$ qrcp
Transfer files over Wi-Fi from your computer to a mobile device by scanning a QR code without leaving the terminal.
You can support development by donating with 
Join the Telegram channel qrcp_dev for news about the development.
How does it work?
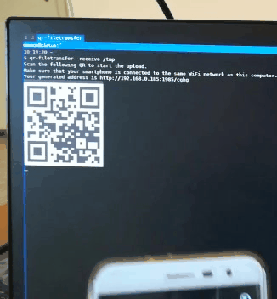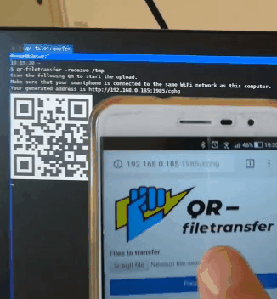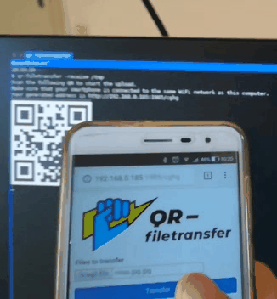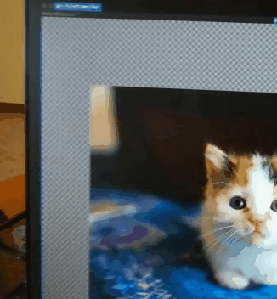
qrcp binds a web server to the address of your Wi-Fi network interface on a random port and creates a handler for it. The default handler serves the content and exits the program when the transfer is complete. When used to receive files, qrcp serves an upload page and handles the transfer.
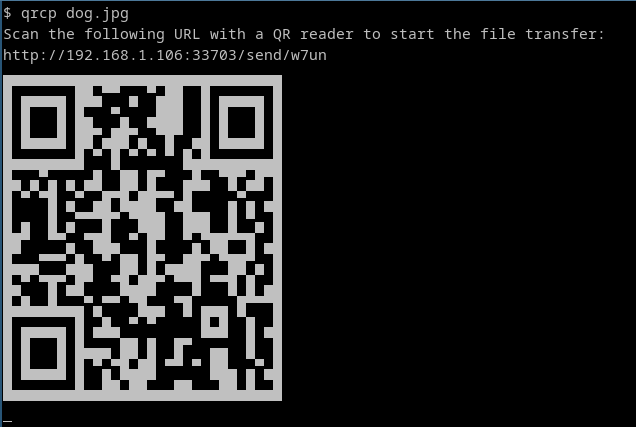
The tool prints a QR code that encodes the text:
http://{address}:{port}/{random_path}
Most QR apps can detect URLs in decoded text and act accordingly (i.e. open the decoded URL with the default browser), so when the QR code is scanned the content will begin downloading by the mobile browser.
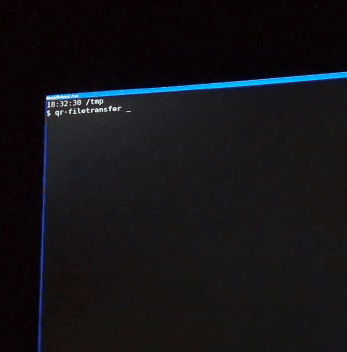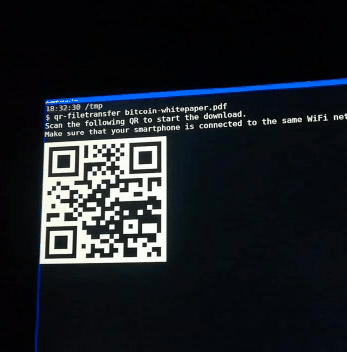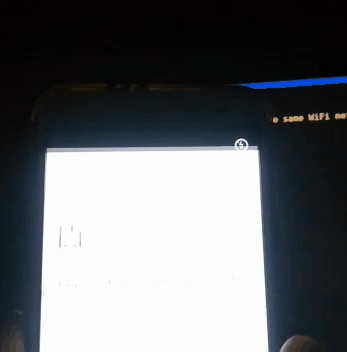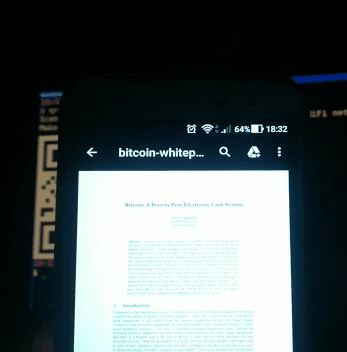
Send files to mobile:
Receive files from mobile:
Tutorials
Installation
Install the latest development version with Go
Note: it requires go 1.8
go get github.com/claudiodangelis/qrcp
Linux
Download the latest Linux .tar.gz archive from the Releases page, extract it, move the binary to the proper directory, then set execution permissions.
