This code example demonstrates the implementation of a Bluetooth LE Perodic ADV Sync functionality using AIROC™ CYW20829B0/CYW89829.
- ModusToolbox™ software v3.2 or later (tested with v3.2)
- Board support package (BSP) minimum required version for :
- CYW920829M2EVK-02 : v2.0.0
- CYW989829M2EVB-01 : v2.0.0
- CYW989829M2EVB-03 : v2.0.0
- Programming language: C
- Associated parts: AIROC™ CYW20829 Bluetooth® LE SoC
- GNU Arm® embedded compiler v10.3.1 (
GCC_ARM) - Default value ofTOOLCHAIN
- AIROC™ CYW20829 Bluetooth® LE evaluation kit (
CYW920829M2EVK-02) - AIROC™ CYW89829 Bluetooth® LE Evaluation Kit (
CYW989829M2EVB-01,CYW989829M2EVB-03)
This example uses the board's default configuration. See the kit user guide to ensure that the board is configured correctly.
The AIROC™ CYW20829 Bluetooth® kit (CYW920829M2EVK-02) ships with KitProg3 version 2.21 installed. The ModusToolbox™ software requires KitProg3 with latest version 2.40. Before using this code example, make sure that the board is upgraded to KitProg3. The tool and instructions are available in the Firmware Loader GitHub repository. If you do not upgrade, you will see an error such as "unable to find CMSIS-DAP device" or "KitProg firmware is out of date".
Install a terminal emulator if you don't have one. Instructions in this document use Tera Term.
BTSpy
ClientControl
Sync to BLE Device Address: 20829B012233
Extened BLE SCAN Parameters: Passive Scan, 60ms interval, 60ms window(Once synced with peer adv, the extened ble scan will stop)
The ModusToolbox™ tools package provides the Project Creator as both a GUI tool and a command line tool.
Use Project Creator GUI
-
Open the Project Creator GUI tool.
There are several ways to do this, including launching it from the dashboard or from inside the Eclipse IDE. For more details, see the Project Creator user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/tools_{version}/project-creator/docs/project-creator.pdf).
-
On the Choose Board Support Package (BSP) page, select a kit supported by this code example. See Supported kits.
Note: To use this code example for a kit not listed here, you may need to update the source files. If the kit does not have the required resources, the application may not work.
-
On the Select Application page:
a. Select the Applications(s) Root Path and the Target IDE.
Note: Depending on how you open the Project Creator tool, these fields may be pre-selected for you.
b. Select this code example from the list by enabling its check box.
Note: You can narrow the list of displayed examples by typing in the filter box.
c. (Optional) Change the suggested New Application Name and New BSP Name.
d. Click Create to complete the application creation process.
Use Project Creator CLI
The 'project-creator-cli' tool can be used to create applications from a CLI terminal or from within batch files or shell scripts. This tool is available in the {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/tools_{version}/project-creator/ directory.
Use a CLI terminal to invoke the 'project-creator-cli' tool. On Windows, use the command-line 'modus-shell' program provided in the ModusToolbox™ installation instead of a standard Windows command-line application. This shell provides access to all ModusToolbox™ tools. You can access it by typing "modus-shell" in the search box in the Windows menu. In Linux and macOS, you can use any terminal application.
The following example clones the "le-periodic-sync" application with the desired name "MyLEPeriodicSync" configured for the CYW989829M2EVB-01 BSP into the specified working directory, C:/mtb_projects:
project-creator-cli --board-id CYW989829M2EVB-01 --app-id mtb-example-btstack-freertos-le-periodic-sync --user-app-name MyLEPeriodicSync --target-dir "C:/mtb_projects"
The 'project-creator-cli' tool has the following arguments:
| Argument | Description | Required/optional |
|---|---|---|
--board-id |
Defined in the field of the BSP manifest | Required |
--app-id |
Defined in the field of the CE manifest | Required |
--target-dir |
Specify the directory in which the application is to be created if you prefer not to use the default current working directory | Optional |
--user-app-name |
Specify the name of the application if you prefer to have a name other than the example's default name | Optional |
Note: The project-creator-cli tool uses the
git cloneandmake getlibscommands to fetch the repository and import the required libraries. For details, see the "Project creator tools" section of the ModusToolbox™ tools package user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mtb_user_guide.pdf).
