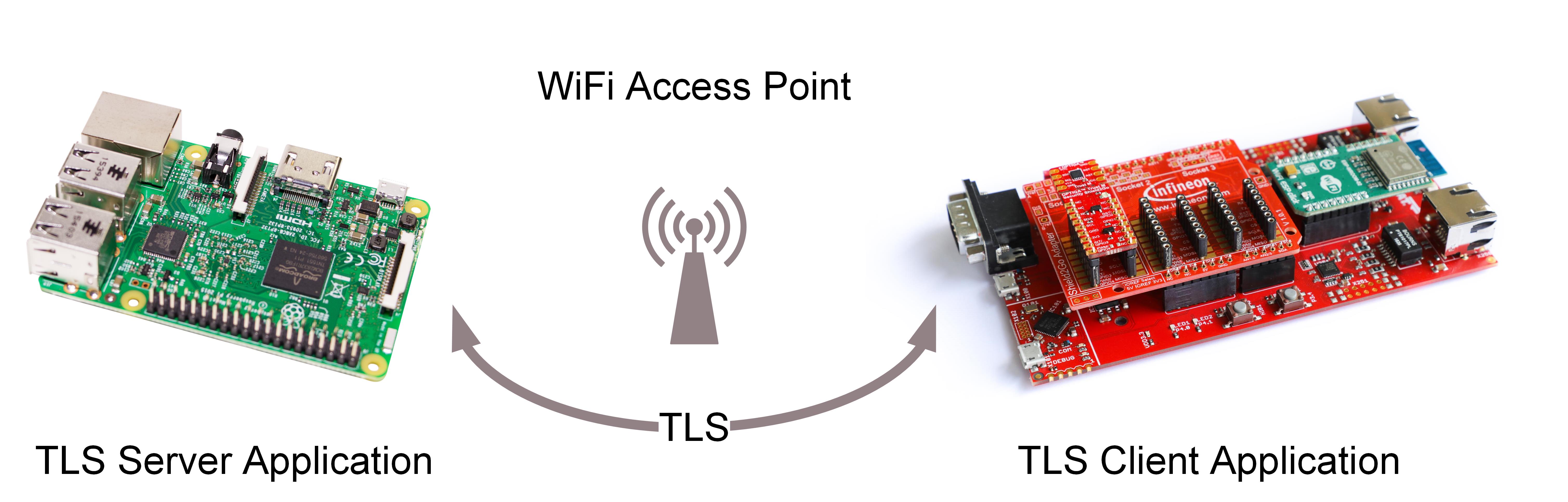
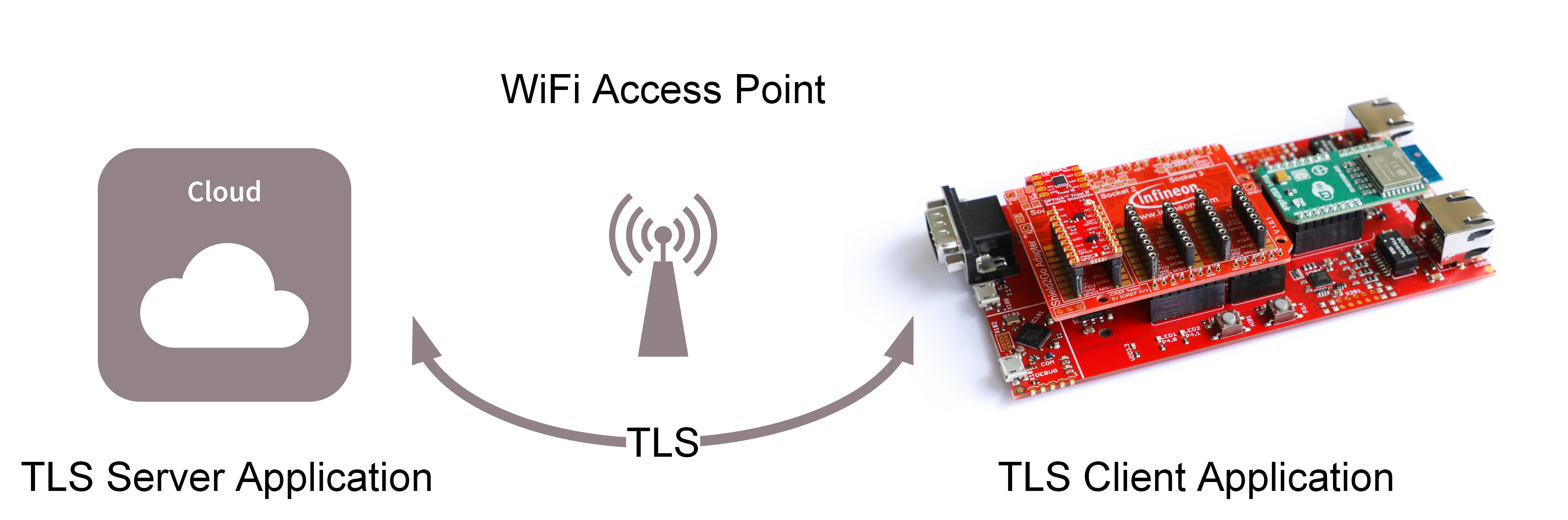
This repository contains one of the Application Notes for OPTIGATM Trust M security chip, showing how to perform TLS handshake with mutual authentication with an echo TLS server. The TLS client is implemented using XMC4800 running FreeRTOS version 10.2 (adopted from AWS FreeRTOS) with mbed TLS. Several server options are also provided with this application note as reference.
Note: This AppNote is applicable only for the Trust M V3:
Note: Please keep in mind there is submodule included, you need to clone with the --recurse-submodules option; i.e.:
$ git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/Infineon/mbedtls-optiga-trust-m.git-
TLS Server Setup
-
TLS Client Setup
-
Appendix A: Memory usage of Software mbedTLS vs Hardware supported mbedTLS
-
Appendix B: TLS Server and Client Certificate Provisioning
-
Appendix C: Functional Testing
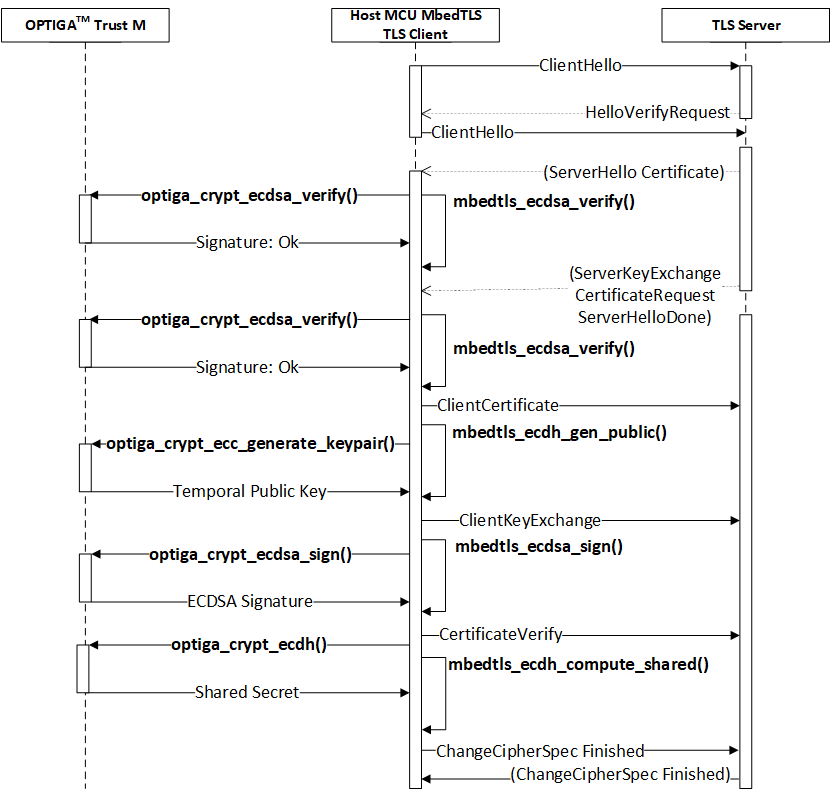
This section shows how to setup TLS client connecting to TLS server hosted on AWS EC2 Windows server. One of the easiest remote configuration is AWS EC2 Windows instance. EC2 server setup instruction can be found here: Remote server setup using EC2 Windows In this setup, XMC4800 is programmed as a TLS client which runs on FreeRTOS with MBedTLS. OPTIGATM Trust M stores the secret key used to establish the secure communication. The figure below illustrates the MbedTLS API used by Trust M.
