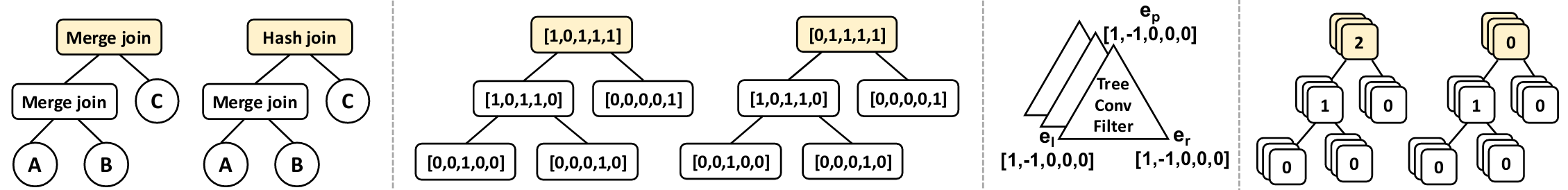
This is an implementation of tree convolution in PyTorch, as described in the paper:
Lili Mou, Ge Li, Lu Zhang, Tao Wang, and Zhi Jin. “Convolutional Neural Networks over Tree Structures for Programming Language Processing.” In Proceedings of the Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 1287–1293. AAAI ’16. Phoenix, Arizona: AAAI Press, 2016. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.5718.pdf
This implementation of tree convolution is the one used in Neo:
Ryan Marcus, Parimarjan Negi, Hongzi Mao, Chi Zhang, Mohammad Alizadeh, Tim Kraska, Olga Papaemmanouil, and Nesime Tatbul. “Neo: A Learned Query Optimizer.” PVLDB, VLDB ’19, 12, no. 11 (2019): 1705–18. http://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol12/p1705-marcus.pdf
This is only an implementation of the tree convolution operator, not the rest of the paper. Furthermore, this implementation uses only "binary" tree convolution (where each tree node has exactly two or zero children). A complete (unofficial) implementation of the Mou et al. paper is available in TensorFlow here.
The file tcnn.py contains:
BinaryTreeConv(in_channels, out_channels), a module mapping a tree where each node is a vector of sizein_channelsto a new tree where each node is a vector of sizeout_channels. The transformation is performed with a triangular linear kernel.TreeActivation(f), a module applying an activation functionfto each entry of each vector in a tree.TreeLayerNorm(), a module applying layer normalization to a tree (this was not described in Mou et al., but is straightforward and improves training stability).
The file util.py contains:
prepare_trees(trees, transformer, left_child, right_child): this function produces the input for theBinaryTreeConvoperator. You can provide as many trees as you'd like astrees. The parametertransformermust be a function that maps a tree node to a feature vector. The parametersleft_childandright_childmust be functions mapping a tree node to its left/right child, orNoneis the node is a leaf. This is best understood by example (see below).
The file example.py contains a self-contained example which you can run. It is reproduced below.
import numpy as np
from torch import nn
from util import prepare_trees
import tcnn
# First tree:
# (0, 1)
# (1, 2) (-3, 0)
# (0, 1) (-1, 0) (2, 3) (1, 2)
tree1 = (
(0, 1),
((1, 2), ((0, 1),), ((-1, 0),)),
((-3, 0), ((2, 3),), ((1, 2),))
)
# Second tree:
# (16, 3)
# (0, 1) (2, 9)
# (5, 3) (2, 6)
tree2 = (
(16, 3),
((0, 1), ((5, 3),), ((2, 6),)),
((2, 9),)
)
trees = [tree1, tree2]
# function to extract the left child of a node
def left_child(x):
assert isinstance(x, tuple)
if len(x) == 1:
# leaf.
return None
return x[1]
# function to extract the right child of node
def right_child(x):
assert isinstance(x, tuple)
if len(x) == 1:
# leaf.
return None
return x[2]
# function to transform a node into a (feature) vector,
# should be a numpy array.
def transformer(x):
return np.array(x[0])
# this call to `prepare_trees` will create the correct input for
# a `tcnn.BinaryTreeConv` operator.
prepared_trees = prepare_trees(trees, transformer, left_child, right_child)
# A tree convolution neural network mapping our input trees with
# 2 channels to trees with 16 channels, then 8 channels, then 4 channels.
# Between each mapping, we apply layer norm and then a ReLU activation.
# Finally, we apply "dynamic pooling", which returns a flattened vector.
net = nn.Sequential(
tcnn.BinaryTreeConv(2, 16),
tcnn.TreeLayerNorm(),
tcnn.TreeActivation(nn.ReLU()),
tcnn.BinaryTreeConv(16, 8),
tcnn.TreeLayerNorm(),
tcnn.TreeActivation(nn.ReLU()),
tcnn.BinaryTreeConv(8, 4),
tcnn.TreeLayerNorm(),
tcnn.TreeActivation(nn.ReLU()),
tcnn.DynamicPooling()
)
# output: torch.Size([2, 4])
print(net(prepared_trees).shape)The primary trick used by this implementation is to (1) flatten the input tree in preorder, (2) build indexes that, when used to access the flattened vector, create a new vector where a 1D convolution with stride 3 and kernel size 3 is equivalent to tree convolution. These same indexes can be used on the output of this 1D convolution, allowing the convolution operator to be stacked.