This Python 3 library provides SRL parser for Russian based on neural network models trained on FrameBank corpus -- semantically annotated corpus of texts in Russian. The parser should be used in conjunction with IsaNLP library and can be considered its module.
Disclaimer: the code is in alpha stage.
Note: the library is considered for Python 3.6. If you do not have one, checkout pyenv or this docker container powered with the data science tools: jupyter, keras, sklearn, gensim, tensorflow, pytorch, etc.
- Install IsaNLP and its dependencies:
pip install grpcio
pip install git+https://github.com/IINemo/isanlp.git
- Install IsaNLP SRL FrameBank library:
pip install git+https://github.com/IINemo/isanlp_srl_framebank.git
- Do the same steps for Quick installation.
- Install gensim, tensorflow, numpy, sklearn:
pip install gensim==3.6.0 smart-open==1.7.0 tensorflow==1.12.0 numpy sklearn
- Load the neural models from Git LFS
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/github/git-lfs/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
sudo apt-get install git-lfs
git lfs install
git-lfs pull
- Deploy docker containers for morphology, syntax, and SRL parsing:
docker run --rm -p 3333:3333 inemo/isanlp
docker run --rm --shm-size=1024m -ti -p 3334:9999 inemo/syntaxnet_rus server 0.0.0.0 9999
docker run --rm -p 3335:3333 inemo/isanlp_srl_framebank
- Connect from python using
PipelineDefault:
#
from isanlp_srl_framebank.pipeline_default import PipelineDefault
#
ppl = PipelineDefault(address_morph=('localhost', 3333),
address_syntax=('localhost', 3334),
address_srl=('localhost', 3335))
res = ppl('Мы поехали на дачу.')
#- The
resvariable should contain all annotations including SRL annotations stored inres['srl']:
{'text': 'Мы поехали на дачу.',
'tokens': [<isanlp.annotation.Token at 0x7f2290211240>,
<isanlp.annotation.Token at 0x7f22902112e8>,
<isanlp.annotation.Token at 0x7f2290211320>,
<isanlp.annotation.Token at 0x7f22902113c8>,
<isanlp.annotation.Token at 0x7f2290211438>],
'sentences': [<isanlp.annotation.Sentence at 0x7f2290211470>],
'mystem_postag': [['SPRO,мн,1-л=им',
'V,сов,нп=прош,мн,изъяв',
'PR=',
'S,жен,неод=вин,ед',
'']],
'lemma': [['мы', 'поехать', 'на', 'дача', '.']],
'morph': [[{'fPOS': 'PRON', 'Number': 'Plur', 'Person': '1', 'Case': 'Nom'},
{'fPOS': 'VERB',
'Aspect': 'Perf',
'Valency': 'INTR',
'Tense': 'Past',
'Number': 'Plur',
'VerbForm': 'Fin'},
{'fPOS': 'ADP'},
{'fPOS': 'NOUN',
'Gender': 'Fem',
'Animacy': 'Inan',
'Case': 'Acc',
'Number': 'Sing'},
{}]],
'postag': [['PRON', 'VERB', 'ADP', 'NOUN', '']],
'syntax_dep_tree': [[<isanlp.annotation.WordSynt at 0x7f2290211630>,
<isanlp.annotation.WordSynt at 0x7f2290211668>,
<isanlp.annotation.WordSynt at 0x7f22902116d8>,
<isanlp.annotation.WordSynt at 0x7f2290211710>,
<isanlp.annotation.WordSynt at 0x7f2290211748>]],
'srl': [[<isanlp.annotation.Event at 0x7f229021f278>]]}
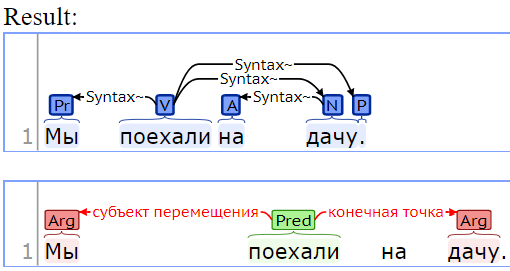
- The variable
res['srl']can be visualized as:
- The semantic role labeler. The SRL parser is implemented in
ProcessorSrlFramebankclass. Path:src/isanlp_srl_framebank/processor_srl_framebank.py. - Trained neural network models for SRL parser: model for "known" predicates and model for "unknown" predicates. Path:
models. - Docker container inemo/isanlp_srl_framebank that contains preinstalled libraries and models. The container provides gRPC service for SRL parsing. Path:
docker/parser. The container can be obtained with the command:
docker run --rm -p 3335:3333 inemo/isanlp_srl_framebank - Dockerized web demo for visualization of SRL annotations via brat annotation tool: inemo/isanlp_srl_framebank_demo. Path:
docker/demo. For example, the container can be obtained with the command (note, you need NLP services started on the corresponding ports, see Quick start section):
docker run --rm -p 1111:80 -e IP_ADDRESS=10.0.0.9 -e MORPH_PORT=3333 -e SYNTAX_PORT=3334 -e SEM_PORT=3335 inemo/isanlp_srl_framebank_demo
For version of parsing with less code (using docker) see Quick start section.
