First Contributions
Read this in other languages: English, Spanish
If you don't have git on your machine, install it
Fork this repo by clicking on the fork button
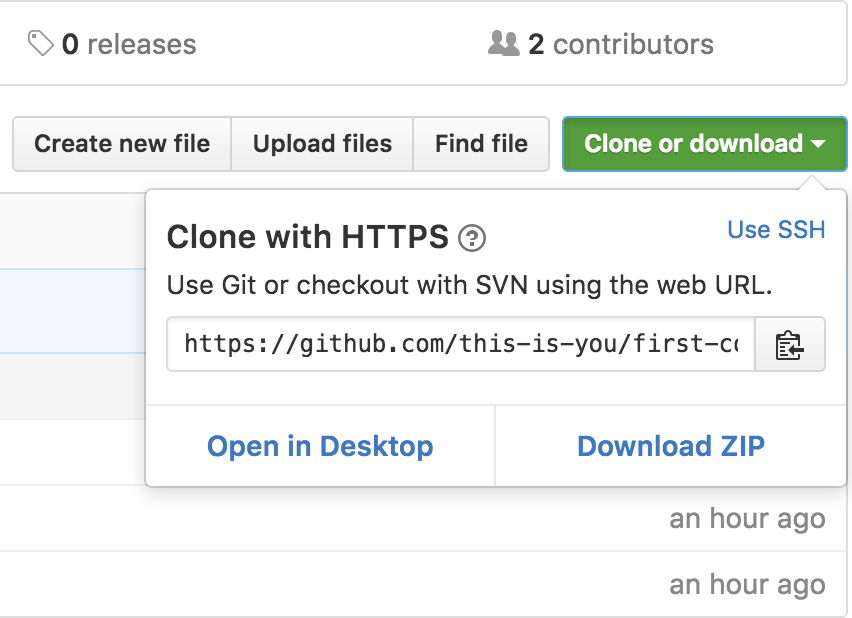
Now clone this repo to your machine. Click on clone button and then copy to clipboard icon
Open a terminal and run
git clone <url you just copied>
Where the url can be pasted from clipboard For example
git clone https://github.com/this-is-you/first-contributions.git
Here you're copying the contents of first-contributions repository in github to your computer
Go in to that directory
cd first-contributions
Now create a branch using git checkout command
git checkout -b <add-your-name>
For example
git checkout -b add-alonzo-church
Now open Contributors.md file in a text editor and add your name to it, save the file
If you go to the project directory and do git status, you'll see there are changes
Add those change using git add
git add Contributors.md
Now commit those changes using git commit
git commit -m "Add <your-name> to Contributors list"
replace <your-name> with your name