After the project has been created, you can open it in your preferred development environment.
Eclipse IDE
If you opened the Project Creator tool from the included Eclipse IDE, the project will open in Eclipse automatically.
For more details, see the Eclipse IDE for ModusToolbox™ user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mt_ide_user_guide.pdf).
Visual Studio (VS) Code
Launch VS Code manually, and then open the generated {project-name}.code-workspace file located in the project directory.
For more details, see the Visual Studio Code for ModusToolbox™ user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mt_vscode_user_guide.pdf).
Keil µVision
Double-click the generated {project-name}.cprj file to launch the Keil µVision IDE.
For more details, see the Keil µVision for ModusToolbox™ user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mt_uvision_user_guide.pdf).
IAR Embedded Workbench
Open IAR Embedded Workbench manually, and create a new project. Then select the generated {project-name}.ipcf file located in the project directory.
For more details, see the IAR Embedded Workbench for ModusToolbox™ user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mt_iar_user_guide.pdf).
Command line
If you prefer to use the CLI, open the appropriate terminal, and navigate to the project directory. On Windows, use the command-line 'modus-shell' program; on Linux and macOS, you can use any terminal application. From there, you can run various make commands.
For more details, see the ModusToolbox™ tools package user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mtb_user_guide.pdf).
-
Connect the board to your PC using the provided USB cable through the KitProg3 USB connector.
-
Use your favorite serial terminal application tool and connect to the KitProg3 COM port. Configure the terminal application to access the serial port using the following settings:
Baud rate: 115200 bps; Data: 8 bits; Parity: None; stop: 1 bit; Flow control: None; New line for receiving data: Line Feed(LF) or auto setting
-
Program the board using one of the following:
Using Eclipse IDE for ModusToolbox™ software
-
Select the application project in Project Explorer.
-
In the Quick Panel, scroll down, and click <Application Name> Program (KitProg3_MiniProg4).
Using CLI
From the terminal, execute the
make programcommand to build and program the application using the default toolchain to the default target. The default toolchain and target are specified in the application's Makefile but you can override those values manually:make program TARGET=<BSP> TOOLCHAIN=<toolchain>Example:
make program TARGET=CYW920829M2EVK-02 TOOLCHAIN=GCC_ARM BRD=2 -
-
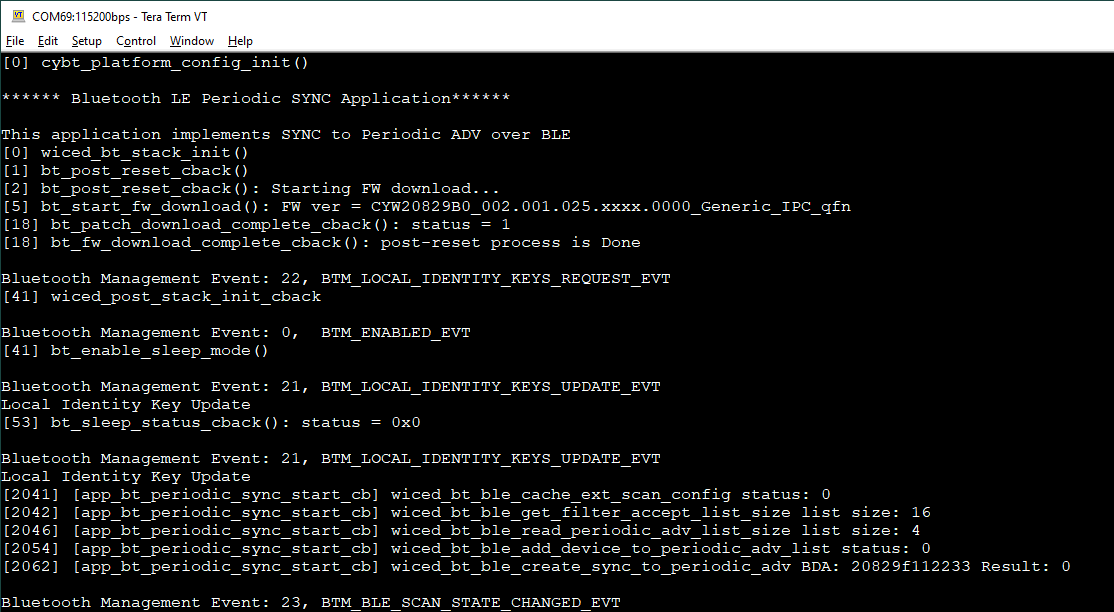
After programming, the application starts automatically. Observe the messages on the UART terminal, and wait for the device to sync with the peer advertiser (le-periodic-adv). Use the KitProg3 COM port to view the Bluetooth® stack and application trace messages in the terminal window:
Figure 1. Log messages on KitProg3 COM port
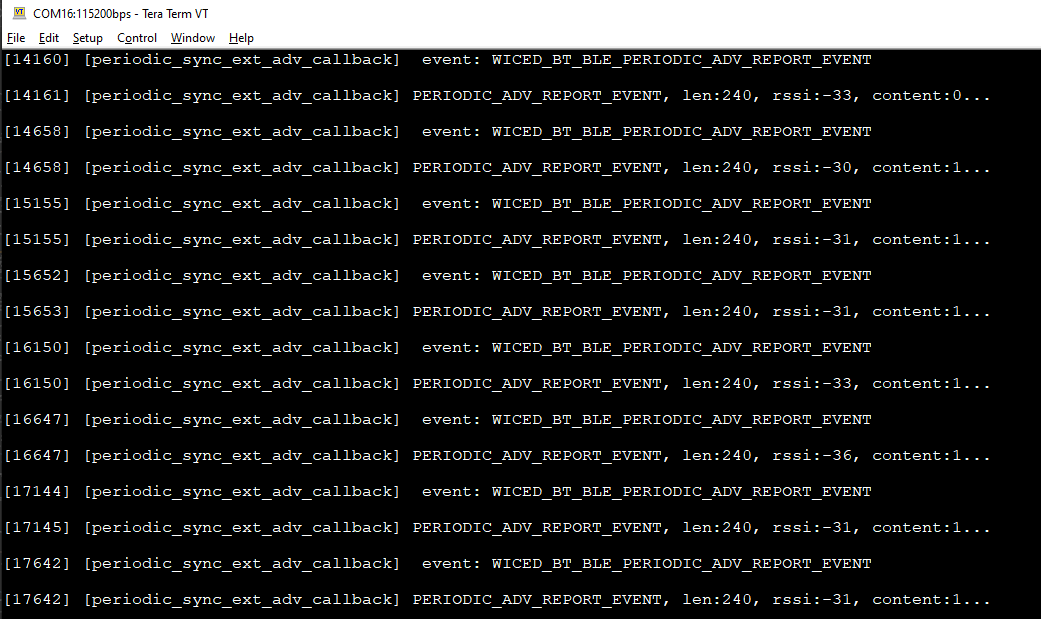
Sync device prints the same fakedata for 10 times with an interval of 500msec.
Figure 2. Sync side receive the peer periodic advertisement data log message
-
Connect the board to your machine.