The TLS client needs to be connected to the network which is accessible to the server. Upon successful TLS handshake, the TLS client will send some data to the TLS server and the echo server shall return the data to the client. On XMC4800, the output can be monitor using serial monitor using the FTDI serial cable connecting to RX and TX of XMC4800 board.
For Trust M connectivity to the XMC4800, the source code is configured using the below pinout.
| Trust M | XMC4800 |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3V3 |
| SDA | P1.5 |
| SCL | P0.8 |
| Reset | P0.6 |
In order to compile and run the TLS client, DAVE IDE is required. Download from below link: Development IDE: * IDE: DAVE
Once, DAVE IDE has been downloaded and installed, the TLS client can be downloaded from a release or cloned from this repository.
Note: Please keep in mind there is submodule included, you need to clone with the --recurse-submodules option; i.e.:
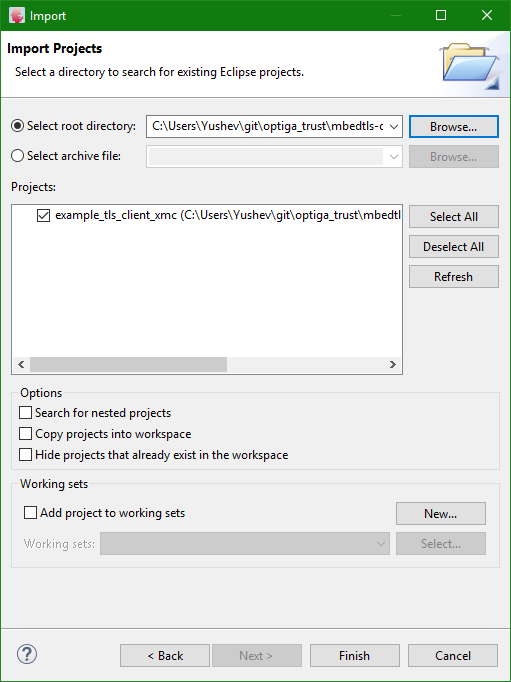
$ git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/Infineon/mbedtls-optiga-trust-m.gitImport (File -> Import ... -> Existing Project into Workspace) the project from the following path mbedtls-optiga-trust-m\example_tls_client_xmc\xmc4800_iot_kit
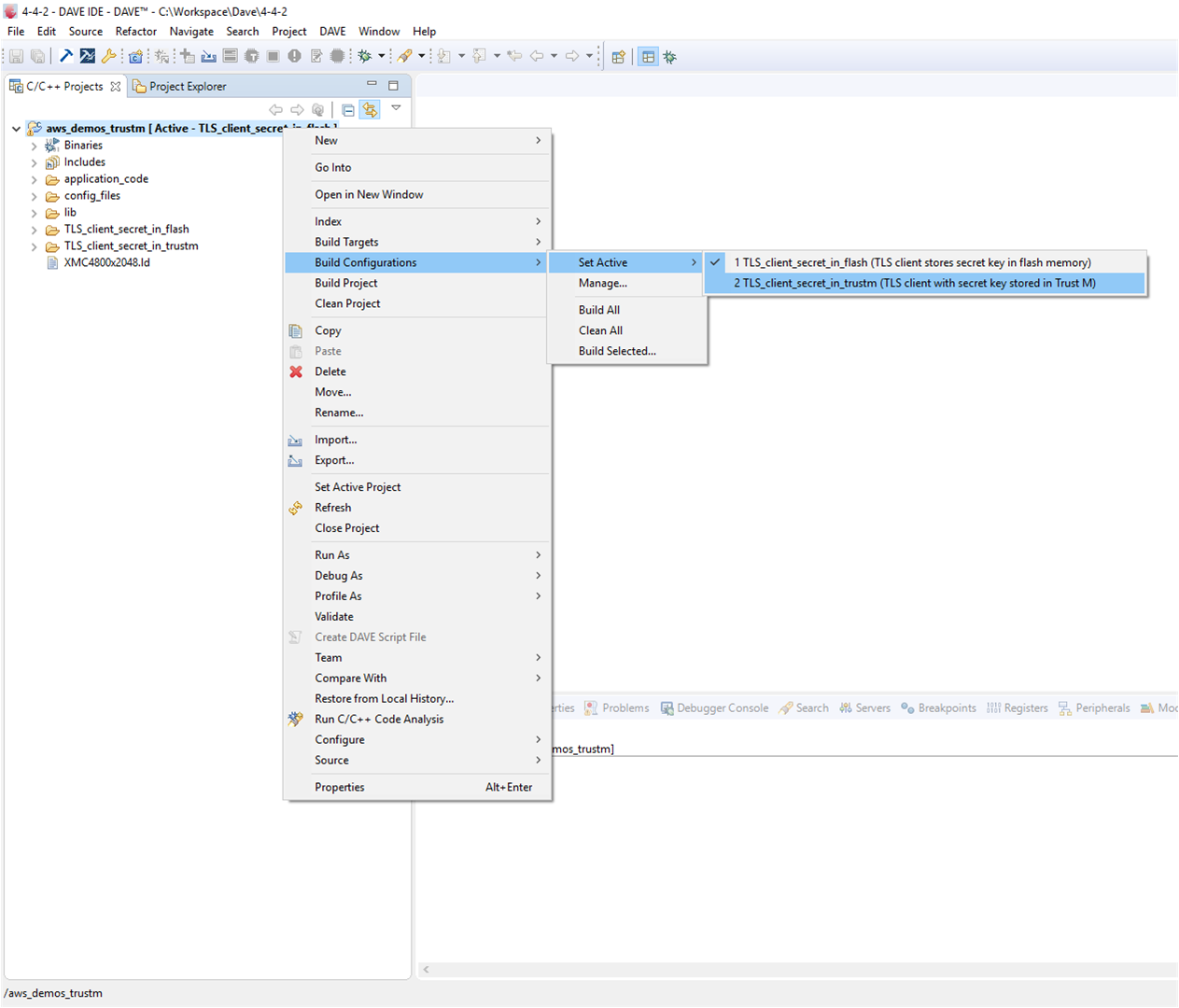
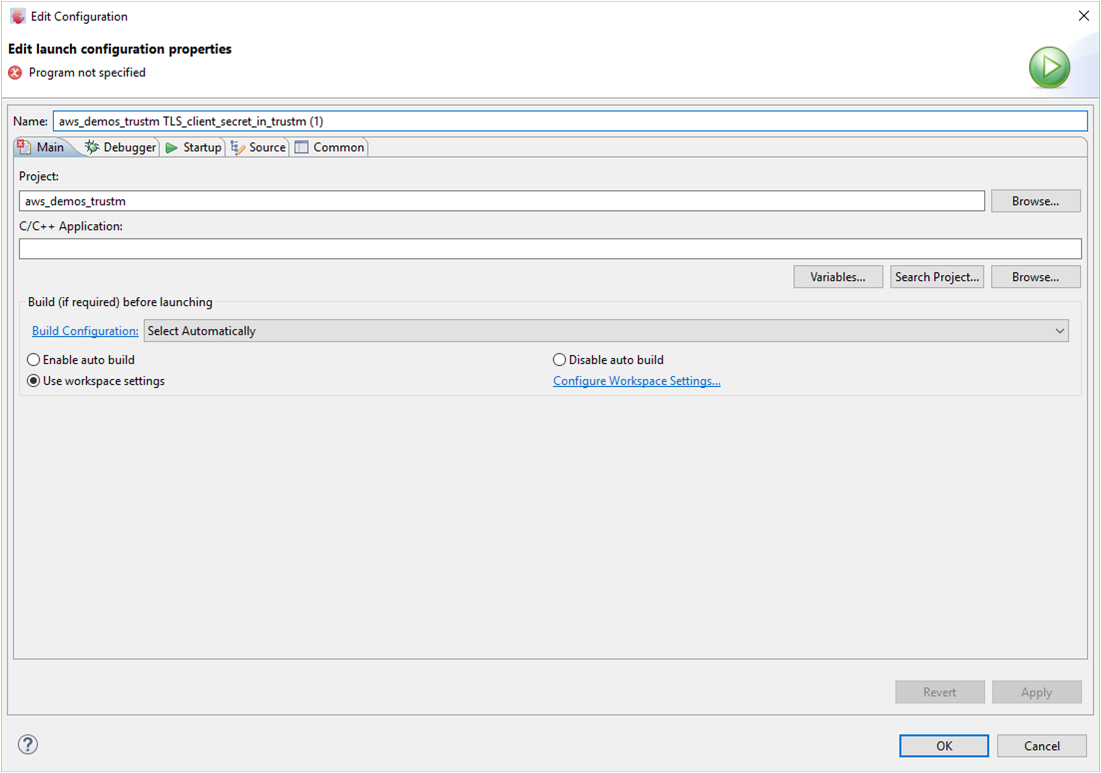
Select the project, right-click on it and press "Set Active Project", then select the profile in "Build Configurations" -> "Set Active" -> "TLS_client_secret_in_trustm". This project enables MACRO which uses Trust M to stores the secret key.
