Created with the TechZone Accelerator Toolkit
This collection of IBM Cloud terraform automation bundles has been crafted from a set of Terraform modules created by Ecosystem Engineering
Three different flavors of the reference architecture are provided with different levels of complexity.
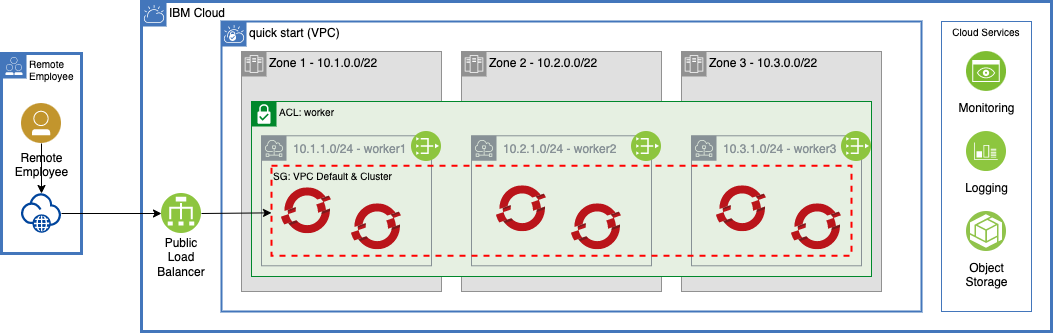
- QuickStart - minimum to get OpenShift with public endpoints running on basic VPC + Subnet with ROKS
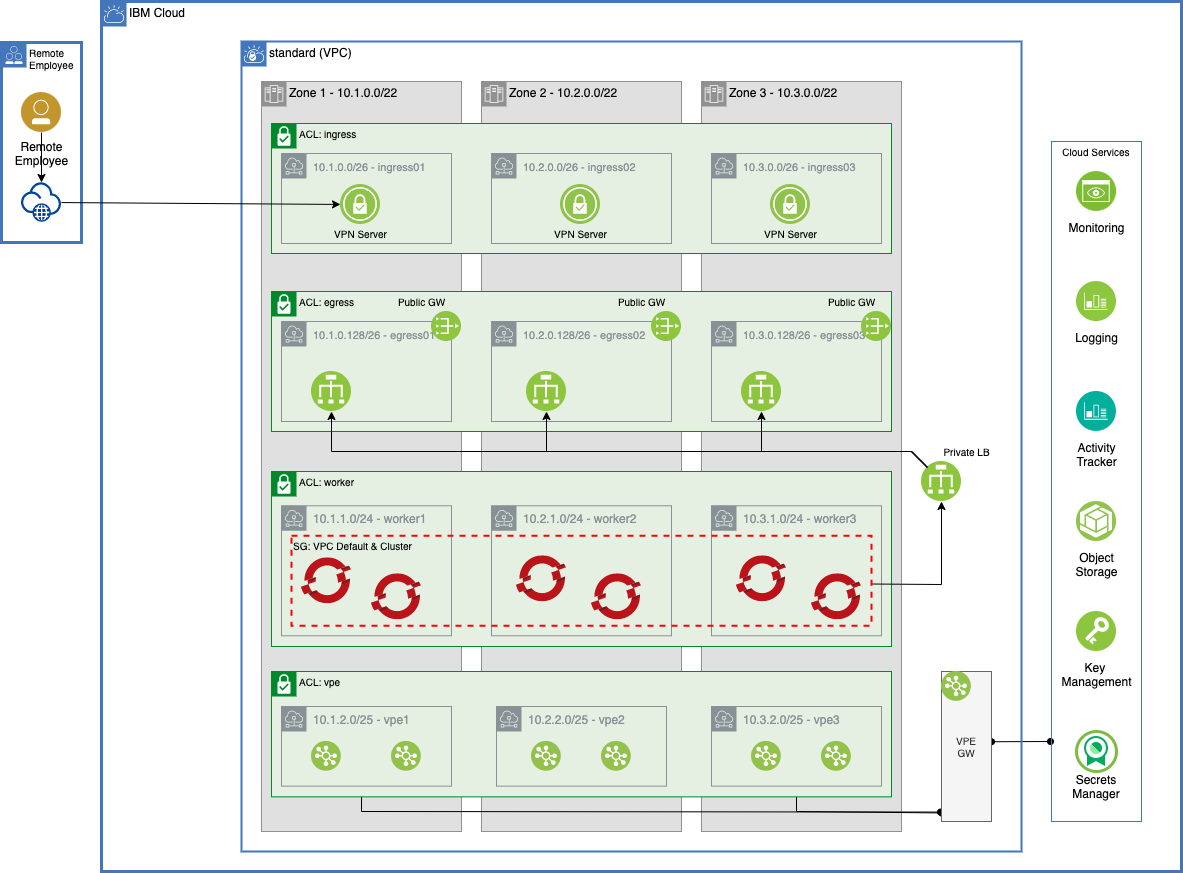
- Standard - a simple robust architecture that can support a production workload in a single VPC with a VPN+Private Endpoints and a ROKS cluster
- Advanced - a sophisticated architecture isolating DMZs, Development and Production VPCs for best practices
This set of automation packages was generated using the open-source isacable tool. This tool enables a Bill of Material yaml file to describe your IBM Cloud architecture, which it then generates the terraform modules into a package of infrastructure as code that you can use to accelerate the configuration of your IBM Cloud environment. Iascable generates standard terraform templates that can be executed from any terraform environment.