Push your changes using git push
git push origin <add-your-name>
Replace <add-your-name> with the name of the branch you created earlier
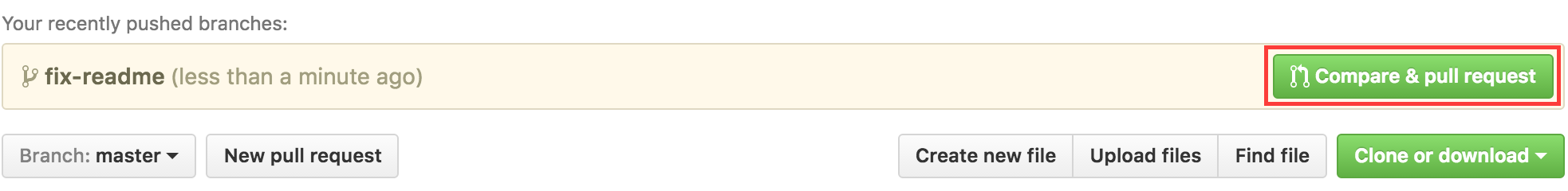
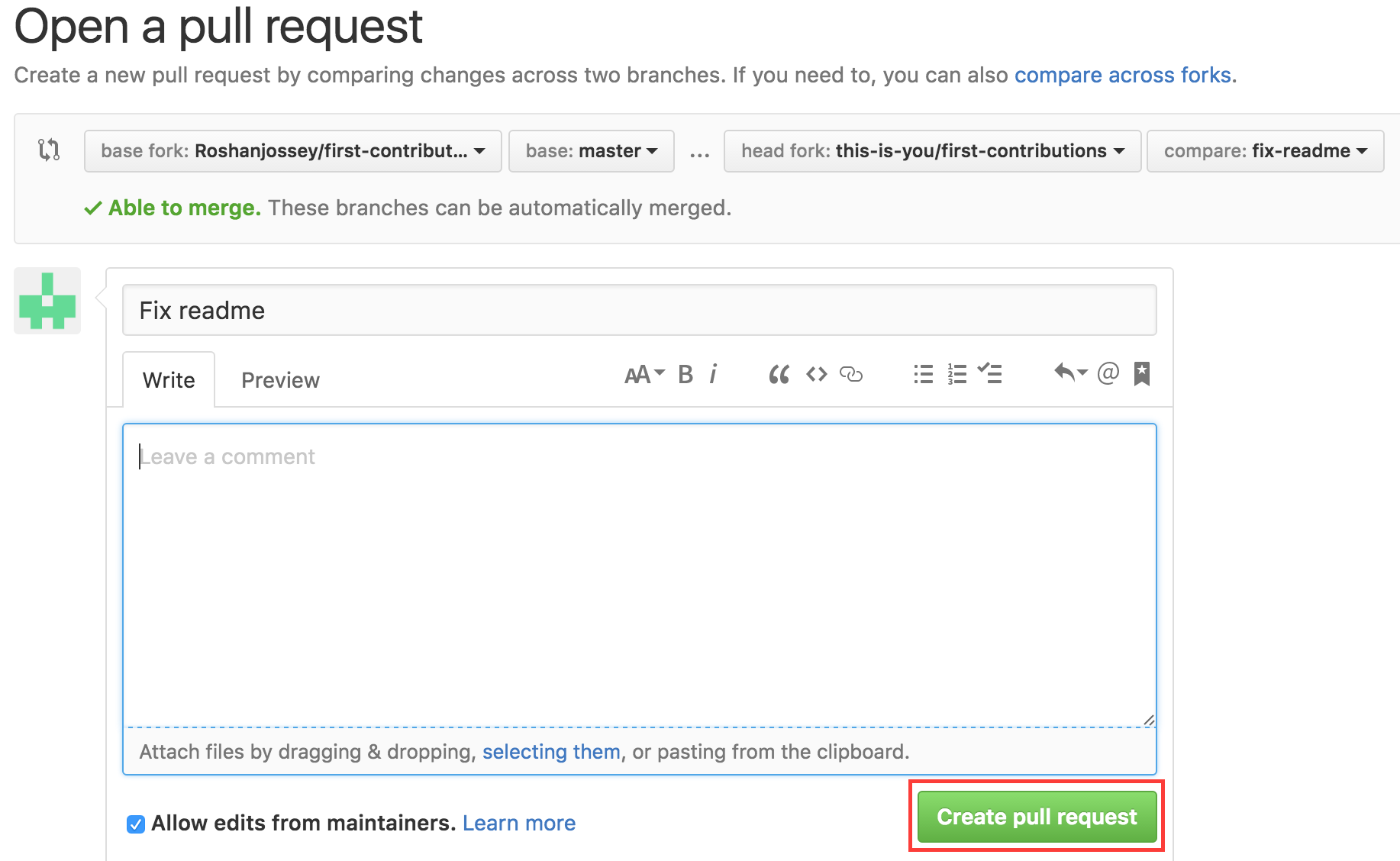
If you go to your repo on github, you'll see a button to open a pull request. click on that button
Now submit the pull request
Keeping your fork synced with this repo
Now I'll be merging all your changes in to master branch of this project. Then your fork won't have those changes. In order to keep your fork synced with mine,
Add my repo's url as upstream remote url
git remote add upstream https://github.com/Roshanjossey/first-contributions
This is a way of telling git that another version of this project exists in the specified url and we're calling it master.
git fetch upstream
Here we're fetching all the changes in my fork (upstream remote)
git rebase upstream/master
Here you're applying all the changes you fetched to master branch. If you push master branch now, your fork will also have the changes
git push origin master
Notice here you're pushing to the remote named origin