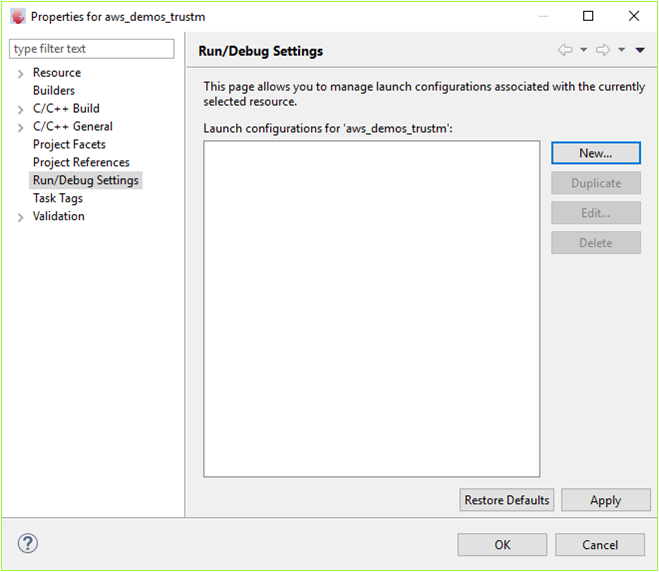
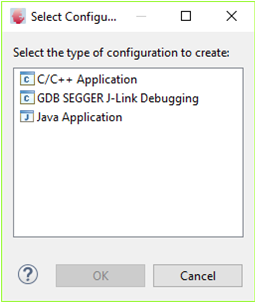
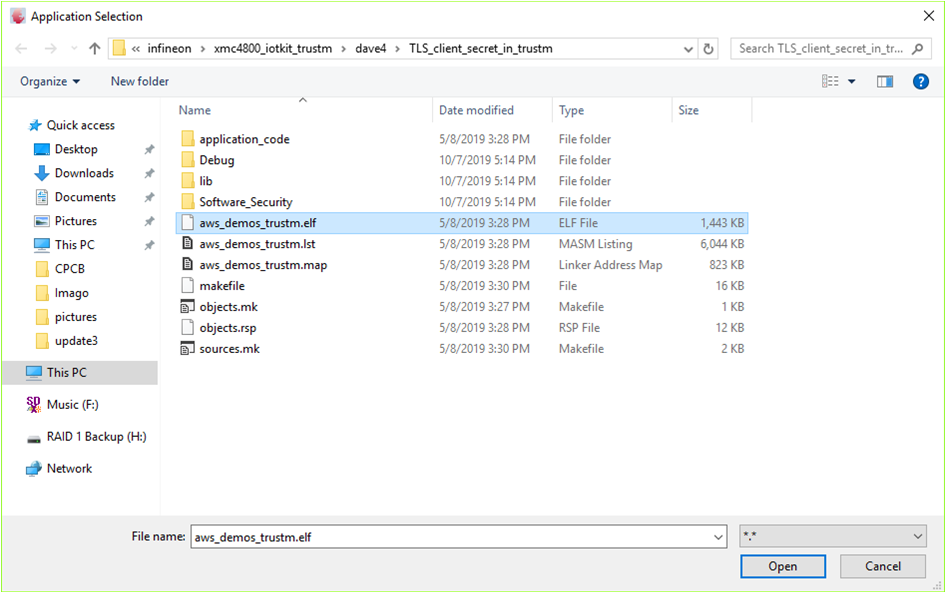
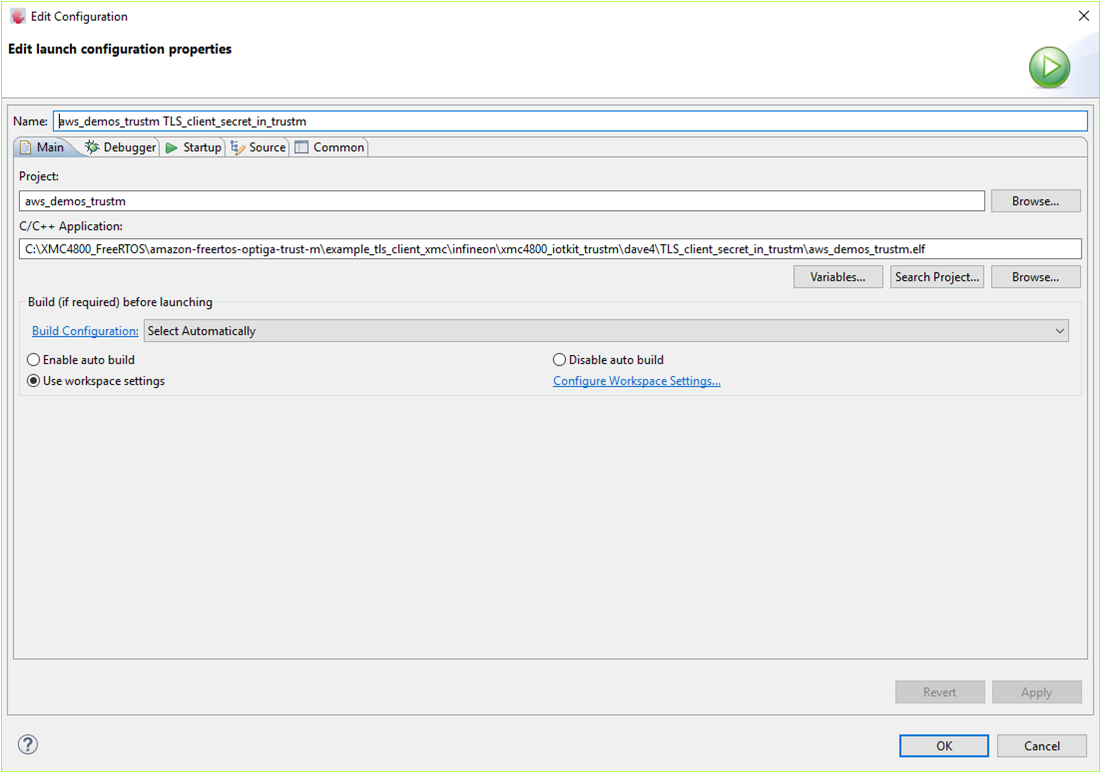
Right-click on the project name and select "properties". Click on "New..." to create a new debug instance. Select GDB SEGGER J-Link Debugging followed by selecting the image to load and debug.
From the menu select Project->Build Active Project. The project should be compiled with no error.
Click on the execute debug button and the project will be launched and a breakpoint halt in main().
A serial terminal with the following settings can be launched to monitor the output. Baud:115200 Data: 8-bit Parity: none Stop bits: 1-bit Flow control: none
Modify the TLS client source code to connect to a hotspot and TLS echo server.
Configure the aws_clientcredential.h for the Wifi SSID and password. The Wifi SSID and password can be obtain from respective DHCP source.
Example:
/*
* Wi-Fi network to join.
*/
#define clientcredentialWIFI_SSID "Apple7"
//#define clientcredentialWIFI_SSID "AndroidMobileAP"
//#define clientcredentialWIFI_SSID "raspi-webgui"
/*
* Password needed to join Wi-Fi network.
*/
#define clientcredentialWIFI_PASSWORD "password123"
//#define clientcredentialWIFI_PASSWORD "ChangeMe"The TLS echo server address can be configured in config_files\FreeRTOSConfig.h For remote server address, this value can either be taken from EC2 console. For local server, this is the fixed local IP address of the TLS server.
