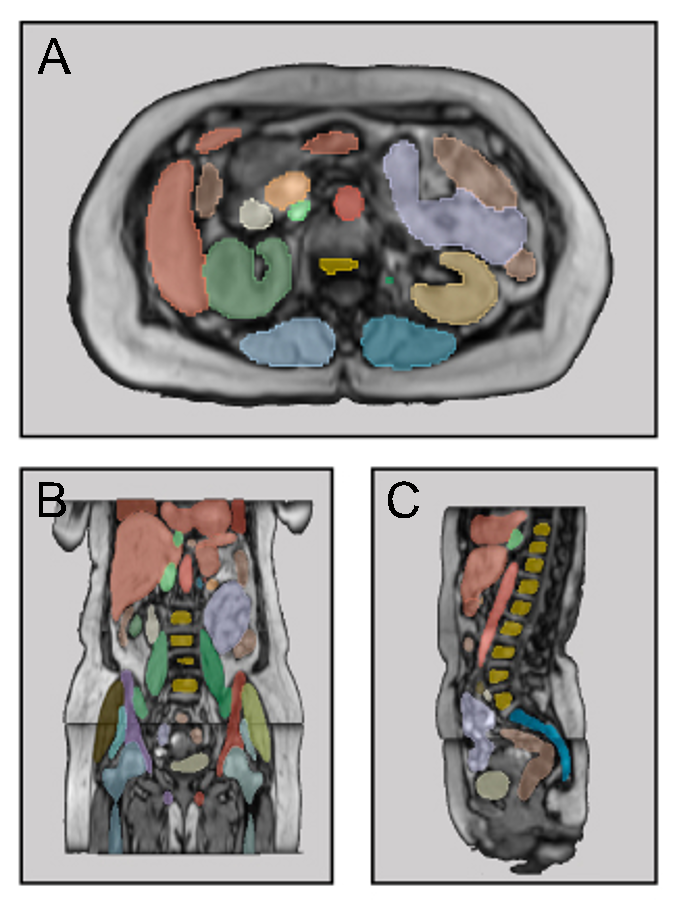
Detect and segment 40 classes in MRI scans of the abdominal / pelvic / thorax region
Contrary to CT scans, where tools for automatic multi-structure segmentation are quite mature, segmentation tasks in MRI scans are often either focused on the brain region or on a subset of few organs in other body regions. MRSegmentator aims to extend this and accurately segment 40 organs and structures in human MRI scans of the abdominal, pelvic and thorax regions. The segmentation works well on different sequence types, including T1- and T2-weighted, Dixon sequences and even CT images. Read more about it in our preprint: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2405.06463.
Check out some sample segmentations on our Hugging Face Space! 🤗
MRSegmentator v1.0.0 did occasionally mix left & right classes. I retrained the model using the nnUNetTrainerNoMirroring trainer. The new version is vastly better in this regard.
The updated weights will be automatically downloaded with the latest pip release. You can update with:
python -m pip install --upgrade mrsegmentator==1.1
(Make sure to include the version number, sometimes pip doesn't do what you'd expect it to do.)
Install MRSegmentator with pip:
# Create virtual environment
conda create -n mrseg python=3.11 pip
conda activate mrseg
# Install MRSegmentator
python -m pip install mrsegmentator(Optionally) If the installed pytorch version coming with nnunet is not compatible to your system, you might need to install it manually, please refer to PyTorch.
MRSegmentator segments all .nii and .nii.gz files in an input directory and writes segmentations to the specified output directory. MRSegmentator requires a lot of memory and can run into OutOfMemory exceptions when used on very large images (e.g. some CT scans). You can reduce memory usage by setting --split_level to 1 or 2. Be aware that this increases runtime and possibly reduces segmentation performance.
mrsegmentator --input <nifti file or directory>Options:
-i, --input <str> [required] # input directory or file
--outdir <str> # output directory
--fold <int> # use only a single model for inference
--postfix <str> # postfix that will be added to segmentations, default: "seg"
--split_level <int> # split images to reduce memory usage. Images are split recusively: A split level of x will produce 2^x smaller images.
--batchsize <int> # how many images can be loaded to memory at the same time, default: 8
--nproc <int> # number of processes
--nproc_export <int> # number of processes for exporting the segmentations
--cpu_only # don't use a gpu
--verbosefrom mrsegmentator import inference
import os
outdir = "outputdir"
images = [f.path for f in os.scandir("image_dir")]
folds = [0]
inference.infer(images, outdir, folds)If you use our work in your research, please cite our preprint on arXiv: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2405.06463.
Hartmut Häntze, Lina Xu, Felix J. Dorfner, Leonhard Donle, Daniel Truhn, Hugo Aerts, Mathias Prokop, Bram
van Ginneken, Alessa Hering, Lisa C. Adams, and Keno K. Bressem. MRSegmentator: Robust multi-modality
segmentation of 40 classes in MRI and CT sequences. arXiv, 2024.
| Index | Class |
|---|---|
| 0 | background |
| 1 | spleen |
| 2 | right_kidney |
| 3 | left_kidney |
| 4 | gallbladder |
| 5 | liver |
| 6 | stomach |
| 7 | pancreas |
| 8 | right_adrenal_gland |
| 9 | left_adrenal_gland |
| 10 | left_lung |
| 11 | right_lung |
| 12 | heart |
| 13 | aorta |
| 14 | inferior_vena_cava |
| 15 | portal_vein_and_splenic_vein |
| 16 | left_iliac_artery |
| 17 | right_iliac_artery |
| 18 | left_iliac_vena |
| 19 | right_iliac_vena |
| 20 | esophagus |
| 21 | small_bowel |
| 22 | duodenum |
| 23 | colon |
| 24 | urinary_bladder |
| 25 | spine |
| 26 | sacrum |
| 27 | left_hip |
| 28 | right_hip |
| 29 | left_femur |
| 30 | right_femur |
| 31 | left_autochthonous_muscle |
| 32 | right_autochthonous_muscle |
| 33 | left_iliopsoas_muscle |
| 34 | right_iliopsoas_muscle |
| 35 | left_gluteus_maximus |
| 36 | right_gluteus_maximus |
| 37 | left_gluteus_medius |
| 38 | right_gluteus_medius |
| 39 | left_gluteus_minimus |
| 40 | right_gluteus_minimus |