Welcome to our image clustering project, where we leverage the power of DINOv2 embeddings and advanced clustering techniques to group similar images effectively. This project explores various steps, including feature extraction, dimensionality reduction, duplicates removal, and clustering optimization, to achieve meaningful and accurate image clusters.
Welcome to our image clustering project, where we leverage the power of DINOv2 embeddings and advanced clustering techniques to group similar images effectively. This project explores various steps, including feature extraction, dimensionality reduction, duplicates removal, and clustering optimization, to achieve meaningful and accurate image clusters.
We performed clustering on the train part of the DermNet dataset available on Kaggle.
To get started, clone the repository and install the necessary dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/IgorKolodziej/DERMNET.git
cd DERMNET
pip install -r requirements.txt- '00_presentation.pdf': Presentation slides.
01_EDA.ipynb: Exploratory Data Analysis of the dataset.- '02_dermnet_clustering.ipynb': Complete pipeline for image clustering.
embeddings_dino_base.npy: DINOv2 embeddings for the dataset without duplicates.- 'embeddings_dino_base_with_duplicates.npy': DINOv2 embeddings for the dataset with duplicates.
- 'cluster_labels.csv': Cluster labels for the train part of the dataset.
We utilize the DINOv2 model for image feature extraction due to its superior performance in generating rich and discriminative embeddings, essential for effective clustering.
Before extracting embeddings, we remove duplicate images using a SHA-256 hashing technique to ensure a unique and diverse dataset.
We experiment with PCA and UMAP to reduce the dimensionality of DINOv2 embeddings. UMAP was found to significantly outperform PCA, providing a more meaningful representation of the data's intrinsic structure.
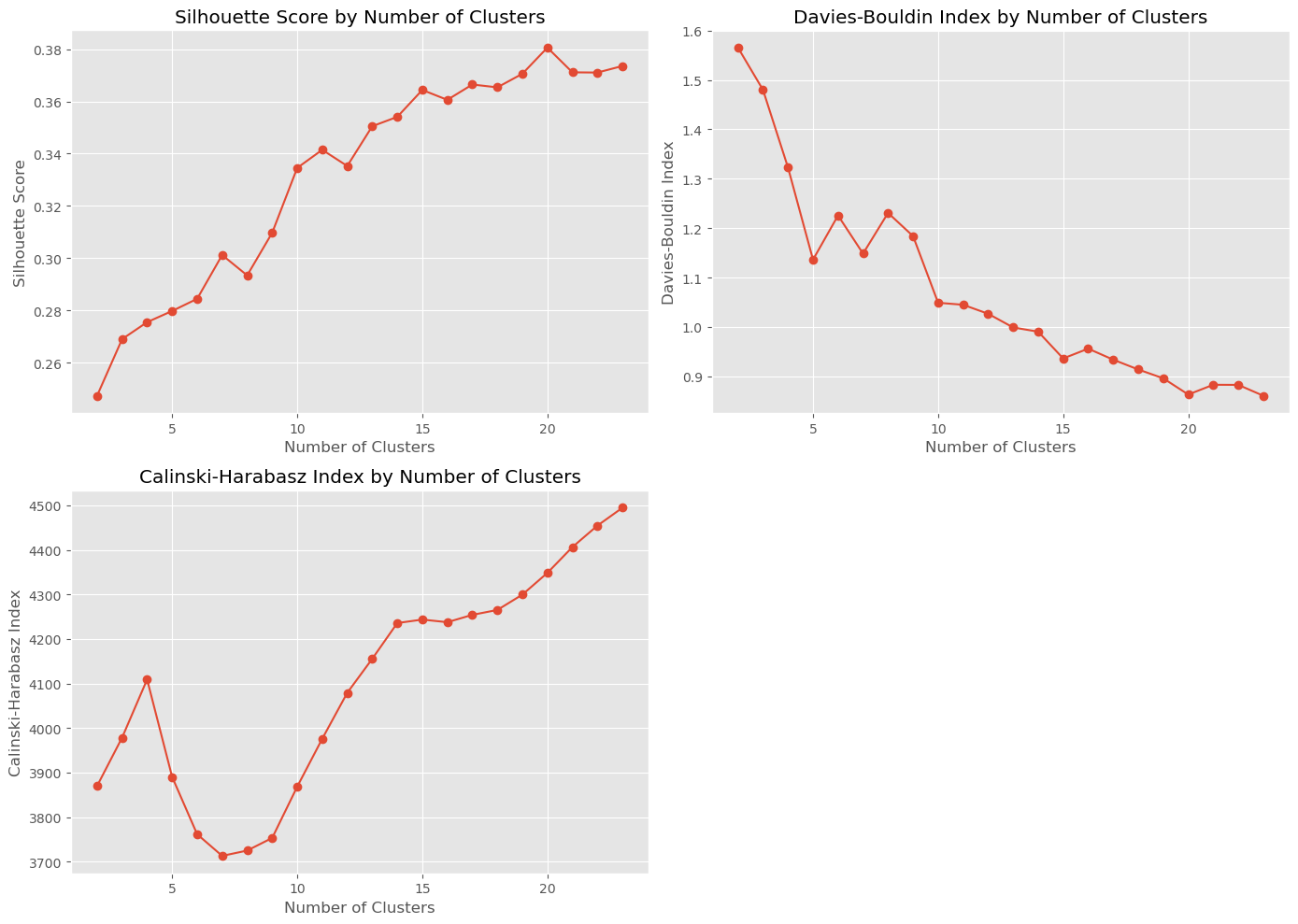
To determine the optimal number of UMAP components, we test various n_components values with KMeans and OPTICS algorithms, evaluating the results using clustering metrics such as the Silhouette score, Calinski-Harabasz index, and Davies-Bouldin index.