/* The address of an echo server that will be used by the two demo echo client
* tasks:
* http://www.freertos.org/FreeRTOS-Plus/FreeRTOS_Plus_TCP/TCP_Echo_Clients.html,
* http://www.freertos.org/FreeRTOS-Plus/FreeRTOS_Plus_TCP/UDP_Echo_Clients.html. */
#define REMOTE_TLS_SERVER 1
#if (REMOTE_TLS_SERVER == 1)
//EC2 Instance IP address
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR0 35
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR1 164
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR2 96
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR3 35
#else
//RaspAP local AP
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR0 10
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR1 3
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR2 141
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR3 1
#endif
#define configTCP_ECHO_SECURE_CLIENT_PORT 9000
#define configTCP_ECHO_CLIENT_PORT 9001
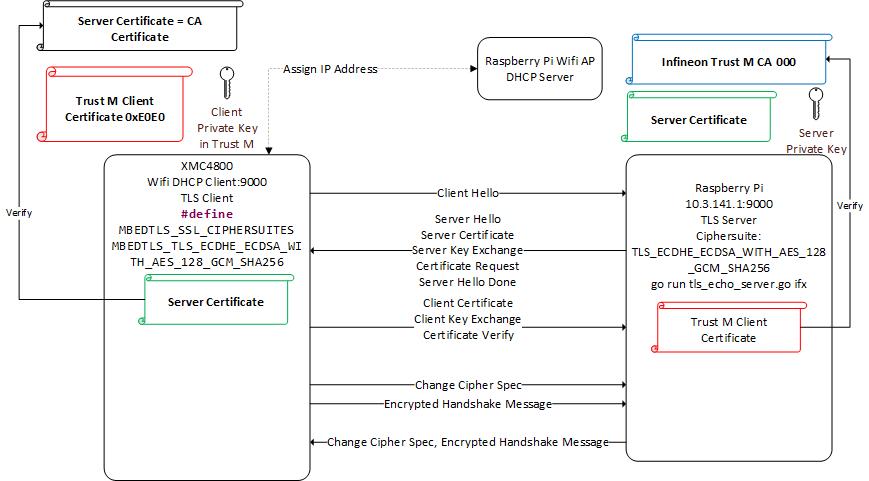
The purpose of this repository is to demonstrate XMC4800 together with OPTIGATM Trust M cryptographic IC operating as a TLS client. This demonstration requires a remote TLS server listening to an incoming TLS Client handshake request where Trust M which stores the secret key required for generating the digital signature.
TLS client can be configured with 3 different Wifi options for obtaining IP connectivity.
- Raspberry Pi operating as a Wifi hotspot.
- Using Wifi access point such as Wifi router.
- Android or iOS mobile phone with hotspot capability can be used to provide IP address to the TLS client.