The
iascabletool is targeted for use by advanced SRE developers. It requires deep knowledge of how the modules plug together into a customized architecture. This repository is a fully tested output from that tool. This makes it ready to consume for projects.
-
Have access to an IBM Cloud Account, Enterprise account is best for workload isolation but if you only have a Pay Go account this set of terraform can be run in that level of account.
-
At this time the most reliable way of running this automation is with Terraform in your local machine either through a bootstrapped docker image or Virtual Machine. We provide both a container image and a virtual machine cloud-init script that have all the common SRE tools installed.
-
Requires use of terraform 1.2.x. Versions 1.3 and above are not supported with this automation at this time.
We recommend using Docker Desktop if choosing the container image method, and Multipass if choosing the virtual machine method. Detailed instructions for downloading and configuring both Docker Desktop and Multipass can be found in RUNTIMES.md
- Determine which flavor of reference architecture you will provision: Quick Start, Standard, or Advanced.
- View the README in the automation directory for detailed instructions for installation steps and required information:
-
Clone this repository to your local SRE laptop or into a secure terminal. Open a shell into the cloned directory.
-
Copy credentials.template to credentials.properties.
cp credentials.template credentials.properties
-
Provide values for the variables in credentials.properties (Note:
*.propertieshas been added to .gitignore to ensure that the file containing the apikey cannot be checked into Git.)- TF_VAR_ibmcloud_api_key - The API key for the IBM Cloud account where the infrastructure will be provisioned.
- TF_VAR_gitops_repo_host - (Optional) The host for the git repository (e.g. github.com, bitbucket.org). Supported Git servers are GitHub, Github Enterprise, Gitlab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps, and Gitea. If this value is left commented out, the automation will default to using Gitea.
- TF_VAR_gitops_repo_username - The username on git server host that will be used to provision and access the gitops repository. Leave commented out if using Gitea..
- TF_VAR_gitops_repo_token - The personal access token that will be used to authenticate to the git server to provision and access the gitops repository. (The user should have necessary access in the org to create the repository and the token should have
delete_repopermission.) Leave commented out if using Gitea. - TF_VAR_gitops_repo_org - (Optional) The organization/owner/group on the git server where the gitops repository will be provisioned/found. If not provided the org will default to the username. Leave blank if using Gitea.
- TF_VAR_gitops_repo_project - (Optional) The project on the Azure DevOps server where the gitops repository will be provisioned/found. This value is only required for repositories on Azure DevOps.
- TF_VAR_purge_volumes - (Optional) Uncomment this line and set to true if you are testing. This will force the volumes to be purged/deleted during the destroy process.
-
Run ./launch.sh. This will ask you whether you want to setup workspace or not.
- Hitting return to select
Ywill guide you through the setup of the workspace environment in a container. - At the end of which you can choose to use the configured variables. Choosing to use the configured variables will configure the environment in a container ready for the build. If you choose not to use the configured variables, the script will exit and you can start again to create a new set.
- Once configured, you will be asked whether to proceed. Typing yes will launch the build of the requested environment. Typing anything else will exit the setup, but the environment will still be configured in the container and you can proceed manually run the build by starting at step 3 in the below section.
- At the end of the build (or if you chose to configure the environment, but not proceed with the build), you will be in the container environment opened to the
/terraformdirectory. To manage the completed build, change to the workspace directory/workspaces/current.
- Hitting return to select
If you chose not to setup workspace, then use the following steps to manually configure the workspace and kick off the environment build.
-
This will start a container image with the prompt opened in the
/terraformdirectory, pointed to the repo directory. -
Create a working copy of the terraform by running ./setup-workspace.sh. The script makes a copy of the terraform in
/workspaces/currentand set up "cluster.tfvars" and "gitops.tfvars" files populated with default values. The setup-workspace.sh script has a number of optional arguments.Usage: setup-workspace.sh [-f FLAVOR] -s STORAGE [-n PREFIX_NAME] [-r REGION] [-g GIT_HOST] options: -f (optional) the flavor to use (quickstart) -s the storage option to use (none or odf) -n (optional) prefix that should be used for all variables -r (optional) the region where the infrastructure will be provisioned -g (optional) the git host that will be used for the gitops repo. If left blank gitea will be used by default. (Github, Github Enterprise, Gitlab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps, and Gitea servers are supported) -h Print this help -
Change the directory to the current workspace where the automation was configured (e.g.
/workspaces/current). -
Two different configuration files have been created: cluster.tfvars and gitops.tfvars. cluster.tfvars contains the variables specific to the infrastructure and cluster that will be provisioned. gitops.tfvars contains the variables that define the gitops configuration. Inspect both of these files to see if there are any variables that should be changed. (The setup-workspace.sh script has generated these two files with default values and can be used without updates, if desired.)
If using podman on RHEL it is the same process as above, except include podman as a command line argument when running the launch script and run as root the following:
./launch.sh podmanFrom the /workspace/current directory, run the following:
./apply.sh -aThe script will run through each of the terraform layers in sequence to provision the entire infrastructure.
From the /workspace/current directory, change the directory into each of the layer subdirectories, in order, and run the following:
./apply.shNote this will delete the entire environment, including anything created on the cluster. Ensure you backup anything you whish to keep before proceeding.
From the /workspace/current directory, run the following:
./destroy.sh -a