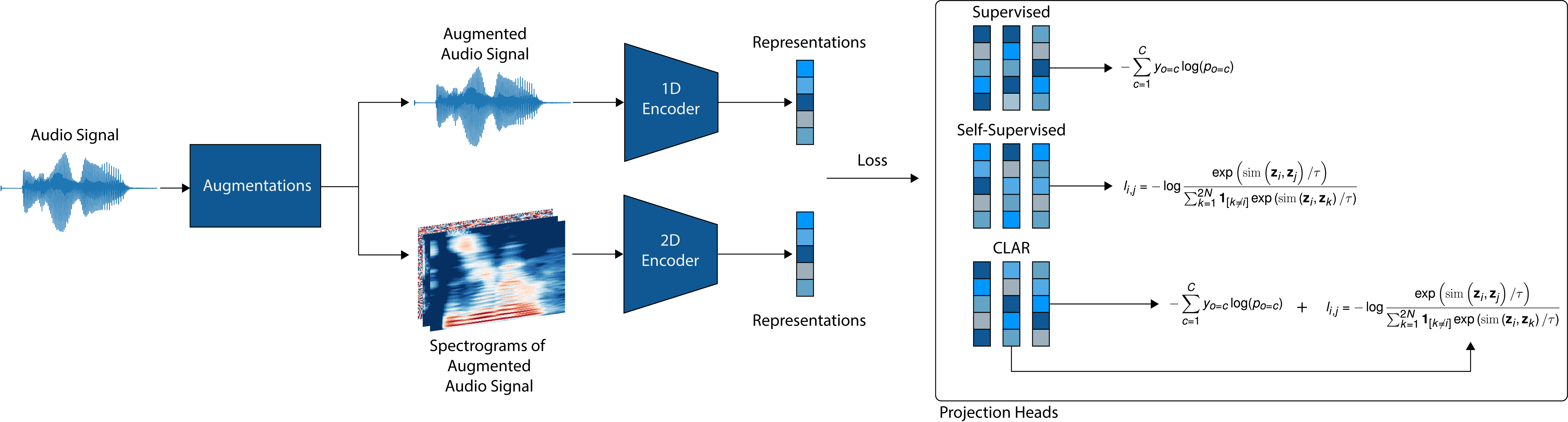
This repository contains an unofficial pytorch implementation of the paper CLAR:Contrastive Learning of Auditory Representations. Paper Link
Before running the scripts, install conda, requirements and activate the environment env
$ conda create --name env --file requirements.txt
$ conda activate env
\CLAR
├── augmentation.py - implements augmentation of the paper
├── contrastiveloss.py - implements contrastive loss (NT-Xent)
├── dataset - contains implementation to obatin dataloader for train , test and validation set
│ ├── data.py
│ └── speechcommands.py
├── EvaluationHead.py - implements the evaluation head
├── net.py - implements CLAR-net with projection head
├── README.md
├── requirements.txt
├── resnet - implements the encoders
│ ├── resnet_1D.py
│ └── resnet_2D.py
├── selfsupervised.py - implement the selfsupervised version of CLAR
├── semisupervised.py - implement the semisupervised(CLAR) version
├── Spectrograms.py - implement the stft class to extract magnitude and phase spectogram
└── supervised.py - implement the supervised version of CLAR
You can run these tests separately. Make sure you activate the env before.The hyperparamter can be found inside each file.
$python supervised.py --epochs=100 --Batch_size=256 --wandb='run'
$python selfsupervised.py --epochs=100 --Batch_size=256 --wandb='run'
$python semisupervised.py --epochs=100 --Batch_size=256 --wandb='run' --lab_percentage=1
We higly reccomand to install wandb and run with --wandb='run' if you desire to log the metrics, otherwise leave it --wandb='disabled'.
The paper CLAR adopted three different datasets: Speech Commands, NSynth, and Environmental Sound Classification. However, this repository only utilizes the Speech Commands dataset, which can be easily downloaded through the PyTorch Audio library. Therefore, the repository focuses on implementing and applying the CLAR method specifically to the Speech Commands dataset. SpeechCommand dataset will be automatically download in a folder when you run the code!
The paper CLAR studied various augmentations, including Pitch Shift (High and Low steps), Fade In/Out, Time Masking, Time Shift, Time Stretch (Low and High Rate), and Noise (White, Pink, Brown). In this implementation, four augmentations are presented: Fade In/Out, White Noise, Time Masking and Pitch Shfit. To add other augmentations, you should insert them into the augmentation.py file. And call them in the function createModelInput()
def createModelInput(audio,mel_transform, stft_trasform, augmentation=True):
# Calcualate the first and the second augmentation
if augmentation == True:
audio = augmentation_1(audio)
audio = augmentation_2(audio)
# Create the augmented spectograms size [BATCH_SIZE, 3, 128, 126]
spectograms = createSpectograms(audio, stft_trasform, mel_transform)
spectograms = spectograms.to(device)
return spectograms, audio
The file Spectograms.py serve to achive the magnitude and phase spectogram, the melspectograms is achived using directly torchaudio. The function createSpectograms() will create the batch composed by stacked Magnitude, Mel and Phase spectograms.
This implementation use half-precision floating-point format to use large batch size in your GPU, which helps the contrastive loss to operater better and lastly making the training process faster. This leads to a slightly worse accuracy than using FP32!