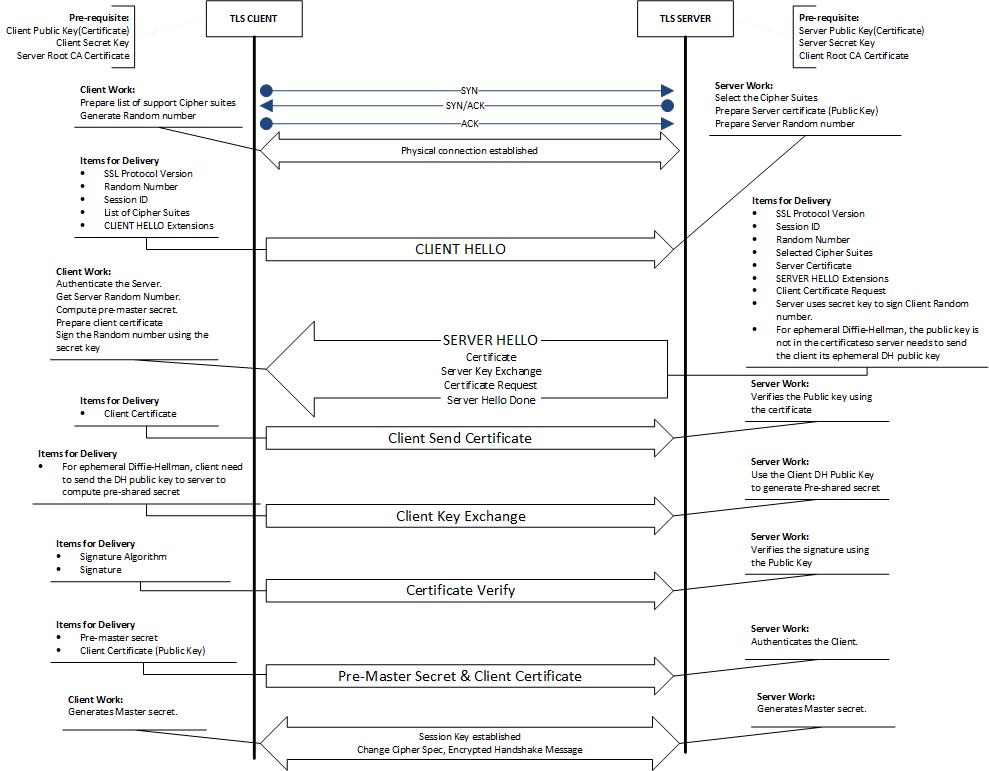
Summary of TLS client and sever establishing mutual authentication over TLS.
- Agreement on the protocol version to use.
- Select cryptographic algorithms.
- Authenticate each other by exchanging and validating digital certificates.
- Use asymmetric encryption techniques to generate a shared secret key. Data is encrypted using the shared key.
The TLS echo Server can runs any platform that supports the server scripting language. These platform can range from low-end system such as embedded system (Raspberry Pi) or remote server such as AWS EC2. Both TLS server options will be presented here.
In this configuration, a Raspberry Pi is used locally as TLS echo server. There are several possible IP assigning network configuration such as network router or mobile phone assigning IP. For this setup, the Raspberry Pi will operates as a DHCP server and assigning IP address to XMC 4800 IoT kit. After the sever is launched on the Raspberry Pi, the TLS server will wait and listen to port 9000.
- Download the latest Raspberry Pi image at https://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/raspbian/
- Following instruction here: https://www.raspberrypi.org/help/noobs-setup/2/
- Update Raspberry Pi with the latest update
$sudo apt-get update- Optional Install Wireshark
$sudo apt-get install wireshark- Install Go Programming
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/golang/go1.10.1.linux-armv6l.tar.gz
sudo tar -C /usr/local -xvf go1.10.1.linux-armv6l.tar.gz
cat >> ~/.bashrc << 'EOF'
export GOPATH=$HOME/go
export PATH=/usr/local/go/bin:$PATH:$GOPATH/bin
EOF
source ~/.bashrc- Check the that Go programming is installed correctly
go --version- Installing RaspAP RaspAP is a software package that allows Raspberry Pi to work as a local network Access Point(AP). This is also known as Wifi Hotspot.
Update Raspberry Pi with all the latest updates
$sudo apt-get update- Quick Installer guide with RaspAP The installer guide will ask several questions in the console installer. Press y for all.
wget -q https://git.io/voEUQ -O /tmp/raspap && bash /tmp/raspapQuestions from RaspAp installation scripts.
-
Complete installation with these values? [y/N]: y
-
Do you want to continue? [Y/n]
-
Enable HTTPOnly for session cookies (Recommended)? [Y/n]: Y
-
Enable PHP OPCache (Recommended)? [Y/n]: Y
-
Enable RaspAP control service(Recommended)? [Y/n]: Y
-
The system needs to be rebotted as a final step. Reboot now? [y/N]: y
-
Reboot the Raspberry Pi for all the software to take effect.
Connecting to RaspAP, first time
Using another computer, "raspi-webgui network" should be visible on the list of accessible networks.
Here are the default RaspAP Wifi connection settings:
SSID: raspi-webgui Secret: ChangeMe
Optional: Login to the application: Enter the URL below into your browser and login (credentials below as well)
IP address: 10.3.141.1
Username: admin
Password: secret-
Connecting to RaspAP Once you have connected to the device with the RaspAP default settings, you have changed (and noted down) the configuration. The next connections will be in your hands: your IP range, your SSID, your admin access etc.
-
Configuring Ethernet Modify the /etc/dhcpcd.conf and adds the following lines to add static IP address. This allows another host machine can debug the system.
interface eth0
static ip_address=10.1.1.30/24
static routers=10.1.1.1
static domain_name_servers=10.1.1.1- Running the TLS echo server
pi@raspberrypi:~/projects/tls3 $ go run tls_server.go ifx
2019/05/28 15:05:20 listen on localhost:9000When the TLS echo server is successfully launched, it will look as follows:
pi@raspberrypi:~/projects/tls_server_client $ go run tls_echo_server.go ifx
2019/06/16 00:15:08 Root CA: credential/Infineon_OPTIGA_TrustM_CA_101.pem
2019/06/16 00:15:08 Listening to port 9000- Expected output When the TLS client is running, this is the expected output from the server.
Expected Output:
pi@raspberrypi:~/projects/tls_server_client $ go run tls_echo_server.go ifx
2
2019/06/20 23:40:34 Root CA: credential/Infineon_OPTIGA_TrustM_CA_101.pem
2019/06/20 23:40:34 Listening to port 9000
2019/06/20 23:41:02 1: 10.3.141.1:9000 <-> 10.3.141.202:1531
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: T
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: Tx
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxR
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx m
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx me
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx mes
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx mess
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx messa
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx messag
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx message
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx message
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx message n
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx message nu
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx message num
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx message numb
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx message numbe
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx message number
2019/06/20 23:41:03 Echo Out: TxRx message number
...In this configuration, an AWS EC2 instance is used remotely as a TLS echo server. There are several possible IP assigning network configuration such as network router or mobile phone assigning IP. For this setup, a mobile phone Android or IOS device will operates as a DHCP server and assigning IP address to XMC 4800 IoT kit. After the sever is launched on the EC2 instance, the TLS server will wait and listen to port 9000.
Deploying AWS EC2 for TLS echo server with assumption that you already have the appropriate Amazon account and all required access rights.
