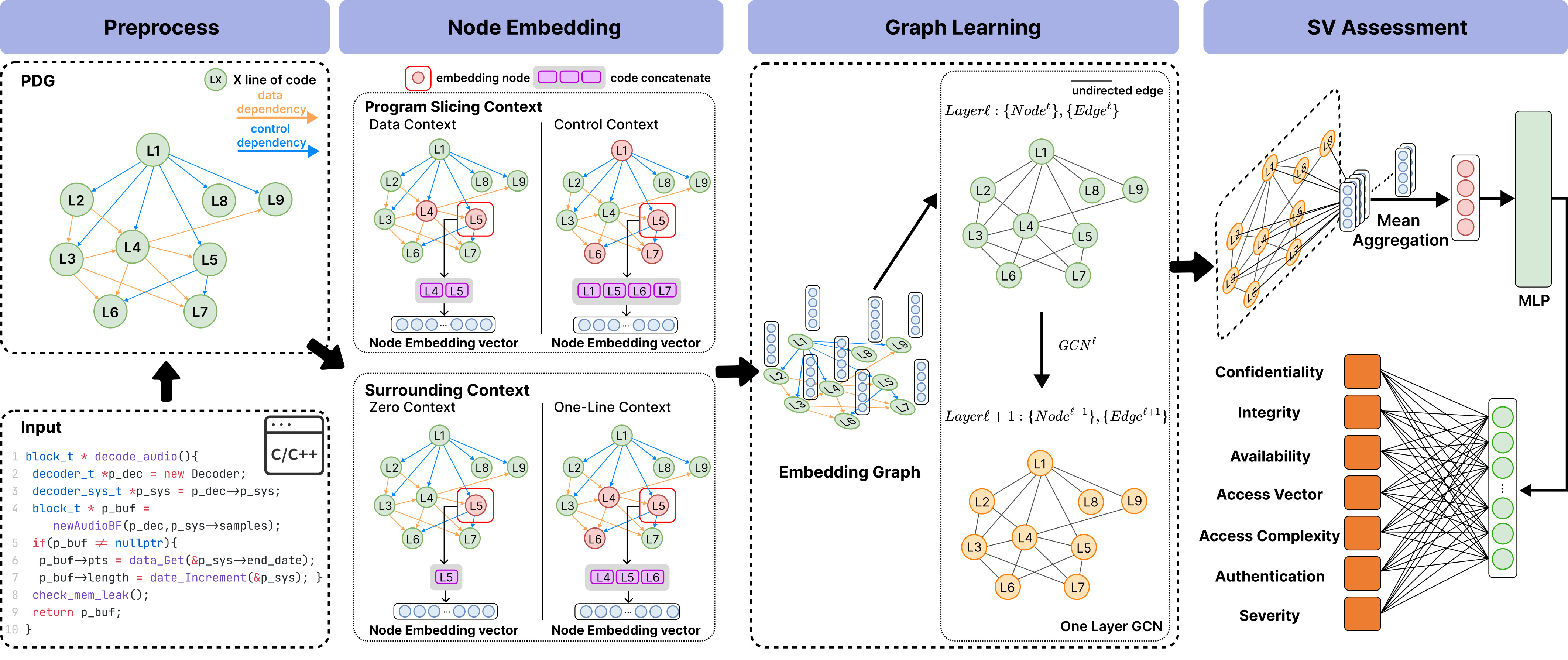
FVA: Assessing Function-Level Vulnerability by Integrating Flow-Sensitive Structure and Code Statement Semantic
You can download the preprocessed dataset from HERE and unzip it.
The folder structure should be organized as follows.
FVA_data.zip
├── metric.csv
├── mydata_split.csv
├── blaming_result.csv
The project will read the mydata_split.csv file, which contains the information about the division of the dataset. Each row corresponds to a function where the fields starting with cvss2_ store the Vulnerability Metrics.
func_before represents the function with the vulnerability, func_after represents the function after the vulnerability is fixed.
pre_context and cur_context record the context information of the vulnerable statements.
We also provide dataset processing scripts, please refer to Data_processing/readme.md and Data_processing/blaming/data/readme.md
- Linux
- Python 3.7+ (Tested on 3.7)
- PyTorch 1.8 or higher (Tested on 1.8.0)
- CUDA 11.1 or higher (Tested on 11.1)
- dgl 0.8.2+ (Tested on 0.8.2)
conda environment and dataset installation
# clone this project
git clone https://github.com/Icyrockton/FVA.git
cd FVA
# create conda environment FVA
conda env create -f environment.yml
# move FVA_data.zip uncompressed files to FVA/Data
mv FVA_data/* ./dataJoern installation
cd script
# we use the following joern version, please make sure the versions are the same
wget https://github.com/joernio/joern/releases/download/v1.1.260/joern-cli.zip
unzip joern-cli.zip
# if you have any questions about installing joern, please refer to the official documentation
# https://docs.joern.io/installation/
# we use script/joern.py to call joernWe compared the performance with the other four baselines, average performance is reported in the following table. If you want to see more detailed result, see the paper.