-
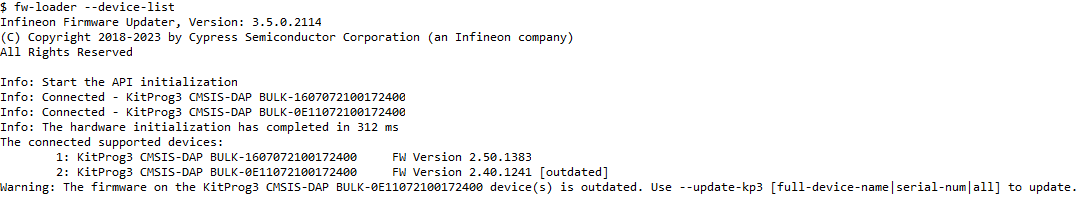
Go to {ModusToolbox™ software install directory}/tools_{version}/fw-loader/bin and open the command prompt.
-
Run the following command:
fw-loader.exe --device-list -
On the text that appears, locate the following message starting with
Connected supported devices:. -
Note the 16-digit number that is listed. This is the serial number of the board.
In this example,
0B0B03B803260400is the serial number for the board. -
Copy and pass the got serial number to _MTB_RECIPE_OPENOCD_CUSTOM_COMMAND+=adapter serial
0B0B03B803260400; in the makefile for board 2.
-
Go to your application and open the Makefile.
-
Add the following to the Makefile (in the "Advanced Configuration" section):
CY_OPENOCD_CUSTOM_COMMAND += cmsis_dap_serial <SERIAL_NUMBER>;Note: Ensure that a semicolon is added at the end of the line as shown above.
You can program the board using the make program command from the ModusToolbox™ terminal.
On Eclipse IDE for ModusToolbox™ software, you need to edit the 'Program' configurations to bind them with a specific CMSIS-DAP serial number. See the following sections of the ModusToolbox™ user guide:
- 5.1.6 "Select specific CMSIS-DAP device"
- 5.1.6.2 "Selecting by serial number"
-
Select Run > Debug Configurations, and then select GDB OpenOCD Debugging on the Create, manage, and run configurations window.
-
Select "Bluetooth_LE_Long_Range_Peripheral Program (KitProg3_MiniProg4)".
-
On the right pane, select the Debugger tab.
-
In Config options, insert the following line after
-c "source [find interface/kitprog3.cfg]":-c "cmsis_dap_serial <serial_num_1>" -
Select Apply and Debug for the change to take effect.
-
Similar to Step 2, select "Bluetooth_LE_Long_Range_Central Program (KitProg3_MiniProg4)".
-
On the right pane, select the Debugger tab.
-
In Config options, insert the following line after
-c "source [find interface/kitprog3.cfg]":-c "cmsis_dap_serial <serial_num_2>" -
Click Apply and Debug for the change to take effect.
Note: This feature is available only for CYW920829M2EVK-02.
-
Navigate to the application Makefile and open it. Find the Makefile variable
ENABLE_SPY_TRACESand set it to the value 1 as shown:ENABLE_SPY_TRACES = 1 -
Save the Makefile, and then build and program the application to the board.
-
Open the ClientControl application and make the following settings:
- Set the baud rate to 3000000.
- Deselect the flow control checkbox.
- Select the serial port and click on an open port.
-
Launch the BTSpy tool.
-
Press and release the reset button on the board to get the BTSpy logs on the BTSpy tool.
You can debug the example to step through the code. In the IDE, use the <Application Name> Debug (KitProg3_MiniProg4) configuration in the Quick Panel. For more details, see the "Program and debug" section in the Eclipse IDE for ModusToolbox™ software user guide.
Note: When connected multiple boards on the same PC, it needs to modify the cmsis_dap_serial <SERIAL_NUMBER> into the debug settings for the ModusToolbox™ software.
Document title: CE238425 – AIROC™: Bluetooth® Low Energy Periodic Sync
| Version | Description of change |
|---|---|
| 1.0.0 | New code example |
| 1.1.0 | Added support for CYW989829M2EVB-01 |
| 2.0.0 | Added support for CYW989829M2EVB-03, BSP and BTStack-integration major update for BT Firmware as a separate asset |
All referenced product or service names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
The Bluetooth® word mark and logos are registered trademarks owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc., and any use of such marks by Infineon is under license.