- Create an EC2 instance.
- Choose an AMI (Amazon Machine Image). Choose “Amazon Linux AMI 2019.06.12 X86_64” . The exact versions may change with time. option is sufficient for the TLS server.
- Configure Instance Details. Left all option as default.
- Click on “Add Storage”. Left all options as default.
- In the "Add Tags", leaving it empty is fine.
- In the "Configure Security Group", enable TCP port 9000 for TLS server connection and set the source column to "Anywhere 0.0.0.0/0"
- Click on "Review And Launch" then "Launch".
- Select the appropriate keypair to be used for connection to the EC2 instance.
- In the instance page, set the instance to "running" and take note of the IP address. The IP Address needs to be programmed in the TLS client.
- Login to SSH and install Golang.
$sudo yum update -y
$sudo yum install -y golang- In the user profile "~/.bash_profile" file, configure the Go environment variables as follow.
# GOROOT is the location where Go package is installed on your system
export GOROOT=/usr/lib/golang
# GOPATH is the location of your work directory
export GOPATH=$HOME/projects
# PATH in order to access go binary system wide
export PATH=$PATH:$GOROOT/bin- Check that Go is operating by using the following commands.
$go version- FTP the TLS echo server files into the EC2 instance. You can do this either by means of FTP or install git on you instance and clone this repository.
- Launch the TLS server.
$go run tls_echo_server.go ifx- Expected output When the TLS client is running, this is the expected output from the server.
Expected Output:
[ec2-user@ip-172-31-26-254 tls_server_client]$ go run tls_echo_server.go ifx
2
2019/06/21 01:44:32 Root CA: credential/Infineon_OPTIGA_TrustM_CA_101.pem
2019/06/21 01:44:32 Listening to port 9000
2019/06/21 01:46:44 1: 172.31.26.254:9000 <-> 122.11.221.246:24852
2019/06/21 01:46:46 Echo Out: T
2019/06/21 01:46:46 Echo Out: Tx
2019/06/21 01:46:47 Echo Out: TxR
2019/06/21 01:46:47 Echo Out: TxRx
2019/06/21 01:46:47 Echo Out: TxRx
2019/06/21 01:46:47 Echo Out: TxRx m
2019/06/21 01:46:47 Echo Out: TxRx me
2019/06/21 01:46:48 Echo Out: TxRx mes
2019/06/21 01:46:48 Echo Out: TxRx mess
2019/06/21 01:46:48 Echo Out: TxRx messa
2019/06/21 01:46:48 Echo Out: TxRx messag
2019/06/21 01:46:49 Echo Out: TxRx message
2019/06/21 01:46:49 Echo Out: TxRx message
2019/06/21 01:46:49 Echo Out: TxRx message n
2019/06/21 01:46:49 Echo Out: TxRx message nu
2019/06/21 01:46:50 Echo Out: TxRx message num
2019/06/21 01:46:50 Echo Out: TxRx message numb
2019/06/21 01:46:50 Echo Out: TxRx message numbe
2019/06/21 01:46:50 Echo Out: TxRx message number
2019/06/21 01:46:50 Echo Out: TxRx message number
...In this configuration, an AWS EC2 instance is used remotely as a TLS echo server. There are several possible IP assigning network configuration such as network router or mobile phone assigning IP. For this setup, a mobile phone Android or IOS device will operates as a DHCP server and assigning IP address to XMC 4800 IoT kit. After the sever is launched on the EC2 instance, the TLS server will wait and listen to port 9000.
Deploying AWS EC2 for TLS server with assumption that you already have the appropriate Amazon account and all required access rights.
- Create an EC2 instance.
- Choose an Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Base. Choose “Microsoft Windows 2019 Datacenter edition [English]” . The exact versions may change with time.
- Configure Instance Details. Left all option as default.
- Click on “Add Storage”. Left all options as default.
- In the "Add Tags", leaving it empty is fine.
- In the "Configure Security Group", enable TCP port 9000 for TLS server connection and set the source column to "Anywhere 0.0.0.0/0"
- Click on "Review And Launch" then "Launch".
- Select the appropriate keypair to be used for connection to the EC2 instance.
- Enable Elastic IP address and tag to the instance for fixing the IP address. Note: This service is chargable.
- In the instance page, set the instance to "running" and take note of the IP address. The IP Address needs to be programmed in the TLS client.
- Launch Windows Remote Desktop Connection to connect to EC2 Windows instance.
- Provide the user name and password to login.
- Enable Windows Server incoming Firewall to enable TCP port 9000 which is used for this demo.
- For testing the availability of the EC2 server, optionally enable the Custom ICMP Rule - IPv4 which allows ping commands to be responded.
For the first time, install Go programming for windows https://golang.org/doc/install. Install Wireshark https://www.wireshark.org/#download for the Windows server.
Using the browser, download this GitHub contents on the EC2 instance. Using the command prompt, navigate and launch the Go program script and wait for TLS client connection.
This is a general description for cloud provider of your choice that supports elastic computing. Please check your cloud distribution support for elastic computing instance that supports GO programming language. Once the instance has been initialized, ensures that the TCP port 900 access has been granted on the cloud console. The instance firewall must be also be configured to allow TCP port access. In the instance page, once the instance is "running", take note of the IP address. The IP Address needs to be programmed in the TLS client.
The TLS client is implemented using the following Infineon MCU and development environment. Infineon - Infineon XMC4800 IoT Connectivity Kit * Getting Started Guide * Getting Started Guide for Hardware Security Add-On
Development IDE: * IDE: DAVE
Cloning this repository, which comes with the DAVE project environment. Import the project into your workspace. Configure the aws_clientcredential.h for the Wifi SSID and password. The Wifi SSID and password can be obtain from respective DHCP source.
Example:
/*
* Wi-Fi network to join.
*/
#define clientcredentialWIFI_SSID "MY_SSID"
/*
* Password needed to join Wi-Fi network.
*/
#define clientcredentialWIFI_PASSWORD "MY_PASSWORD"The TLS echo server address can be configured in config_files\FreeRTOSConfig.h For remote server address, this value can either be taken from EC2 console. For local server, this is the fixed local IP address of the TLS server.
/* The address of an echo server that will be used by the two demo echo client
* tasks:
* http://www.freertos.org/FreeRTOS-Plus/FreeRTOS_Plus_TCP/TCP_Echo_Clients.html,
* http://www.freertos.org/FreeRTOS-Plus/FreeRTOS_Plus_TCP/UDP_Echo_Clients.html. */
#define REMOTE_TLS_SERVER 1
#if (REMOTE_TLS_SERVER == 1)
//EC2 Instance IP address
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR0 35
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR1 164
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR2 96
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR3 35
#else
//RaspAP local AP
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR0 10
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR1 3
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR2 141
#define configECHO_SERVER_ADDR3 1
#endif
#define configTCP_ECHO_SECURE_CLIENT_PORT 9000
#define configTCP_ECHO_CLIENT_PORT 9001
There are 2 build options for Trust M TLS client. These build options can be selected using the DAVE Active configuration.
