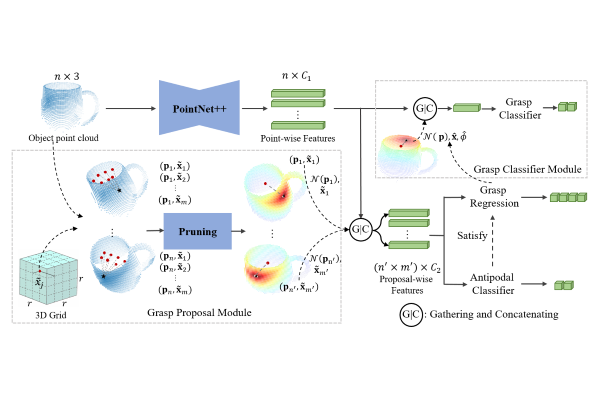
Pytorch implementation of GPNet.
conda activate gym
- Ubuntu 16.04
- pytorch 0.4.1
- torchvision 0.2.1
- CUDA 8.0 or CUDA 9.2
Our depth images are saved in .exr files, please install the OpenEXR, then run pip install OpenEXR.
cd lib/pointnet2mkdir build && cd buildcmake .. && make
Our dataset is available at Google Driver. Backup (2qln).
The simulation environment is built on PyBullet. You can use pip to install the python packages:
pip install pybullet
pip install attrdict
pip install trimesh
pip install collections
pip install joblib
pip install gc
Please look for the details of our simulation configurations in the directory simulator. The simulation environment will be available soon.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 python train --tanh --grid --dataset_root path_to_dataset
For our situtation, only 1 GPU, the following items shoud be changed accordingly. 1.change the following lines with cuda(0) in train.py file
proposal_PC, grids1, contact_index1, center1, scores1 = pc_.float().cuda(0),\
grids_.float().cuda(0),\
contact_index_.long().cuda(0),\
center_.float().cuda(0),\
scores_.float().cuda(0)
grasp_center1 = grasp_center_.cuda(0)
grasp_contact1 = grasp_contact_.cuda(0)
2.Changing the values in file gpnet.py
emacs ../lib/gpnet.py #L345
emacs ../lib/gpnet.py #L404
change the 5000 to 1000
Then, run the training by
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python train.py --tanh --grid --dataset_root /home/user/GPNet/dataset/GPNet_release_data
- ImportError: cannot import name 'pytorch_utils'
copy the file pytorch_utils.py from https://github.com/sshaoshuai/Pointnet2.PyTorch/tree/master/pointnet2
and paste to ~/GPNet/lib/pointnet2/utils
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 python test --tanh --grid --dataset_root path_to_dataset --resume pretrained_model/checkpoint_440.pth.tar
In our situation, we only have 1 GPU
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python test.py --tanh --grid --dataset_root /home/user/GPNet/dataset/GPNet_release_data --resume /home/user/GPNet/log_exp_tanh_grid/gridlen22_gridnum10/bs1_wd0.0001_lr0.001_lamb0.01_ratio1.0_posi0.3_sgd/checkpoint_500.pth.tar
Then it will generate the predicted grasps saved in .npz files in pretrained_model/test/epoch440/view0. The file pretrained_model/test/epoch440/nms_poses_view0.txt contains the predicted grasps after nms.
You can use the following script to abtain the success rate and coverage rate.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python topk_percent_coverage_precision.py -pd pretrained_model/test/epoch440/view0 -gd path_to_gt_annotations
i.e.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python topk_percent_coverage_precision.py -pd /home/user/GPNet/log_exp_tanh_grid/gridlen22_gridnum10/bs1_wd0.0001_lr0.001_lamb0.01_ratio1.0_posi0.3_sgd/test/epoch500/view0 -gd /home/user/GPNet/dataset/GPNet_release_data
To test the predicted grasps in simulation environment:
cd simulator
python -m simulateTest.simulatorTestDemo -t pretrained_model/test/epoch440/nms_poses_view0.txt
i.e.
python -m simulateTest.simulatorTestDemo -t /home/user/GPNet/log_exp_tanh_grid/gridlen22_gridnum10/bs1_wd0.0001_lr0.001_lamb0.01_ratio1.0_posi0.3_sgd/test/epoch500/nms_poses_view0.txt
Results of the scripts in simulator
python -m simulateTest.gripperSimpleCollision
python -m simulateTest.gripperPoseTransform
python -m simulateTest.visualization
@article{wu2020grasp,
title={Grasp Proposal Networks: An End-to-End Solution for Visual Learning of Robotic Grasps},
author={Wu, Chaozheng and Chen, Jian and Cao, Qiaoyu and Zhang, Jianchi and Tai, Yunxin and Sun, Lin and Jia, Kui},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.12606},
year={2020}
}
The code of pointnet2 are borrowed from Pointnet2_PyTorch.