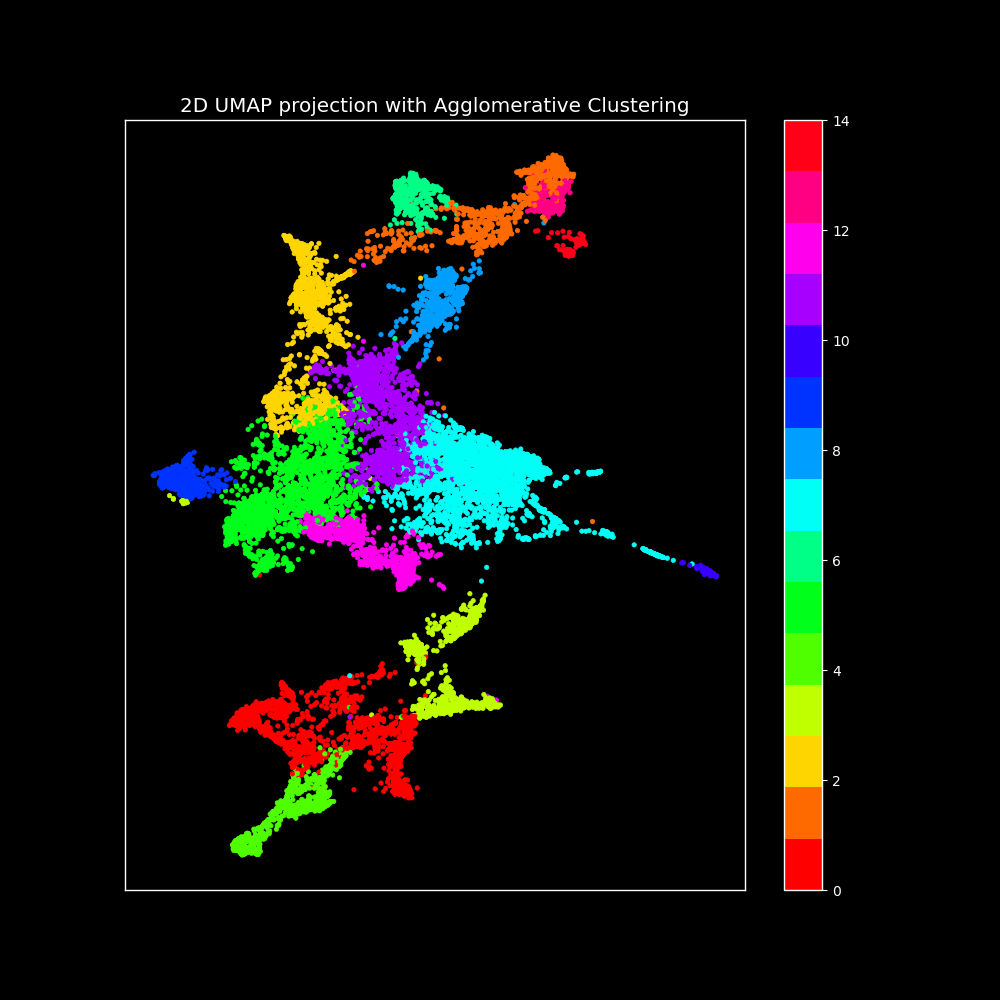
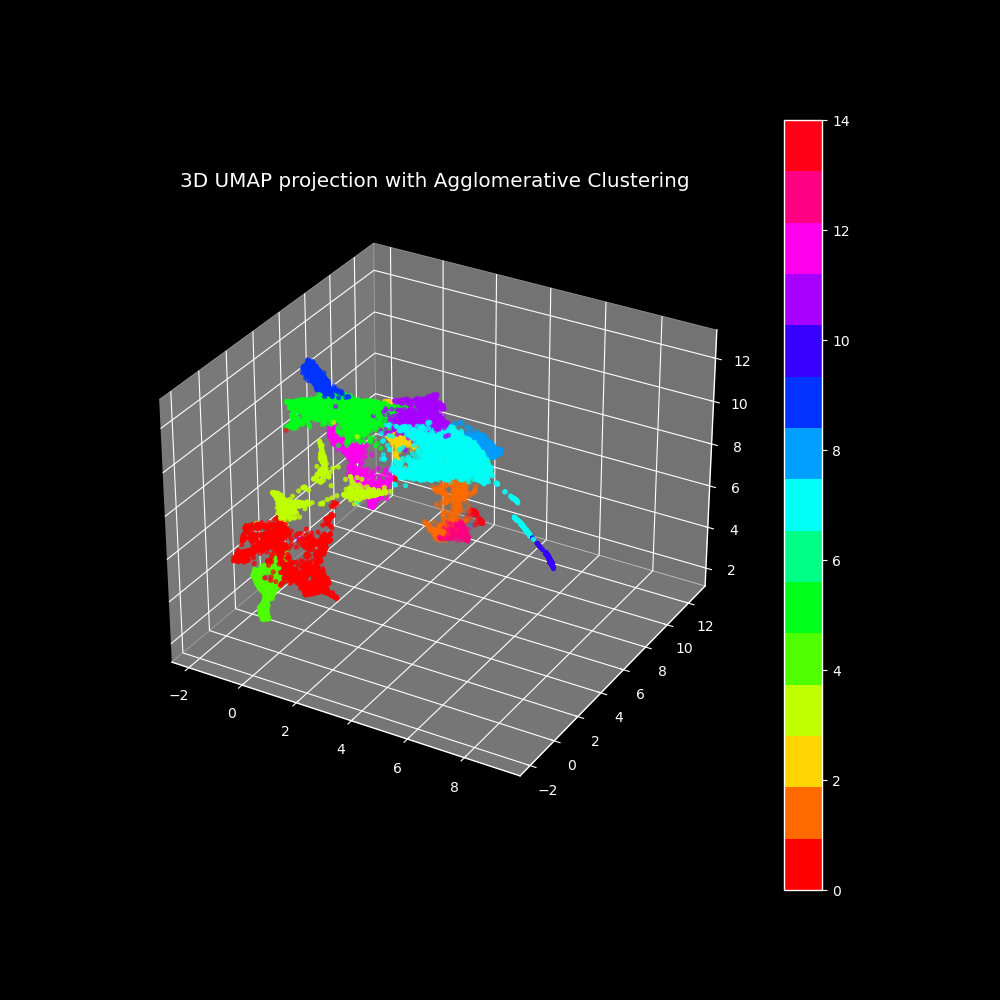
The final clustering results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, leveraging DINOv2 embeddings and Agglomerative Clustering to produce meaningful and well-defined image clusters.
DINOv2 embeddings provided high-quality features essential for effective clustering. We experimented with ResNet50 for feature extraction, but it was significantly outperformed by DINOv2.
UMAP outperformed PCA, preserving the intrinsic geometry of the data better.
Experimentation showed that tuning the number of UMAP projection components significantly improved clustering performance.