- Secret_Key_Store_In_Flash option.
- Secret_Key_Store_In_TrustM option.
When build using option 1, the secret key is stored in plain in the XMC4800 flash memory. This is an insecure implementation. This secret key can be found in aws_clientcredential_keys.h.
#define keyCLIENT_PRIVATE_KEY_PEM \
"-----BEGIN EC PRIVATE KEY-----\n"\
"MHcCAQEEIGCBtvwZmgDsq+NLz6jLseKUiHYBTlAdOilBPubkZ6AKoAoGCCqGSM49\n"\
"AwEHoUQDQgAEw86sjS4Ef7EUkHKUXnph0AnqH6IFau+ryBTMkWcS8ud7NO+4twEW\n"\
"paMiJTzhZXDbNF9eUt2DJGr0AuQIgqI60g==\n"\
"-----END EC PRIVATE KEY-----"
#endifUsing the option 2, the secret key is stored in Trust M which is a highly secure implementation. During the cryptographic operation, Trust M is used to perform ECC sign, ECC verify, ECDH Key generation and ECDH compute share secret.
Configure the FreeRTOSConfig.h for the server connectivity. The server must be running and listening to the respective TCP port. The TCP port should be opened and not blocked by any firewall.
Refer the key generation in make_ecc_cert.sh script.
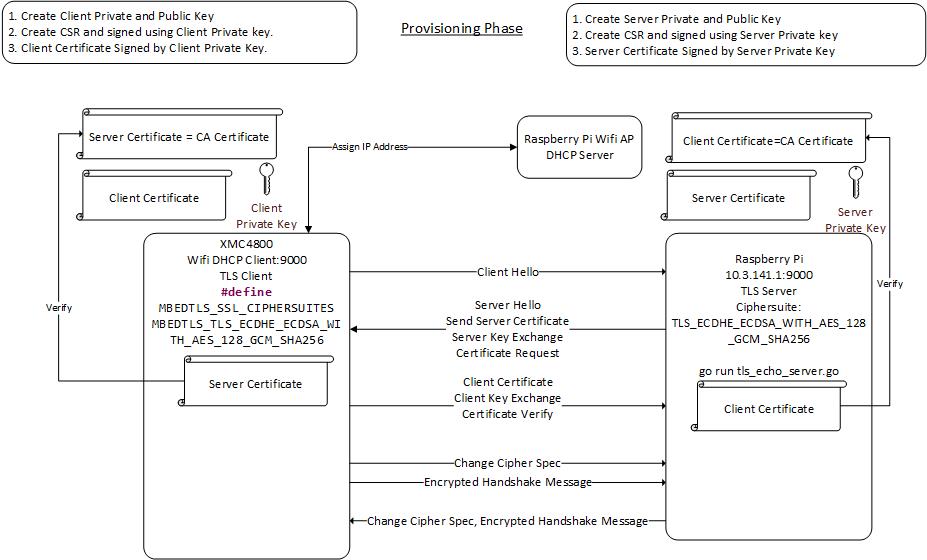
A set of Server Private and Public Key is created. The Server Public Key is signed using the Server Private key and generated as a Certificate. This can be created using the make_ecc_cert.sh script. The script also helps to generate client private key and certificate stored in flash. On the client side, a set of Client Private and Public Key is created. The Client Public Key is signed using the Client Private key and generated as a Certificate. The Server Certificate is served as a Server CA certificate and placed in the Client (XMC4800 IoT kit). The Client Certificate is served as a Client CA certificate and placed in TLS server.
As the CA Certificate (essentially a Public Key) is the same key pair of the private key, verification will certain pass if done correctly.
#!/bin/bash
#Create the credential folder is not exists
if [ ! -d credential ]; then
mkdir -p credential;
fi
echo "Make TLS Server cert"
echo "Create server public and secret key"
openssl ecparam -genkey -name prime256v1 -out credential/server.secretkey.pem
echo "Create CSR using server private key"
openssl req -new -key credential/server.secretkey.pem -out credential/server.csr.pem -subj "/C=SG/ST=Singapore/L=Singapore/O=Infineon Technologies/OU=DSS/CN=TLS_Server"
echo "Create a PEM (Base64 encoded ASCII) format server certificate signed by CA"
openssl x509 -req -in credential/server.csr.pem -set_serial 0x88888888888888888888888888888888 -signkey credential/server.secretkey.pem -out credential/server.cert.pem
echo "Display the server certificate"
openssl x509 -noout -text -in credential/server.cert.pem
echo "Make TLS client cert"
openssl ecparam -genkey -name prime256v1 -out credential/client.secretkey.pem
echo "Create CSR using client private key"
openssl req -new -key credential/client.secretkey.pem -out credential/client.csr.pem -subj "/C=SG/ST=Singapore/L=Singapore/O=Infineon Technologies/OU=DSS/CN=TLS_Client"
echo "Create a PEM (Base64 encoded ASCII) format client certificate"
openssl x509 -req -in credential/client.csr.pem -set_serial 0x77777777777777777777777777777777 -signkey credential/client.secretkey.pem -out credential/client.cert.pem
echo "Display the client certificate"
openssl x509 -noout -text -in credential/client.cert.pemAdd the server CA certificate PEM in aws_tcp_echo_client_single_task.c
static const char cTlsECHO_SERVER_CERTIFICATE_PEM[] =
"-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\n"
"MIIB6TCCAY4CEQCIiIiIiIiIiIiIiIiIiIiIMAoGCCqGSM49BAMCMHgxCzAJBgNV\n"
"BAYTAlNHMRIwEAYDVQQIDAlTaW5nYXBvcmUxEjAQBgNVBAcMCVNpbmdhcG9yZTEe\n"
"MBwGA1UECgwVSW5maW5lb24gVGVjaG5vbG9naWVzMQwwCgYDVQQLDANEU1MxEzAR\n"
"BgNVBAMMClRMU19TZXJ2ZXIwHhcNMTkwNzE1MDIzNTI0WhcNMjkwNzEyMDIzNTI0\n"
"WjB4MQswCQYDVQQGEwJTRzESMBAGA1UECAwJU2luZ2Fwb3JlMRIwEAYDVQQHDAlT\n"
"aW5nYXBvcmUxHjAcBgNVBAoMFUluZmluZW9uIFRlY2hub2xvZ2llczEMMAoGA1UE\n"
"CwwDRFNTMRMwEQYDVQQDDApUTFNfU2VydmVyMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0D\n"
"AQcDQgAE0jLl4KdE8eJGdV9RzI9+kzkUIt5dZq8JyOLhzxyOCMLo0GZ6zDs8nkno\n"
"Gmt1RX7aj7nqp0/rfODnFdZQVPEwnTAKBggqhkjOPQQDAgNJADBGAiEAucb4OgdZ\n"
"ubMiQwCiKkOTJKxir4ZUoRbP/Bb40YQ13FYCIQCx/Y5VPNyeL+P+IcQH+g2Dkc5p\n"
"30ByOlKA2QXAfzUYoA==\n"
"-----END CERTIFICATE-----\n";Build and execute the Trust M software in DAVE. Connect up the USB and open up the serial terminal.
