Lambda provides functional constructs for SObject collections!
List<Account> accounts = new List<Account>{
new Account(Name = 'Foo', AnnualRevenue = 50000),
new Account(Name = 'Bar', AnnualRevenue = 30000)
}
Collection accountCollection = Collection.of(accounts);
Collection filtered = accountCollection.filter(Match.field(Account.AnnualRevenue).greaterThan(40000));
Collection mapped = filtered.mapAll(CopyFields.fromRecord(new Account(High_Value__c = true)));
Collection remaining = mapped.remove(Match.record(new Account(Name = 'Bar')));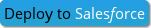
| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
Boolean |
isEmpty() |
Returns true if this collection contains no elements. |
| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
Collection |
difference(Collection other, Set<Schema.SObjectField> comparisonFields) |
Returns a collection view of those records that are not equal in the other list, considering only comparisonFields in the comparison. |
| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
Collection |
filter(SObjectPredicate predicate) |
Returns a Collection view of records that satisfied predicate |
Two predicates are provided out of the box, FieldsMatch and RecordMatch. They are instantiated through factory methods on Match:
Collection accountCollection = Collection.of(accounts);
Account prototype = new Account(Name = 'Foo');
Collection recordMatched = accountCollection.filter(Match.record(prototype));
Collection fieldMatched = accountCollection.filter(Match.field(Account.Name).equals('Foo'));FieldsMatch returns true if a record satisfies all field matching conditions.
FieldsMatch is constructed with a fluent interface. Match factory method field returns an IncompleteFieldsMatch.
FieldsMatch is obtained from the IncompleteFieldsMatch by providing a matching condition on the field. FieldsMatch
can be expanded with a new matching condition to get another IncompleteFieldsMatch. The process is continued until all
desired matching conditions are defined.
FieldsMatch m = Match.field(Account.Name).equals('Foo').also(Account.AnnualRevenue).greaterThan(100000);FieldsMatch can be provided directly to filter method:
Collection filtered = Collection.of(accounts).filter(Match.field(Account.Name).equals('Foo').also(Account.AnnualRevenue).greaterThan(100000));| Modifier and type | Method | Alias | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
FieldsMatch |
equals(Object value) |
eq |
Defines an equality comparison condition for the current field |
FieldsMatch |
notEquals(Object value) |
neq |
Defines an inequality comparison condition for the current field |
FieldsMatch |
lessThan(Object value) |
lt |
Defines a less than comparison condition for the current field |
FieldsMatch |
lessThanOrEquals(Object value) |
leq |
Defines a less than or equals condition for the current field |
FieldsMatch |
greaterThan(Object value) |
gt |
Defines a greater than condition for the current field |
FieldsMatch |
greaterThanOrEquals(Object value) |
geq |
Defines a greaterThanOrEquals condition for the current field |
FieldsMatch |
isIn(Object value) |
Defines a set membership condition for the current field | |
FieldsMatch |
isNotIn(Object value) |
notIn |
Defines a set non-membership condition for the current field |
FieldsMatch |
hasValue() |
notNull |
Defines a non-null condition for the current field |
Additional conditions can be defined with also, or its alias, field:
| Modifier and type | Method | Alias | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
IncompleteFieldsMatch |
also(Schema.SObjectField field) |
field |
Defines another condition to match |
IncompleteFieldsMatch |
also(String fieldPath) |
field |
Defines another condition to match |
isIn and isNotIn support a Set of one of the following types:
BooleanDateDatetimeDecimalDoubleIdIntegerLongString
Other types are not supported and will throw an exception.
Fields used in field conditions must be available on the collection which is filtered, otherwise a System.SObjectException: SObject row was retrieved via SOQL without querying the requested field exception can be thrown.
RecordMatch returns true if record fields are equal to those defined on a “prototype” record. Fields that are not
defined on a prototype record do not have to match.
