This repository is an algorithm that allows you to decompose the number of a given set of numbers. For example, we
we have a set of numbers 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6. How many ways can we get the number 5? Obviously:
1, 4
1, 2, 2
2, 3
2, 3
Thus, we went through all possible solutions. Please note that one of the solutions is repeated. It is important take into account and avoid unnecessary repetitions.
Let's match the bitmask to the set of numbers:
[0, 0, 1, 0]
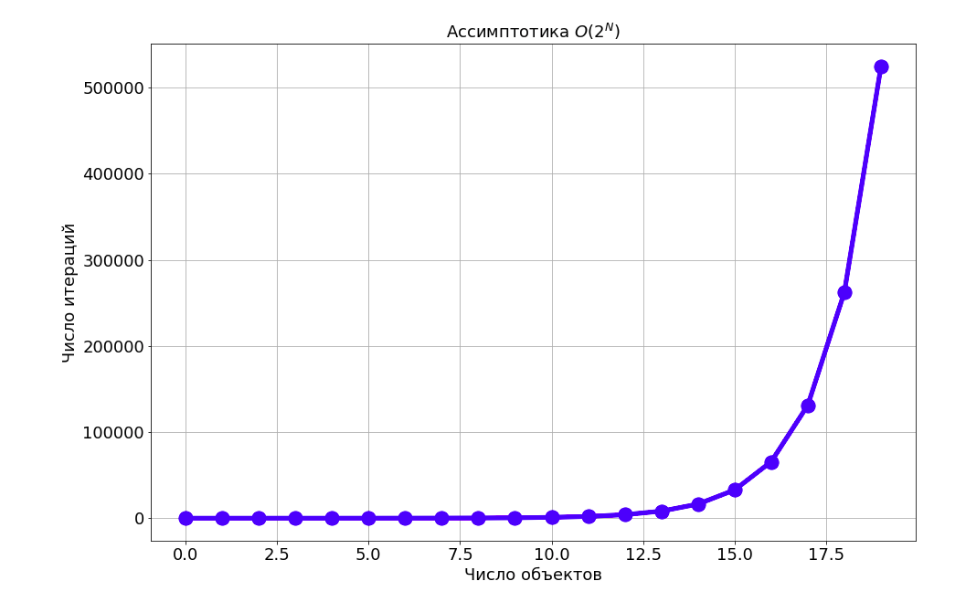
Then, in order to get a solution, it is enough to go through all the bit masks. The complexity of this algorithm will be:
It should be noted here that any solution can be found rather quickly. But if we want to make sure there are no solutions, to prove that it is unique or to find everything, the execution time of the algorithm will be delayed.
Consider an applied problem that I solved in my practice.
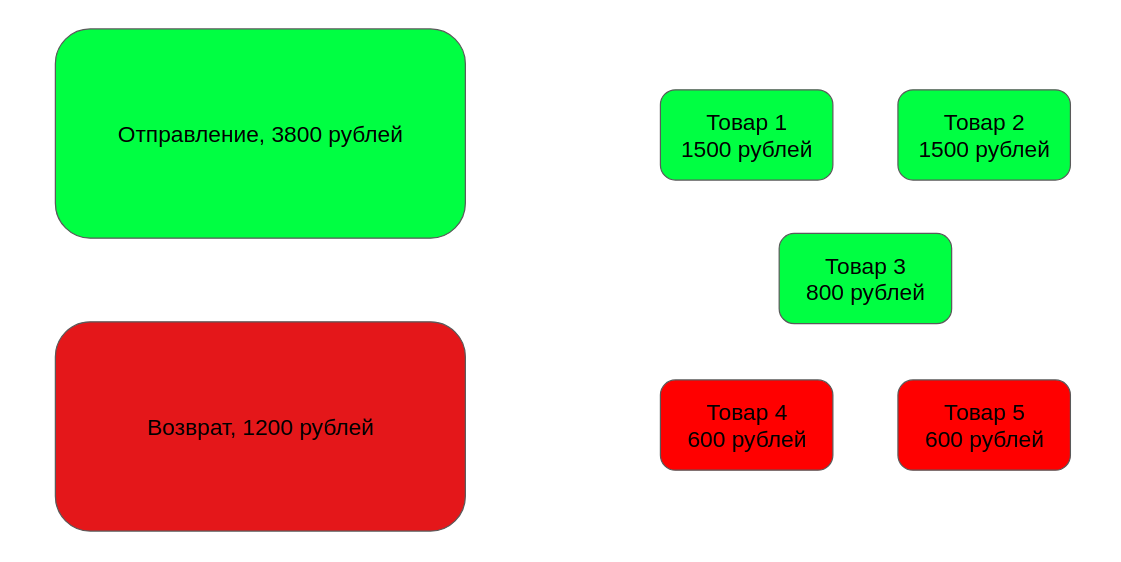
May we have a purchase. We know the total price, i.e. the total amount of all goods and the price of each product. At the same time, the client returned some of the goods. It is required to understand which of the goods the customer bought.