This script creates a self-signed server and client certificates. Note: Using the script below generates certificate valid for 30 days only.
For more information on Amazon FreeRTOS, refer to the Getting Started section of Amazon FreeRTOS webpage.
Infineon generates the first manufacturer key pair in 0xE0E0 and 0xE0F0 in the Infineon factory. This key pair can also be used for mutual authentication during the TLS handshaking.
The s_server command can be used to implement a generic SSL/TLS server that listens for connections on a given port using SSL/TLS. It can be used for TLS client testing.
openssl s_server -accept 9000 -key credential/server.secretkey.pem -cert credential/server.cert.pem -CAfile credential/Infineon_OPTIGA_TrustM_CA_101.pem -Verify 1There is a small overhead when using additional hardware security device. This is due to I2C and some additional cryptographic library. An effective method of comparing or deriving the additional overhead is to deploy the exact operation both in hardware and software implementation. For the purpose of this comparison, the edge device hardware, operating system and type of server connectivity are kept constant. The only difference is the implementation of credential exchange and establishment using hardware or software method.
In the software Mbedtls method, the secret key is stored in flash and it is visible in plaintext in the source code. Secret key is exposed to anyone who has access to the source code. On the other hand hardware MbedTLS method stores the secret key in Trust M. There is no risk of secret key exposure.
Important: Functionality of the source code has only been tested in none optimized compilation only.
Example output from DAVE 4.4.2 compilation result using none(-O0) compilation option. Secret key in flash implementation: "C:/Users/limtsesi/Desktop/DAVE_4-4-2_64bit_2018-02-23/DAVE-IDE-4.4.2-64Bit/eclipse/ARM-GCC-49/bin/arm-none-eabi-size" --format=berkeley -t "aws_demos_trustm.elf" text data bss dec hex filename 228472 600 177716 406788 63504 aws_demos_trustm.elf 228472 600 177716 406788 63504 (TOTALS) 'Finished building: aws_demos_trustm.siz'
Secret key in Trust M implementation: "C:/Users/limtsesi/Desktop/DAVE_4-4-2_64bit_2018-02-23/DAVE-IDE-4.4.2-64Bit/eclipse/ARM-GCC-49/bin/arm-none-eabi-size" --format=berkeley -t "aws_demos_trustm.elf" text data bss dec hex filename 260788 1912 180112 442812 6c1bc aws_demos_trustm.elf 260788 1912 180112 442812 6c1bc (TOTALS) 'Finished building: aws_demos_trustm.siz'
| Options | Flash | TrustM | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| None(-O0) | 228472 | 260788 | 32316 |
| Optimize(-01) | 149376 | 169292 | 19916 |
| Optimize more(-02) | 149140 | 168360 | 19220 |
| Optimize most(-03) | 182532 | 205664 | 23132 |
| Optimize size(-0s) | 135836 | 153120 | 17284 |
| Optimize for debug(-0g) | 148816 | 169300 | 20484 |
In the most size optimized option, the difference between hardware and software implementation is about 17KB.
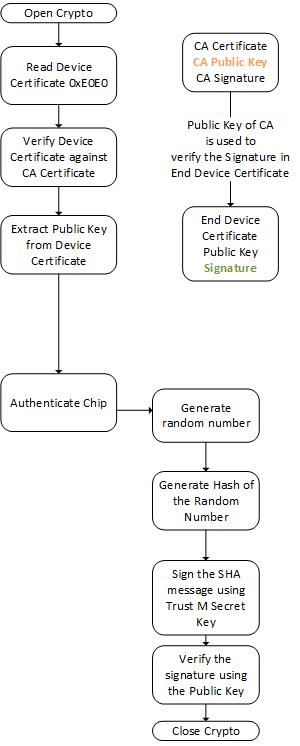
Trust M comes with a device certificate pre-programmed in OID location 0xE0E0. This end device certificate is generated using the Infineon CA private key. The Infineon CA private key is stored in Infineon secure facility. The corresponding public key in CA certificate is provided as part of the evaluation kit and in this case can be used to check if the end device certificate is valid. An example of the end device certificate
In this captured log message.
openssl verify -CAfile .\RootCA.pem -untrusted .\Infineon_OPTIGA_TrustM_CA_101.pem .\TrustM_device_certificate.pem
where RootCA.pem is Trust M ECC CA certificate, Infineon_OPTIGA_TrustM_CA_101.pem is the intermediate CA certificate and TrustM_device_certificate.pem is a certificate stored in Trust M.
Trust M end device certificate is dumped out in hex over the I2C bus. It is converted from DER to PEM format and it is later used to verify against the Root CA.
In the TLS handshaking, the Infineon Intermediate CA acts as the Server CA (a.k.a Server Trust Anchor). During the Client certificate exchange, the 0xE0E0 device certificate will be read out and transmitted to the server. The server will verify it using the Server CA.
Since each Trust M is pre-programmed at Infineon factory, it is very easy to deploy Trust M in the field. The server will need to be populated with the Server CA and there is no change on server and client software.
Note: Every Trust M has a unique end device certificate.
During the launching of the TLS server, client will setup the Root CA used for verification as shown in the code snippet in tls_echo_server.go.
//Setup client trust anchor
if arg=="ifx"{
sRootCA = "credential/Infineon_OPTIGA_TrustM_CA_101.pem"
}else{
sRootCA="credential/client.cert.pem"
}There are several software configurations using macro options in aws_tcp_echo_client_single_task.c which allows Trust M functional testing. These functional tests can be used to check Trust M operational behavior, basic usability as well as error conditions.
There are various global loop counters which allows repeatability of the tests. By default, each test will execute only once.
int TRUSTM_UID_LOOP_COUNT =1;
int TRUSTM_AUTH_LOOP_COUNT=1;
int TRUSTM_UNIT_TEST_LOOP_COUNT=1;In this test case, Trust M UID will be dumped out. Set the macro READ_UID_TEST value to "1" in order to turn on the Read UID test.
In this test case, Trust M secret key will be used to generate a signature. The signature can be verified using the public key.
Set the macro AUTH_TEST value to "1" in order to turn on the Authentication test.
In this group of standalone test cases, each function performs a unique test function.
Set the macro EXAMPLE_UNIT_TESTS to "1" to turn on the appropriate unit test cases.
example_optiga_crypt_ecc_generate_keypair();
example_optiga_crypt_ecdsa_sign();
example_optiga_crypt_ecdsa_verify();
example_optiga_crypt_hash();
example_optiga_crypt_random();
example_optiga_crypt_rsa_encrypt_message();
example_optiga_crypt_rsa_generate_keypair();
example_optiga_crypt_rsa_sign();
example_optiga_crypt_rsa_verify();
example_optiga_util_protected_update();
example_optiga_util_read_data();
example_optiga_util_update_count();
example_optiga_util_write_data();
example_optiga_crypt_tls_prf_sha256();
example_optiga_crypt_ecdh();
example_optiga_crypt_rsa_encrypt_session();
example_optiga_crypt_rsa_decrypt_and_export();