The processor for parsing is implemented in ProcessorSrlFramebank class.
from isanlp_srl_framebank.processor_srl_framebank import ProcessorSrlFramebankThe object should be initialized by a path to models and dictionaries of the parser. Example:
srl_proc = ProcessorSrlFramebank(model_dir_path = '~/srl_model_path')The model_dir_path should contain:
- embeddings.vec -- a model of word embeddings that can be loaded with
gensim.models.word2vec.KeyedVectors.load_word2vec_formatfunction. - known_preds.json -- the list of "known" predicates serialized into JSON. These predicates would be processed by the model for "known" predicates.
- known_predicates -- (mandatory) directory with model files for "known" predicates.
- unknown_predicates -- (optional) directory with model files for "unknown" predicates.
- The directory with model files must contain:
- feature_encoder.pckl -- pickled
sklearn.preprocessing.DictVectorizerobject that was used for categorical feature conversion during training. - label_encoder.pckl -- pickled
sklearn.preprocessing.LabelBinarizerobject that was used to encode labels into vectors during training. - feature_model.pckl -- pickled object that was used for extraction of features from linguistic annotations during training. The object should have
extract_featuresmember function. - neural_model.h5 -- saved keras model (with structure and weights).
- feature_encoder.pckl -- pickled
After initialization the object is ready for parsing using __call__ function:
res = srl_proc(tokens, postag, morph, lemma, syntax_dep_tree)The input arguments are:
- tokens -- a list of tokens.
- postag -- a list of lists of postags in Universal Dependencies format (the first list means sentences, the second list means words in the sentence).
- morph -- a list of lists of morphological features in Universal Dependencies format.
- lemma -- a list of lists of lemmas.
- syntax_dep_tree -- a list of syntax dependency trees of sentences in Universal Dependecies format.
The proper annotations can be obtained by other components of IsaNLP library. Example:
from isanlp.processor_remote import ProcessorRemote
from isanlp.ru.converter_mystem_to_ud import ConverterMystemToUd
from isanlp import PipelineCommon
# - To start morphology processor:
#$ docker run -d --rm -p 3333:3333 inemo/isanlp
# - To start ProcessorSyntaxNetRemote:
#$ docker run --shm-size=1024m -ti --rm -p 3334:9999 inemo/syntaxnet_rus server 0.0.0.0 9999
syntax_ppl = PipelineCommon([(ProcessorRemote('10.0.0.9', 3333, 'default'),
['text'],
{'sentences' : 'sentences',
'tokens' : 'tokens',
'postag' : 'mystem_postags',
'lemma' : 'lemma'}),
(ProcessorSyntaxNetRemote('10.0.0.9', 3334),
['tokens', 'sentences'],
{'syntax_dep_tree' : 'syntax_dep_tree',
'morph' : 'morph_syntaxnet'}),
(ConverterMystemToUd(),
['mystem_postags'],
{'morph' : 'morph',
'postag' : 'postag'})])
#
annots = syntax_ppl('Мама мыла раму.')
annots = srl_proc(annots['postag'],
annots['morph'],
annots['lemma'],
annots['syntax_dep_tree'])Finally, you get the SRL annotations:
print(annots['srl'])[[<isanlp.annotation.Event at 0x7f229021f978>]]
The results of SRL parser are stored in a list of lists of isanlp.annotation.Event objects. The first list corresponds to sentences, the second list corresponds to annotations inside a sentence.