In some cases, we want to understand how many solutions this task has?
There are products:
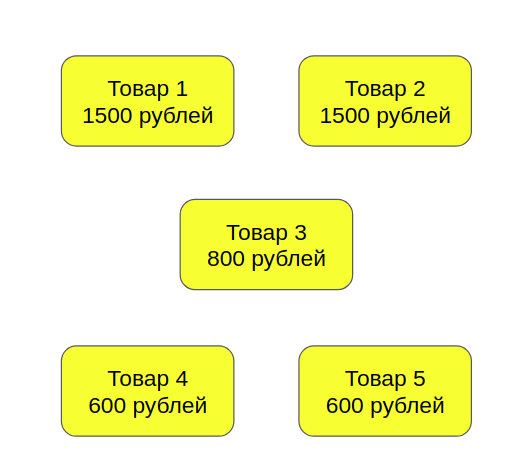
Each of them is worth something:
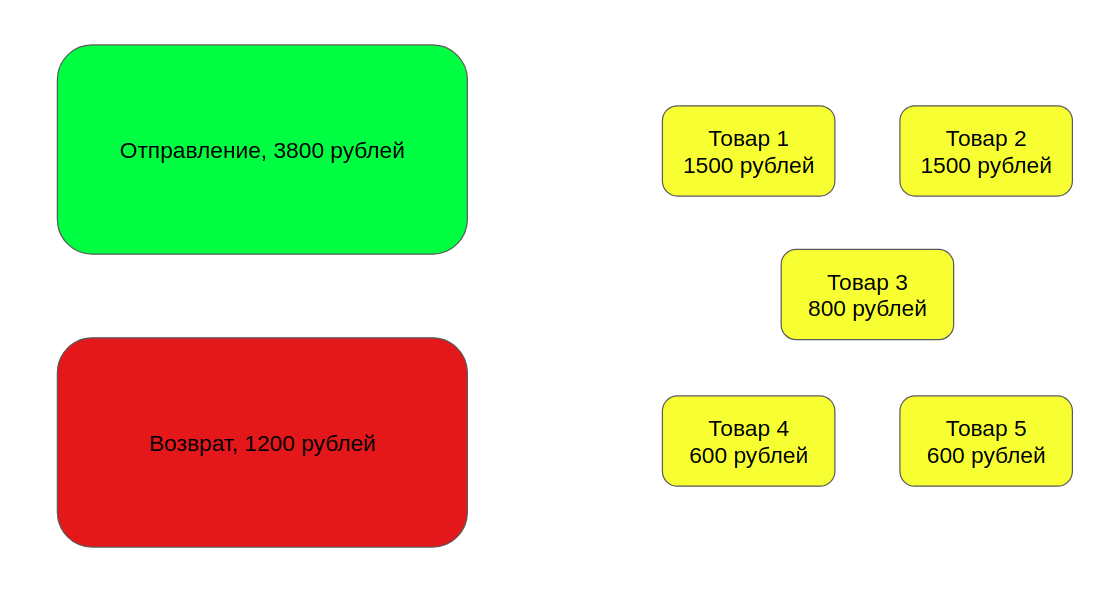
Also there is a departure and return:
There is a solution:
Including and excluding everything in turn in a solution, we can find all possible solutions.
