Learning nonlinear models from privileged time series
This repository contains the code to reproduce the experiments shown in the paper "Efficient learning of nonlinear prediction models with time-series privileged information" presented at NeurIPS 2022. The paper is available on arxiv at https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.07067.
Learning Algorithms
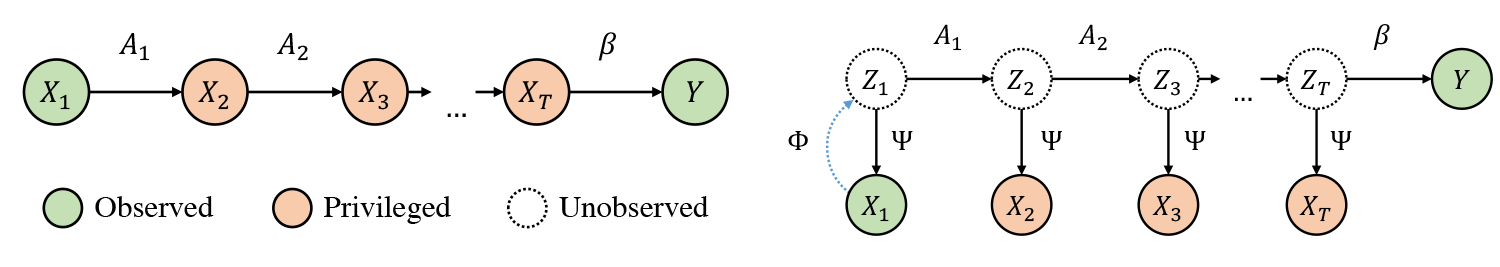
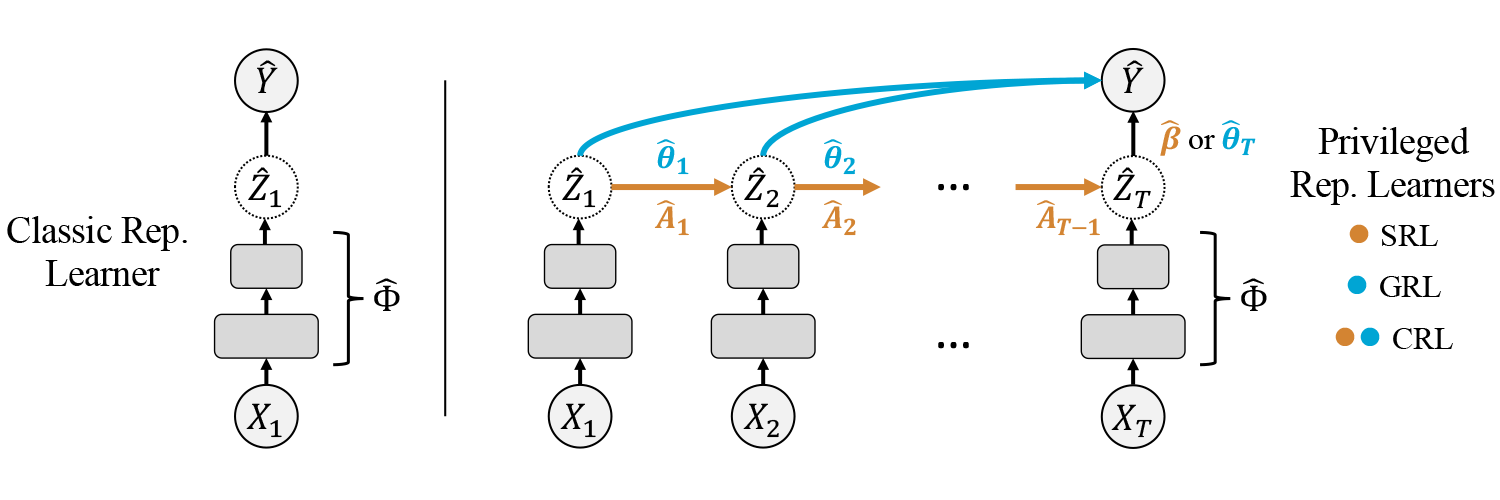
In the models package one finds all relevant algorithms used in the paper. This includes variants of generalized LuPTS as well as the representation learning methods displayed below. For the implementations we mostly made use of Scikit-Learn, Numpy and PyTorch.
Data Sets
Unfortunately, we cannot make the ADNI Alzheimer data set available as part of the repository. The other data sets used, are included and can be used straight away. In addition to the data sets described in the paper there is a synthetic linear Gaussian system as well. This system is fully observed and utilized by the other synthetic data generating processes, but it may be used as a standalone, too. The code producing the Clocks-LGS image data set is available, as well.
Experiments
The repository is structured in packages and contains a folder named Scripts. In there one finds everything that is needed to quickly replicate results.
There are two groups of models and five data sets: The first group of models comprises variants of generalized LuPTS and the corresponding classical learning alternatives. The second group contains representation learning algorithms. For every combination of data set and model group the Scripts folder contains a file with a corresponding experiment, apart from the image prediction task, where we only include one script with representation learners. Each of these experiments computes the coefficient of determination and the mean squared error over a range of settings that can easily be defined in the scripts. For synthetic data sets the mean SVCCA coefficients and the squared bias and variance are computed as well. All result data is stored in csv-files in a folder that is specified at the top of each script, subfolders are created by date and time for each experiment run. Additional python scripts include the code to produce the double descent curve for the LuPTS estimator (Figure 2) and the latent recovery experiment seen in Figure 7b (the latter requires trained models from one of the experiment runs mentioned above).
Visualizations
Note that some visualizations shown in the paper, in particular the SVCCA scatter plot and the bias-variance curves, were created using external software based on the csv files produced by the experiments. The visualizations concerning the prediction accuracy are created automatically using matplotlib. At the end of each script a call is made to the visualization function of the experiment class. It takes keyworded arguments to modify the resulting plots in terms of the axes limits for example.
Resources & SLURM Cluster
We recommend reducing the number of repetitions when running experiments on a single machine. All scripts are configured for single machine computation as this runs without further configuration. One specifies the number of CPUs to use at the top of each script using the worker variable. How to use the code on a SLURM cluster is described below but some code might need small adaptions depending on the cluster setup.
For training on a GPU cluster one needs to adapt the file experiment/gpu_slurm.sh. The scripts need to be changed to call the run_slurm_job method of the experiment class instead of run_single_node. To then collect the results from different nodes one uses the experiment methods merge_slurm_jobs, compute_aggregate_scores and save in this order. One might need to inspect the experiment package to adapt the shell script correctly. The PyTorch models automatically check for CUDA and use a GPU if available.
Random Seeds
Synthetic data sets take a random seed as an argument on creation, this determines their dynamics. During an experiment, when requesting a train and test set, the experiment class passes another random seed that only determines the data sampling.
Requirements
We recommend installing the packages found in requirements.txt via pip in a new environment using python 3.8.
pip install -r requirements.txt