Account prototype = new Account(
Name = 'Test',
AnnualRevenue = 50000000
);
// Accounts named 'Test' with an AnnualRevenue of **exactly** 50,000,000 are matched
Collection filtered = accountCollection.filter(Match.record(prototype));Fields that are present on the prototype object must also be available on the collection which is filtered, otherwise a System.SObjectException: SObject row was retrieved via SOQL without querying the requested field exception will be thrown.
remove works just like filter, but records which match a predicate are removed from the Collection view instead of kept.
Plucks field values from a Collection view of records into a List of appropriate type.
List<Account> accounts = new List<Account>{
new Account(Name = 'Foo'),
new Account(Name = 'Bar')
}
// Names are plucked into a new list, ['Foo', 'Bar']
List<String> names = Collection.of(accounts).pluckStrings(Account.Name);Pluck can also be used for deeper relations by using String field paths instead of Schema.SObjectField parameters.
List<Opportunity> opportunities = new List<Opportunity>{
new Opportunity(Account = new Account(Name = 'Foo')),
new Opportunity(Account = new Account(Name = 'Bar'))
};
// Names are plucked into a new list ['Foo', 'Bar']
List<String> accountNames = Collection.of(opportunities).pluckStrings('Account.Name');| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
List<Boolean> |
pluckBooleans(Schema.SObjectField) |
Plucks Boolean field values |
List<Boolean> |
pluckBooleans(String relation) |
Plucks Boolean relation values |
List<Date> |
pluckDates(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Plucks Date field values |
List<Date> |
pluckDates(String relation) |
Plucks Date relation values |
List<Date> |
pluckDatetimes(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Plucks Datetime field values |
List<Date> |
pluckDatetimes(String relation) |
Plucks Datetime relation values |
List<Decimal> |
pluckDecimals(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Plucks numerical field values |
List<Decimal> |
pluckDecimals(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Plucks numerical relation values |
List<Id> |
pluckIds(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Plucks Id field values |
List<Id> |
pluckIds(String relation) |
Plucks Id relation values |
List<Id> |
pluckIds() |
Plucks values of Id field |
List<String> |
strings(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Plucks String or Id field values |
List<String> |
strings(Schema.SObjectField relation) |
Plucks String or Ids relation values |
Groups records by values of a specified field.
Map<Date, List<Opportunity>> opportunitiesByCloseDate = Collection.of(opportunities).groupByDates(Opportunity.CloseDate, opportunities);| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
Map<Boolean, List<SObject>> |
groupByBooleans(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Groups records by Boolean field values |
Map<Boolean, List<SObject>> |
groupByBooleans(Schema.SObjectField field, Type listType) |
Groups records by Boolean field values, with specified list type |
Map<Boolean, List<SObject>> |
groupByBooleans(String apiFieldName) |
Groups records by Boolean apiFieldName values |
Map<Boolean, List<SObject>> |
groupByBooleans(String apiFieldName, Type listType) |
Groups records by Boolean apiFieldName values, with specified list type |
Map<Date, List<SObject>> |
groupByDates(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Groups records by Date field values |
Map<Date, List<SObject>> |
groupByDates(Schema.SObjectField field, Type listType) |
Groups records by Date field values, with specified list type |
Map<Date, List<SObject>> |
groupByDates(String apiFieldName) |
Groups records by Date apiFieldName values |
Map<Date, List<SObject>> |
groupByDates(String apiFieldName, Type listType) |
Groups records by Date apiFieldName values, with specified list type |
Map<Date, List<SObject>> |
groupByDatetimes(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Groups records by Datetime field values |