average performance
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-score | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepCVA | 0.855 | 0.759 | 0.708 | 0.725 | 0.604 |
| CodeBERT | 0.845 | 0.738 | 0.692 | 0.705 | 0.637 |
| FuncLGBM | 0.850 | 0.858 | 0.719 | 0.754 | 0.673 |
| FuncRF | 0.820 | 0.828 | 0.667 | 0.699 | 0.632 |
| FVA | 0.869 | 0.789 | 0.813 | 0.795 | 0.727 |
FVA support different node embeddings, context selections and graph models.
Our node embedding supports four options
- codebert
- unixcoder
- textcnn
- lstm
Context selection supports four options(Parentheses describe the abbreviations used in our paper).
- nature(one-line context)
- data_flow(data dependency context)
- control_flow(control dependency context)
- sentence(zero context)
We use dgl library to support different graph models.
- gat
- gatv2
- gcn
- SAGEConv
You can switch the configuration of the FVA in the gcn/multi_task/main.py:36 file at any time.
context_type = 'sentence'
token_type = 'codebert'
gnn_type = "gcn"In RQ1 , we compared to baseline models for function-level SV assessment.
We set up the FVA with the following configuration (one-line context, CodeBERT for node embedding, and GCN for graph model).
# gcn/multi_task/main.py
context_type = 'nature'
token_type = 'codebert'
gnn_type = "gcn"To train and test the FVA model , using the following commands. The result logging will be saved in the result directory.
conda activate fva
cd gcb/multi_task
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python ./main.pyThe other four baseline models are in the following directories.
gcn
├── Deepcva # DeepCVA model
├── multi_codebert # Vanilla CodeBERT
├── function_level_Le # LGBM and Random Forest
To train and test DeepCVA model , using the following commands.
cd gcn/Deepcva
python extract_features.py # run this file to get feature
python model.py # train and test DeepCVATo train and test Vanilla CodeBERT , using the following commands.
cd gcn/multi_codebert
python extract_tokens.py # run this file to get cache tokens
python main.py # train and test CodeBERTTo train and test LGBM and Random Forest , using the following commands.
cd gcn/function_level_Le
python extract_feature_codebert.py # get codebert feature
sh evaluate.sh # evaluate model
python get_best_result.py # get best resultIn RQ2,we study the effect of different vulnerable statement contexts on FVA performance.
We used the following four configurations to train the FVA.
# gcn/multi_task/main.py
context_type = 'nature'
token_type = 'codebert'
gnn_type = "gcn"
context_type = 'data_flow'
token_type = 'codebert'
gnn_type = "gcn"
context_type = 'control_flow'
token_type = 'codebert'
gnn_type = "gcn"
context_type = 'sentence'
token_type = 'codebert'
gnn_type = "gcn"In RQ3,we study the effect of different node embeddings on FVA performance.
We used the following three configurations to train the FVA.
# gcn/multi_task/main.py
# CodeBERT node embedding
context_type = 'nature'
token_type = 'codebert'
gnn_type = "gcn"
# UniXcoder node embedding
context_type = 'nature'
token_type = 'unixcoder'
gnn_type = "gcn"
# LSTM node embedding
context_type = 'nature'
token_type = 'lstm'
gnn_type = "gcn"FastText node embedding is stored in a separate folder fasttext_embedding_graph_model,because we need preprocess to get n-gram tokens.Using following commands to train and test FastText node embedding FVA models.
cd gcn/fasttext_embedding_graph_model
python main.pyIn RQ4,we study using different graph embedding models to assess SVs.
# gcn/multi_task/main.py
# GCN Graph Embedding
context_type = 'nature'
token_type = 'codebert'
gnn_type = "gcn"
# GAT Graph Embedding
context_type = 'nature'
token_type = 'codebert'
gnn_type = "gat"
# GAT-V2 Graph Embedding
context_type = 'nature'
token_type = 'codebert'
gnn_type = "gatv2"
# GraphSAGE Graph Embedding
context_type = 'nature'
token_type = 'codebert'
gnn_type = "SAGEConv"We also provide the training and testing time of models as a reference.
computation cost(s)
| DeepCVA | CodeBERT | FuncLGBM | FuncRF | FVA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | 4066.00 | 2821.00 | 394.71 | 6.66 | 18846.00 |
| Test | 11.30 | 2.70 | 0.07 | 0.77 | 30.30 |
The paper is still under review, you can download this repo HERE , and we will push the source code to GitHub when the review is finished.