# Extract the archive
tar xf qrcp_0.5.0_linux_x86_64.tar.gz
# Copy the binary
sudo mv qrcp /usr/local/bin
# Set execution permissions
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/qrcpRaspberry Pi
The following ARM releases are available in the Releases page:
armv7arm64
Using a package manager
ArchLinux
Packages available on AUR:
Deb packages (Ubuntu, Debian, etc)
Download the latest .deb package from the Releases page, then run dpkg:
sudo dpkg -i qrcp_0.5.0_linux_x86_64.deb
# Confirm it's working:
qrcp versionRPM packages (CentOS, Fedora, etc)
Download the latest .rpm package from the Releases page, then run rpm:
sudo rpm -i qrcp_0.5.0_linux_x86_64.rpm
# Confirm it's working:
qrcp --helpWindows
Download the latest Windows .tar.gz archive from the Releases page and extract the EXE file.
Scoop
If you use Scoop for package management on Windows, you can install qrcp with the following one-liner:
scoop install qrcp
MacOS
Download the latest macOS .tar.gz archive from the Releases page, extract it, move the binary to the proper directory, then set execution permissions.
# Extract the archive
tar xf qrcp_0.5.0_macOS_x86_64.tar.gz
# Copy the binary
sudo mv qrcp /usr/local/bin
# Set execution permissions
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/qrcp
# Confirm it's working:
qrcp --helpHomebrew
If you use Homebrew for package management on macOS, you can install qrcp with the following one-liner:
brew install qrcp
Usage
Send files
Send a file
qrcp MyDocument.pdfSend multiple files at once
When sending multiple files at once, qrcp creates a zip archive of the files or folders you want to transfer, and deletes the zip archive once the transfer is complete.
# Multiple files
qrcp MyDocument.pdf IMG0001.jpg# A whole folder
qrcp Documents/Zip a file before transferring it
You can choose to zip a file before transferring it.
qrcp --zip LongVideo.aviReceive files
When receiving files, qrcp serves an "upload page" through which you can choose files from your mobile.
Receive files to the current directory
qrcp receive
Receive files to a specific directory
# Note: the folder must exist
qrcp receive --output=/tmp/dirOptions
qrcp works without any prior configuration, however, you can choose to configure to use specific values. The config command launches a wizard that lets you configure parameters like interface, port, fully-qualified domain name and keep alive.
qrcp configNote: if some network interfaces are not showing up, use the --list-all-interfaces flag to suppress the interfaces' filter.
qrcp --list-all-interfaces config Configuration File
The default configuration file is stored in $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/qrcp/config.json, however, you can specify the location of the config file by passing the --config flag:
qrcp --config /tmp/qrcp.json MyDocument.pdfPort
By default qrcp listens on a random port. Pass the --port (or -p) flag to choose a specific one:
qrcp --port 8080 MyDocument.pdfNetwork Interface
qrcp will try to automatically find the suitable network interface to use for the transfers. If more than one suitable interface is found, it asks you to choose one.
If you want to use a specific interface, pass the --interface (or -i) flag:
# The webserver will be visible by
# all computers on the tun0's interface network
qrcp -i tun0 MyDocument.dpfYou can also use a special interface name, any, which binds the web server to 0.0.0.0, making the web server visible by everyone on any network, even from an external network.