Map<Date, List<SObject>> |
groupByDatetimes(Schema.SObjectField field, Type listType) |
Groups records by Datetime field values, with specified list type |
Map<Date, List<SObject>> |
groupByDatetimes(String apiFieldName) |
Groups records by Datetime apiFieldName values |
Map<Date, List<SObject>> |
groupByDatetimes(String apiFieldName, Type listType) |
Groups records by Datetime apiFieldName values, with specified list type |
Map<Decimal, List<SObject>> |
groupByDecimals(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Groups records by numeric field values |
Map<Decimal, List<SObject>> |
groupByDecimals(Schema.SObjectField field, Type listType) |
Groups records by numeric field values, with specified list type |
Map<Decimal, List<SObject>> |
groupByDecimals(String apiFieldName) |
Groups records by numeric apiFieldName values |
Map<Decimal, List<SObject>> |
groupByDecimals(String apiFieldName, Type listType) |
Groups records by numeric apiFieldName values, with specified list type |
Map<Id, List<SObject>> |
groupByIds(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Groups records by Id field values |
Map<Id, List<SObject>> |
groupByIds(Schema.SObjectField field, Type listType) |
Groups records by Id field values, with specified list type |
Map<Id, List<SObject>> |
groupByIds(String apiFieldName) |
Groups records by Id apiFieldName values |
Map<Id, List<SObject>> |
groupByIds(String apiFieldName, Type listType) |
Groups records by Id apiFieldName values, with specified list type |
Map<String, List<SObject>> |
groupByStrings(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Groups records by String field values |
Map<String, List<SObject>> |
groupByStrings(Schema.SObjectField field, Type listType) |
Groups records by String field values, with specified list type |
Map<String, List<SObject>> |
groupByStrings(String apiFieldName) |
Groups records by String apiFieldName values |
Map<String, List<SObject>> |
groupByStrings(String apiFieldName, Type listType) |
Groups records by String apiFieldName values, with specified list type |
Returns a new Collection view of the collection which keeps just the specified fields, discarding others. Helps reduce overwriting potential for concurrent updates when locking is not an option.
List<Opportunity> opportunities = new List<Opportunity>{
new Opportunity(Name = 'Foo', Amount = 10000, Description = 'Bar')
}
// Picked contains just Name and Amount fields. Description is not present.
Collection picked = Collection.of(opportunities).pick(new Set<String>{'Name', 'Amount'});| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
Collection |
pick(List<Schema.SObjectField> fields) |
Picks fields into a new Collection view |
Collection |
pick(Set<Schema.SObjectField> fields) |
Picks fields into a new Collection view |
Collection |
pick(List<String> apiFieldNames) |
Picks fields into a new Collection view |
Collection |
pick(Set<String> apiFieldNames) |
Picks fields into a new Collection view |
Maps all elements of Collection view into another Collection view with the provided SObjectToSObjectFunction mapping function.
| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
Collection |
mapAll(SObjectToSObjectFunction fn) |
Returns a new Collection view formed by mapping all current view elements with fn |
private class DoubleAmount implements SObjectToSObjectFunction {
public SObject apply(SObject record) {
record.put('Amount', 2 * (Decimal) record.get('Amount'));
return record;
}
}
List<Opportunity> opps = new List<Opportunity>{
new Opportunity(Amount = 100),
new Opportunity(Amount = 150)
};
Collection.of(opps).mapAll(new DoubleAmount()); // amounts have been doubledOne SObjectToSObjectFunction is provided out of the box, CopyFields. It is instantiated through a factory method, CopyFields.fromRecord.
CopyFields copies all defined fields from prototype record to the record it is applied to. Values of fields defined for prototype are overwritten on
target records. Other fields on target record are not modified.