The clusters were mostly divided by body parts, demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach in capturing relevant visual patterns. Additionally, we managed to isolate contaminated clusters of images that should not belong to the dataset.
 An example of a contaminated cluster. Does anyone know what that is?
An example of a contaminated cluster. Does anyone know what that is?
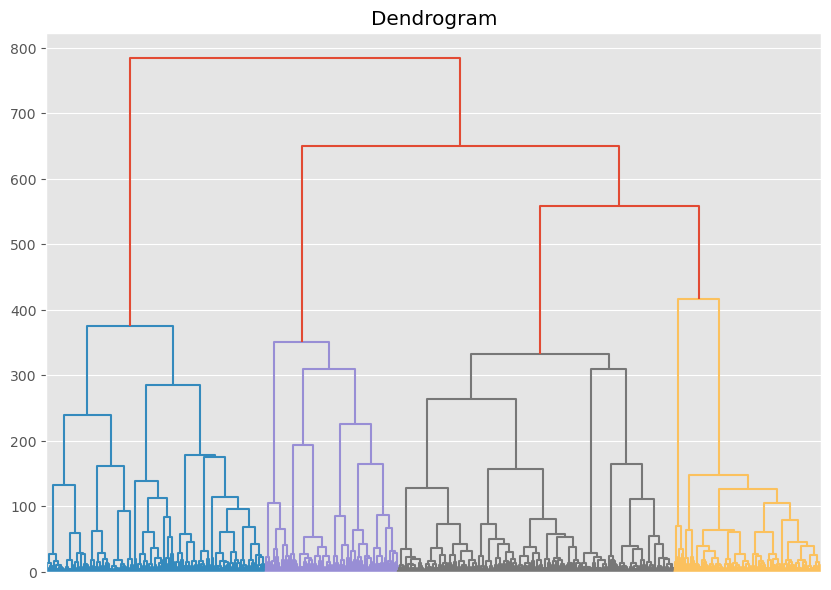
Despite KMeans showing slightly better metrics, we choose Agglomerative Clustering for the final model due to its robustness, flexibility, and ability to handle clusters of arbitrary shapes, providing a hierarchical clustering tree for better insight into the data structure.