You can read more here In this case, the idea is used that it is not necessary to fill in the whole matrix, but it is enough to go from the final decision, those. and recursively iterate over all solutions. Thus, we will answer all questions of the problem. The problem with this approach is that we cannot do this iteratively, which means we will have to store all the decisions in memory, and there may be quite a lot of them.
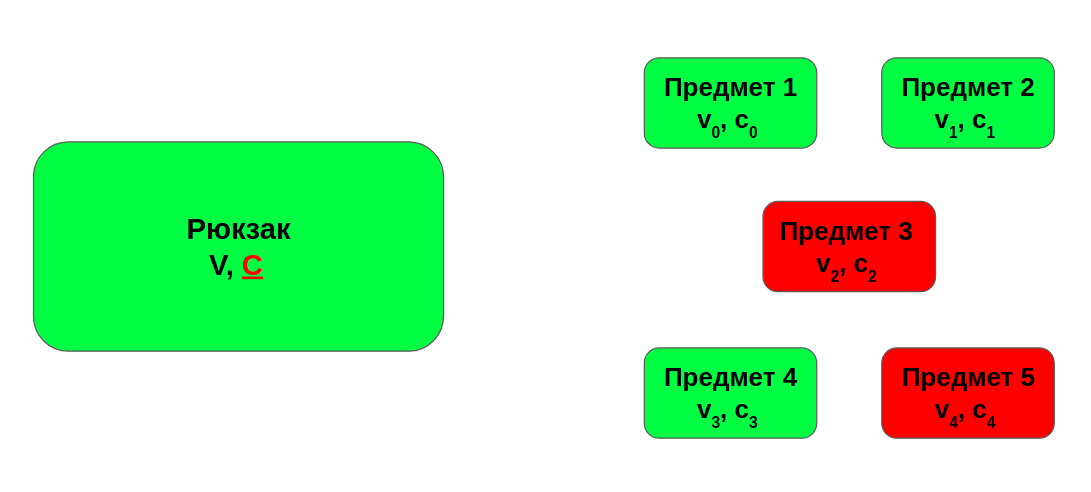
It is important to note that this task is a special case of the backpack problem. The task of the backpack looks like this:
There is a backpack, it has a capacity, and we also want to collect in it items of maximum value so that they all fit in. At the same time, each item has its cost and weight (restriction). Potentially constraints in a task can be more than one.
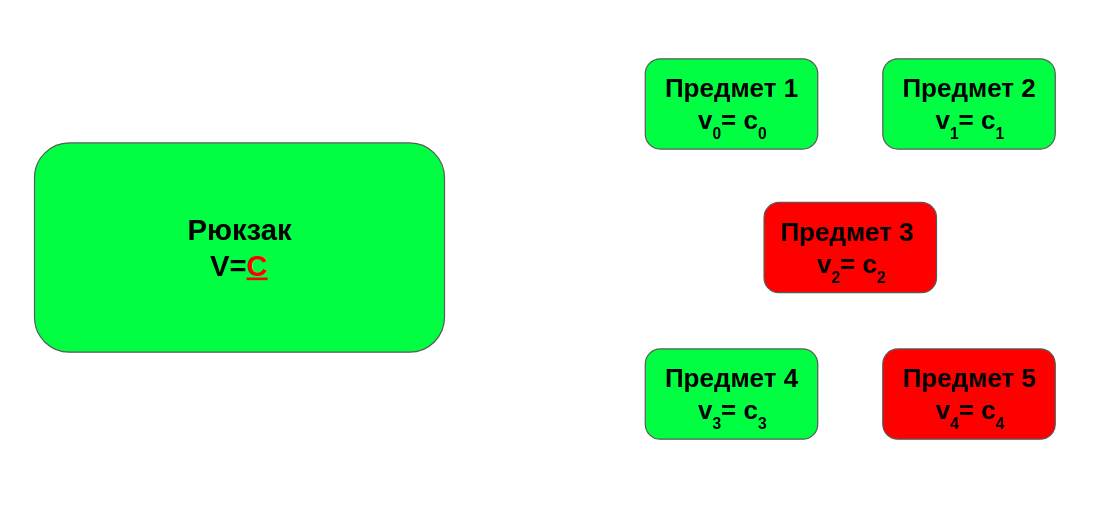
In our case, everything is easier. First, the weight of the backpack and the limit in this case are the same.
