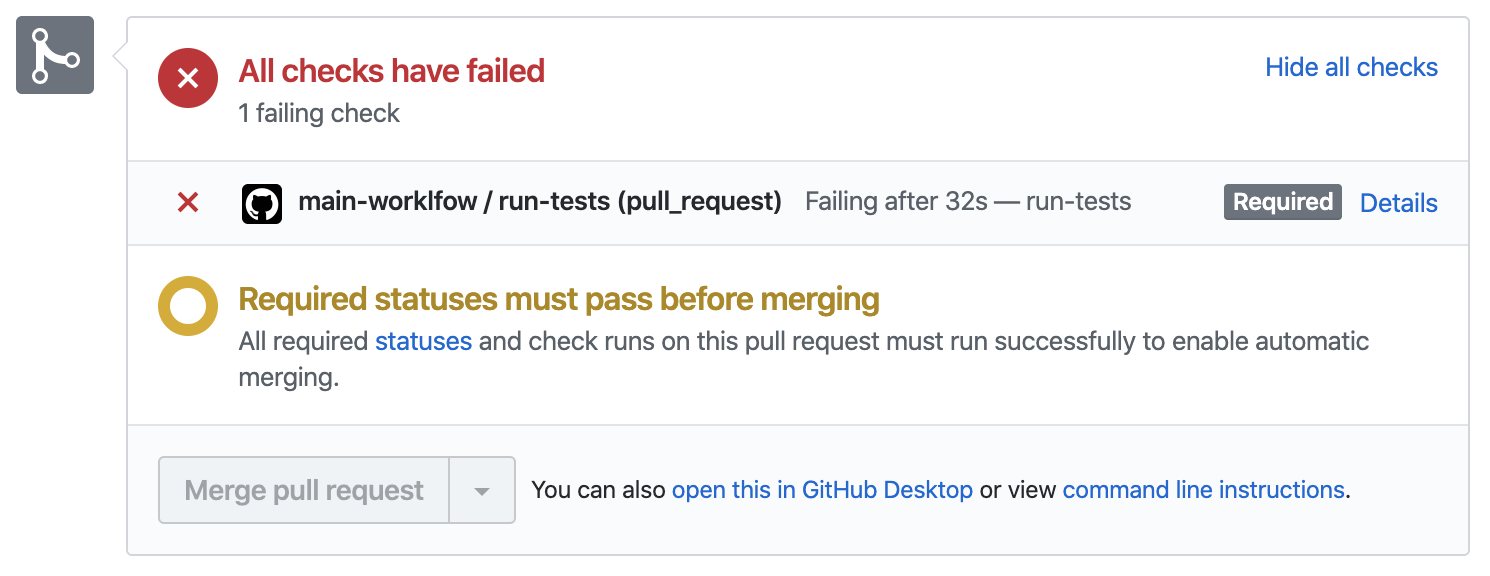
workflow will trigger and Github will display its progress on the pull request's
page:
Since you introduced a breaking change, the unit tests are failing and your workflow as well. Github displays this prominently, so developers are aware of the issue as soon as possible.
Fix the issue in foobar/foobar.go, then commit and push the fix:
git add foobar/foobar.go
git commit -m 'Fix breaking change'
git pushOnce the push is through, Github will trigger the workflow again. This time, it will pass.
You can merge your pull request into the master branch, confident that your awesome feature does not introduce a breaking change.
Now that your application is fully tested, time to package it as a container image, and then push that image to a container registry like DockerHub.
You need a DockerHub account for this step. The image repository will automatically be created when your workflow pushes the first image. The repository should be public, otherwise Kubernetes will not be able to pull any images to deploy without credentials.
Go back to the master branch to keep working on your workflow:
git checkout master
git pullAdd a second job to the workflow, called build-and-release. This job also runs
on Ubuntu and starts by checking out your source code:
# Build and release.
build-and-release:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
# Check out source code.
- name: Check out source code
uses: actions/checkout@v3Docker Inc. has published an action that
builds container images and pushes them to a container registry. This is exactly
what you aim to do, so use docker/build-push-action in your job's next step.
This action requires you specify the repository to push your image to. This is a
great usecase for environment variables. At the top of your workflow file, fill
in the env field to add an IMAGE_REPOSITORY variable equal to the image
repository you wish to store your image in. For example, my DockerHub handle is
busser so I wrote:
env:
IMAGE_REPOSITORY: padok-team/foobarIn order to push images to an image registry, Github Actions requires credentials to authenticate itself. Sensitive information like usernames and passwords should never be written inside files commited to a version control system like git. Thankfully, Github provides a way to manage secret values.
On your repository's webpage, go the Settings tab, then select Secrets
in the left-hand menu. There, add two secrets: DOCKER_USERNAME and
DOCKER_PASSWORD, containing your DockerHub credentials.
You are now ready to add the final step to your job, using a community-built
action, and without compromising on security. You shouldn't simply use the
latest tag for your container image, so tell the docker/build-push-action
action to tag your image with the name of the branch and the hash of the commit
that triggered the workflow.
# Build and release.
build-and-release:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
# Check out source code.
- name: Check out source code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
# Build and push container image.
- name: Build and push container image
uses: docker/build-push-action@v1
with:
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_PASSWORD }}
repository: ${{ env.IMAGE_REPOSITORY }}
tag_with_ref: true
tag_with_sha: true # sha-${GITHUB_SHA::7}Whenever you use ${{ ... }} inside your workflow, Github will dynamically
inject values at run-time for your steps to use.
Commit the updated worflow to the master branch and push the change to Github:
git checkout master
git pull
git add .github/workflows/workflow.yml
git commit -m 'Add build-and-release job to workflow'
git pushThis will trigger a run of the updated pipeline. Follow its progress on Github.