Collection.of(opps).mapAll(CopyFields.fromRecord(new Opportunity(Name = 'Test'))); // Name field has been overwritten with 'Test'Returns a new Collection view formed by mapping those view elements that satisfy predicate, and keeping those that do not unchanged.
private class DoubleAmount implements SObjectToSObjectFunction {
public SObject apply(SObject record) {
record.put('Amount', 2 * (Decimal) record.get('Amount'));
return record;
}
}
List<Opportunity> opps = new List<Opportunity>{
new Opportunity(Amount = 100),
new Opportunity(Amount = 150)
};
Collection.of(opps).mapSome(Match.field('Amount').gt(120), new DoubleAmount()); // 100 remains, but 150 has been doubled to 300| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
Collection |
mapAll(SObjectToSObjectFunction fn) |
Returns a new Collection view formed by mapping current view elements that satisfy predicate with fn, and keeping those that do not satisfy predicate unchanged. |
Maps a numeric field to a DecimalCollection. This is similar to pluckDecimals, but unlike a raw List<Decimal> returns a DecimalCollection which provides further functions.
| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
DecimalCollection |
mapToDecimal(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Plucks Decimal field values into a DecimalCollection. |
DecimalCollection |
mapToDecimal(String relation) |
Plucks Decimal values at relation into a DecimalCollection. |
Functions on DecimalCollection include sum and average.
| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
Decimal |
sum() |
Sums non-null Decimal values. Returns null if no such values exist in the collection. |
Decimal |
average() |
Averages non-null Decimal values. Returns null if no such values exist in the collection. |
DecimalCollection |
filter(ObjectPredicate predicate) |
Filters all values satisfying the predicate into a new DecimalCollection view. |
DecimalCollection |
filter(DecimalPredicate predicate) |
Filters all values satisfying the predicate into a new DecimalCollection view. |
Maps a numeric field to a DoubleCollection. This is similar to pluckDoubles, but unlike a raw List<Double> returns a DoubleCollection which provides further functions.
| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
DoubleCollection |
mapToDouble(Schema.SObjectField field) |
Plucks Double field values into a DoubleCollection. |
DoubleCollection |
mapToDouble(String relation) |
Plucks Double values at relation into a DoubleCollection. |
Functions on DoubleCollection include sum and average.
| Modifier and type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
Double |
sum() |
Sums non-null Double values. Returns null if no such values exist in the collection. |
Double |
average() |
Averages non-null Double values. Returns null if no such values exist in the collection. |
DoubleCollection |
filter(ObjectPredicate predicate) |
Filters all values satisfying the predicate into a new DoubleCollection view. |
DoubleCollection |
filter(DoublePredicate predicate) |
Filters all values satisfying the predicate into a new DoubleCollection view. |
List<Opportunity> opps = new List<Opportunity>{
new Opportunity(Amount = 100),
new Opportunity(Amount = 150)
};
Double average = Collection.of(opps).mapToDouble(Opportunity.Amount).average();Apex allows assignment of SObject lists and sets to its “subclass”, and the other way around:
List<SObject> objects = new List<SObject>();
List<Account> accounts = objects; // compiles!
List<Account> accounts = new List<Account>();
List<SObject> objects = accounts; // compiles as well!An SObject list is an instance of any SObject “subclass” list!
List<SObject> objects = new List<SObject>();
System.debug(objects instanceof List<Account>); // true
System.debug(objects instanceof List<Opportunity>); // trueCollection’s asList() and asSet() return a raw List<SObject> and Set<SObject>. This is more convenient because the type does not need to be provided, and a cast is not required in either case, but instanceof can provide unexpected results.
A concrete type of the list can be passed in as well. When this is done, the returned List or Set are of the correct concrete type instead of generic SObject collection type:
List<Account> filteredAccounts = accountCollection.asList();
// List<SObject> returned!
List<Account> filteredAccounts = accountCollection.asList(List<Account>.class);
// List<Account> returned!Collection also provides asMap() which returns a raw Map<Id, SObject>. Properly typed maps cannot be used without a cast.
Map<Id, Account> accountMap = accountCollection.asMap(); // Illegal assignment from Map<Id, SObject> to Map<Id, Account>
Map<Id, SObject> recordMap = accountCollection.asMap(); // Works!For typed maps, both a cast and the correct concrete type must be provided:
Map<Id, Account> recordMap = (Map<Id, Account>) accountCollection.asMap(Map<Id, Account>.class); // Works!