Event objects have two members:
- pred(tuple): predicate address -- tuple of begin end positions in sentence.
- args(list): list of arguments -- tuples of
isanlp.annotation.TaggedSpanobjects. Each tagged span contains:- begin(int) -- starting position (in tokens in a sentence) of the argument in a sentence.
- end(int) -- ending position of an argument in a sentence.
- tag(string) -- semantic role.
With lemma annotations it is possible to print roles like this:
def print_roles(lemma, role_annot):
for sent_num, ann_sent in enumerate(role_annot):
for event in ann_sent:
print('=====Pred: {}'.format(lemma[sent_num][event.pred[0]]))
for arg in event.args:
print('Arg({}): {}'.format(arg.tag, lemma[sent_num][arg.begin]))Example:
print_roles(annots['lemma'], annots['srl'])The result for 'Дети убежали из дома и заблудились в лесу.':
=====Pred: убегать
Arg(агенс): ребенок
Arg(начальная точка): дом
=====Pred: заблудиться
Arg(место): лес
-
Download and preprocess dataset.
python ./run_download_preproc.py --workdir=<existing_workdir> -
Do the linguistic preprocessing of the dataset (postagging, parsing, etc.)
- Start linguistic preprocessing services:
docker run --rm -d -p 3333:3333 inemo/isanlp
docker run --rm -d -p 3334:3333 inemo/isanlp_udpipe
- Run preprocessing (change 192.168.1.69 to address of the machine, on which you started the linguistic processing services).
python ./run_ling_parse.py --workdir=existing_workdir --isanlp_proc=192.168.1.69:3333 --udpipe_proc=192.168.1.69:3334
- Generate features, embed with ELMo, and train models:
python ./run_training_pipeline.py --data_dir=existing_workdir --workdir=existing_workdir
Finally you can take trained models from directories 'known_preds' and 'unknown_preds' and place them in <project root>/models directory to create updated docker containers (or use them in the processor).
- To start web demo, you should start NLP services for morphology, syntax, and SRL parsing first:
docker run --rm -p 3333:3333 inemo/isanlp
docker run --rm --shm-size=1024m -ti -p 3334:9999 inemo/syntaxnet_rus server 0.0.0.0 9999
docker run --rm -p 3335:3333 inemo/isanlp_srl_framebank
- Start demo web application by the following command:
docker run --rm -d -p 1111:80 -e IP_ADDRESS=10.0.0.9 -e MORPH_PORT=3333 -e SYNTAX_PORT=8111 -e SEM_PORT=3334 inemo/isanlp_srl_framebank_demo
Note: instead of 10.0.0.9 you should use your host ip address (but not localhost or 127.0.0.1).
3. After web server started you can acesses demo interface at http://10.0.0.9:1111/demo/wui.py
The library should be compatible at least with Python 3.7.
Tested with gensim==3.6.0 tensorflow==1.15.0 .
- Models were published in RANLP proceedings
- GOST: Larionov D., Shelmanov A., Chistova E., Smirnov I. Semantic role labeling with pretrained language models for known and unknown predicates // Proceedings of RANLP. — 2019. — P. 245–256.
- BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{devshelm2019ranlp,
author = {Larionov D., Shelmanov A., Chistova E., Smirnov I.},
title = {Semantic role labeling with pretrained language models for known and unknown predicates},
booktitle = {Proceedings of Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing},
year = {2019},
pages = {620--628}
}
- Original models for SRL were published in Dialog proceedings.
- GOST:
Shelmanov A., Devyatkin D. Semantic role labeling with neural networks for texts in Russian // Computational Linguistics and Intellectual Technologies. Papers from the Annual International Conference "Dialogue" (2017). — Vol. 1. — 2017. — P. 245–256. - BibTex:
@INPROCEEDINGS{devshelm2017dialog,
author = {Shelmanov, A.O. and Devyatkin, D.A.},
title = {Semantic role labeling with neural networks for texts in {Russian}},
booktitle = {Computational Linguistics and Intellectual Technologies. Papers from the Annual International Conference "Dialogue" (2017)},
year = {2017},
volume={1},
number = {16},
pages = {245--256}
}