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2020-2024. This document is the property of Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, an Infineon Technologies company, and its affiliates ("Cypress"). This document, including any software or firmware included or referenced in this document ("Software"), is owned by Cypress under the intellectual property laws and treaties of the United States and other countries worldwide. Cypress reserves all rights under such laws and treaties and does not, except as specifically stated in this paragraph, grant any license under its patents, copyrights, trademarks, or other intellectual property rights. If the Software is not accompanied by a license agreement and you do not otherwise have a written agreement with Cypress governing the use of the Software, then Cypress hereby grants you a personal, non-exclusive, nontransferable license (without the right to sublicense) (1) under its copyright rights in the Software (a) for Software provided in source code form, to modify and reproduce the Software solely for use with Cypress hardware products, only internally within your organization, and (b) to distribute the Software in binary code form externally to end users (either directly or indirectly through resellers and distributors), solely for use on Cypress hardware product units, and (2) under those claims of Cypress’s patents that are infringed by the Software (as provided by Cypress, unmodified) to make, use, distribute, and import the Software solely for use with Cypress hardware products. Any other use, reproduction, modification, translation, or compilation of the Software is prohibited.
TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, CYPRESS MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARD TO THIS DOCUMENT OR ANY SOFTWARE OR ACCOMPANYING HARDWARE, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. No computing device can be absolutely secure. Therefore, despite security measures implemented in Cypress hardware or software products, Cypress shall have no liability arising out of any security breach, such as unauthorized access to or use of a Cypress product. CYPRESS DOES NOT REPRESENT, WARRANT, OR GUARANTEE THAT CYPRESS PRODUCTS, OR SYSTEMS CREATED USING CYPRESS PRODUCTS, WILL BE FREE FROM CORRUPTION, ATTACK, VIRUSES, INTERFERENCE, HACKING, DATA LOSS OR THEFT, OR OTHER SECURITY INTRUSION (collectively, "Security Breach"). Cypress disclaims any liability relating to any Security Breach, and you shall and hereby do release Cypress from any claim, damage, or other liability arising from any Security Breach. In addition, the products described in these materials may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. To the extent permitted by applicable law, Cypress reserves the right to make changes to this document without further notice. Cypress does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit described in this document. Any information provided in this document, including any sample design information or programming code, is provided only for reference purposes. It is the responsibility of the user of this document to properly design, program, and test the functionality and safety of any application made of this information and any resulting product. "High-Risk Device" means any device or system whose failure could cause personal injury, death, or property damage. Examples of High-Risk Devices are weapons, nuclear installations, surgical implants, and other medical devices. "Critical Component" means any component of a High-Risk Device whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause, directly or indirectly, the failure of the High-Risk Device, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. Cypress is not liable, in whole or in part, and you shall and hereby do release Cypress from any claim, damage, or other liability arising from any use of a Cypress product as a Critical Component in a High-Risk Device. You shall indemnify and hold Cypress, including its affiliates, and its directors, officers, employees, agents, distributors, and assigns harmless from and against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, arising out of any claim, including claims for product liability, personal injury or death, or property damage arising from any use of a Cypress product as a Critical Component in a High-Risk Device. Cypress products are not intended or authorized for use as a Critical Component in any High-Risk Device except to the limited extent that (i) Cypress’s published data sheet for the product explicitly states Cypress has qualified the product for use in a specific High-Risk Device, or (ii) Cypress has given you advance written authorization to use the product as a Critical Component in the specific High-Risk Device and you have signed a separate indemnification agreement.
Cypress, the Cypress logo, and combinations thereof, WICED, ModusToolbox, PSoC, CapSense, EZ-USB, F-RAM, and Traveo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cypress or a subsidiary of Cypress in the United States or in other countries. For a more complete list of Cypress trademarks, visit www.infineon.com. Other names and brands may be claimed as property of their respective owners.