This is useful when you want to transfer files from your Amazon EC2, Digital Ocean Droplet, Google Cloud Platform Compute Instance or any other VPS.
qrcp -i any MyDocument.pdfURL
qrcp uses two patterns for the URLs:
- send:
http://{ip address}:{port}/send/{random path} - receive:
http://{ip address}:{port}/receive/{random path}
A few options are available that override these patterns.
Pass the --path flag to use a specific path for URLs, for example:
# The resulting URL will be
# http://{ip address}:{port}/send/x
qrcp --path=x MyDocument.pdfPass the --fqdn (or -d) to use a fully qualified domain name instead of the IP. This is useful in combination with -i any you are using it from a remote location:
# The resulting URL will be
# http://example.com:8080/send/xYz9
qrcp --fqdn example.com -i any -p 8080 MyRemoteDocument.pdfHTTPS
qrcp supports secure file transfers with HTTPS. To enable secure transfers you need a TLS certificate and the associated key.
You can choose the path to the TLS certificate and keys from the qrcp config wizard, or, if you want, you can pass the --tls-cert and --tls-key:
qrcp --tls-cert /path/to/cert.pem --tls-key /path/to/cert.key MyDocumentA --secure flag is available too, you can use it to override the default value.
Default output directory
Open in browser
If you need a QR to be printed outside your terminal, you can pass the --browser flag. With this flag, qrcp will still print the QR code to the terminal, but it will also open a new window of your default browser to show the QR code.
qrcp --browser MyDocument.pdf
Keep the server alive
It can be useful to keep the server alive after transferring the file, for example, when you want to transfer the same file to multiple devices. You can use the --keep-alive flag for that:
# The server will not shutdown automatically
# after the first transfer
qrcp --keep-alive MyDocument.pdfShell completion scripts
qrcp comes with a built-in completion command that generates shell completion scripts.
Bash:
$ source <(qrcp completion bash)
To load completions for each session, execute once:
Linux:
$ qrcp completion bash > /etc/bash_completion.d/qrcp
Note: if you don't want to install completion scripts system-wide, refer to Bash Completion FAQ.
MacOS:
$ qrcp completion bash > /usr/local/etc/bash_completion.d/qrcp
Zsh:
If shell completion is not already enabled in your environment you will need to enable it. You can execute the following once:
$ echo "autoload -U compinit; compinit" >> ~/.zshrc
To load completions for each session, execute once:
$ qrcp completion zsh > "${fpath[1]}/_qrcp"
You will need to start a new shell for this setup to take effect.
Fish:
$ qrcp completion fish | source
To load completions for each session, execute once:
$ qrcp completion fish > ~/.config/fish/completions/qrcp.fish
Authors
qrcp, originally called qr-filetransfer, started from an idea of Claudio d'Angelis (@daw985 on Twitter), the current maintainer, and it's developed by the community.
Credits
Logo is provided by @arasatasaygin as part of the openlogos initiative, a collection of free logos for open source projects.
Check out the rules to claim one: rules of openlogos.
Releases are handled with goreleaser.
Clones and Similar Projects
- qr-fileshare - A similar idea executed in NodeJS with a React interface.
- instant-file-transfer (Uncredited) - Node.js project similar to this
- qr-filetransfer - Python clone of this project
- qr-filetransfer - Another Node.js clone of this project
- qr-transfer-node - Another Node.js clone of this project
- QRDELIVER - Node.js project similar to this
- qrfile - Transfer files by scanning a QR code
- quick-transfer - Node.js clone of this project
- share-file-qr - Python re-implementation of this project
- share-files (Uncredited) - Yet another Node.js clone of this project
- ezshare - Another Node.js two way file sharing tool supporting folders and multiple files
- local_file_share - "share local file to other people, OR smartphone download files which is in pc"
- qrcp - a desktop app clone of
qrcp, writing with C# and .NET Core, work for Windows.
License
MIT. See LICENSE.