You may notice that the run-tests and build-and-release jobs ran in
parallel. This is by design: since both jobs are independent of one another,
running them at the same time allows your workflow to run faster and developers
to get feedback on their work sooner.
To deploy to Kubernetes, we will be using the kubectl command-line tool. To
connect and authenticate to the cluster, this will require a configuration file
containing credentials for a service account with sufficient permissions to
deploy. Create a service account called github-actions with permission to
edit the default namespace:
kubectl create serviceaccount github-actions --namespace default
kubectl create rolebinding github-actions --clusterrole edit --serviceaccount default:github-actions
kubectl apply -f scripts/secret.yamlNext, you need to fetch the service account's authentication token and build a
kubectl configuration file. The commands below do this for you, since this
isn't the point of this tutorial:
scripts/generate-kubeconfig.shAdd another secret to your Github repository, called KUBECONFIG, containing
the base64-encoded string printed by the script you just ran.
Now that your application is tested, built, and released, all that remains is to
deploy it. Add a third job called deploy to your workflow:
# Deploy to Kubernetes.
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latestYou only want to deploy to Kubernetes when a new commit is pushed to the master
branch, but your workflow is also triggered by pull requests. Use the job's if
field to make sure it runs only when triggered by the master branch:
# Deploy to Kubernetes.
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/master'If one of the first two jobs fails, either because the tests didn't pass or
because Github failed to build a container image, then the deploy job
shouldn't run. Use the needs field to specify dependencies between jobs:
# Deploy to Kubernetes.
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/master'
needs:
- run-tests
- build-and-releaseOnce more, the first step of this job is to check out your source code:
# Deploy to Kubernetes.
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/master'
needs:
- run-tests
- build-and-release
steps:
# Check out source code.
- name: Check out source code
uses: actions/checkout@v2Use kubectl to interact with the Kubernetes cluster. Add a step that downloads
the binary and installs it on the system:
# Set up kubectl.
- name: Set up kubectl
run: |-
curl -sfLo kubectl https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v${KUBECTL_VERSION}/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
chmod +x kubectl
sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/Notice that a command above uses an environment variable called
KUBECTL_VERSION. Add it to the env field a the top of your workflow file:
env:
IMAGE_REPOSITORY: busser/foobar
KUBECTL_VERSION: "1.14.10"Add a step that decodes the kubectl configuration stored in the KUBECONFIG
secret and writes it to a file for later use:
# Configure kubectl.
- name: Configure kubectl
run: echo ${{ secrets.KUBECONFIG }} | base64 --decode > kubeconfig.ymlIf you took a look at the manifests/deployment.yml file of your repository,
you may have noticed this line:
image: REPOSITORY:TAGUse Kustomize to dynamically inject the name and tag of the image built during
the latest run of your workflow. Add a step that installs the kustomize
binary:
# Set up Kustomize.
- name: Set up Kustomize
run: |-
curl -sfL https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/releases/download/kustomize%2Fv${KUSTOMIZE_VERSION}/kustomize_v${KUSTOMIZE_VERSION}_linux_amd64.tar.gz | tar -xzf -
sudo mv kustomize /usr/local/bin/A command above uses the KUSTOMIZE_VERSION environment variable. Add it the
env field:
env:
IMAGE_REPOSITORY: busser/foobar
KUBECTL_VERSION: "1.14.10"
KUSTOMIZE_VERSION: "3.5.4"Now, add a step that edits the manifests/kustomization.yml file to specify the
container image to deploy. This step needs to run in the manifests directory,
so fill in the step's working-directory field accordingly:
# Kustomize Kubernetes resources.
- name: Kustomize Kubernetes resources
working-directory: ./manifests
run: kustomize edit set image REPOSITORY:TAG=${IMAGE_REPOSITORY}:sha-${GITHUB_SHA::7}Notice the GITHUB_SHA environment variable. No need to add it to the env
field; this variable is set automatically by Github when running the workflow.
It contains the hash of the commit that triggered this particular run.
You are now ready to deploy. Add a step that creates (or updates) your Kubernetes resources:
# Deploy to Kubernetes.
- name: Deploy to Kubernetes
run: kubectl --kubeconfig kubeconfig.yml apply --kustomize manifests/The
--kustomizeflag is available in version 1.14 and above ofkubectl.
Now, wait for Kubernetes to finish updating all pods in your deployment. If
after two minutes the pods have not all started, assume the deployment has
failed. Add a step that uses kubectl to do this:
# Validate deployment.
- name: Validate deployment
run: kubectl --kubeconfig kubeconfig.yml rollout status --timeout 120s deployment/foobarThe deploy job is now ready to deploy your application. Commit the changes you
made to your workflow and push them to Github:
git checkout master
git pull
git add .github/workflows/workflow.yml
git commit -m 'Add deploy job to workflow'
git pushPushing your changes to Github triggered a run of your finalized workflow. Github will first run your tests and build a container image for your service. Once these two jobs have completed successfuly, Github will deploy the latest version of your application to your Kubernetes cluster.
Github will display the results of the workflow run on your repository's main page.
TODO: ADD CONCLUSION
If you wish to keep adding more features to this repository, here are a few ideas:
- Simple:
- Add a workflow status badge to your repository.
- Add more Kubernetes resources to your manifests, like a Service.
- Advanced:
- Use a Helm chart instead of
kubectlandkustomizeto deploy your application to Kubernetes. - Have pull requests trigger deployments to a staging cluster, in separate namespaces. Delete the corresponding namespace when the pull requests is closed or merged.
- Use a Helm chart instead of