Secondly, in contrast to the backpack problem, we need to make up from our objects exactly the maximum weight of the backpack. Do not forget that the weight coincides with the restriction, or say that such a solution does not exist.
Notice how the task of a backpack is similar to the search for masks.
In order to generate solutions iteratively, it is proposed to rank the elements. In this case it is possible, as long as limitation and weight are the same. Then, at each step, we will fill the backpack, iterating from the maximum element to minimum and will recalculate the remainder. As soon as the balance is less than 0, we return to the previous step and continue the search. If the remainder is exactly 0, then we return the solution, and then, from the same place, we continue the search.
Note that this solution works about 2 times longer than solving the backpack problem. At the same time, we can give answers iteratively.
pip install -r requirements
Данный репозиторий представляет собой алгоритм, позволяющий разложить число по заданному множеству чисел. Например, мы
имеем набор чисел 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6. Сколькими способами мы можем получить число 5? Очевидно:
1, 4
1, 2, 2
2, 3
2, 3
Таким образом, мы перебрали все возможные решения. Обратите внимание, что одно из решений повторяется. Это важно учитывать и не допускать лишних повторов.
Давайте сопоставим набору чисел битовую маску:
[0, 0, 1, 0]
Тогда, чтобы получить решение, достаточно перебрать все битовые маски. Сложность такого алгоритма будет:
Здесь следует отметить, что любое решение может найтись довольно быстро. Но если мы хотим убедиться, что решений нет, доказать, что оно единственное или же найти все, то время выполнения алгоритма затянется.
Рассмотрим прикладную задачу, которую я решал в своей практике.
Пусть у нас есть покупки. Мы знаем суммарную цену, т.е. общую сумму всех товаров и цену каждого товара. При этом, клиент вернул некоторые из товаров. Требуется понять, какие из товаров клиент купил.
В ряде случаев, нам хочется понимать, сколько решений есть у этой задачи?
Есть товары:
Каждый из них сколько-то стоит:
Также есть отправление и возврат:
Существует решение:
Включая и исключая по очереди все в решение, мы можем найти все возможные решения.
Прочитать подробнее можно тут В данном случае, используется идея о том, что не обязательно заполнять всю матрицу, а достаточно пойти от финального решения, т.е. и рекурсивно перебрать все решения. Таким образом, мы ответим на все вопросы задачи. Проблема данного подхода в том, что мы не можем делать это итеративно, а значит нам придётся все решения хранить в памяти, а их может быть довольно много.
Важно отметить, что данная задача является частным случаем задачи о рюкзаке. Задача о рюкзаке выглядит так:
Есть рюкзак, у него есть вместимость, а также мы хотим в него набрать предметов максимальной стоимости так, чтобы все они поместились. При этом, у каждого предмета есть его стоимость и вес (ограничение). Потенциально ограничений в задаче может быть более одного.
В нашем случае всё проще. Во-первых, вес рюкзака и ограничение в данном случае совпадают.
Во-вторых, в отличие от задаче о рюкзаке, нам требуется составить из наших предметов в точности максимальный вес рюкзака. Не забываем, что вес совпадает с ограничением, либо сказать, что такого решения не существует.
Обратите внимание, как похожа задача о рюкзаке на перебор масок.
Для того, чтобы генерировать решения итеративно, предлагается отранжировать элементы. В данном случае это возможно, покуда ограничение и вес совпадают. Затем, на каждом шаге, мы будем набивать рюкзак, итерируясь от максимального элемента к минимальному и будем пересчитывать остаток. Как только остаток станет меньше 0, возвращемся к предыдущему шагу и продолжаем поиск. Если остаток равен в точности 0, то возвращаем решение, а затем, с того же места продолжаем поиск.
Заметим, что данное решение работает примерно в 2 раза дольше, чем решение задачи о рюкзаке. При этом, мы можем отдавать ответы итеративно.
pip install -r requirements