
Pointcept is a powerful and flexible codebase for point cloud perception research. It is also an official implementation of the following paper:
-
Masked Scene Contrast: A Scalable Framework for Unsupervised 3D Representation Learning
Xiaoyang Wu, Xin Wen, Xihui Liu, Hengshuang Zhao
IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2023
[ Pretrain ] [ MSC ] - [ arXiv ] [ Bib ] → soon -
Understanding Imbalanced Semantic Segmentation Through Neural Collapse (3D Part)
Zhisheng Zhong*, Jiequan Cui*, Yibo Yang*, Xiaoyang Wu, Xiaojuan Qi, Xiangyu Zhang, Jiaya Jia
IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2023
[ SemSeg ] [ CeCo ] - [ arXiv ] [ Bib ] [ 2D Part ] → soon -
Learning Context-aware Classifier for Semantic Segmentation (3D Part)
Zhuotao Tian, Jiequan Cui, Li Jiang, Xiaojuan Qi, Xin Lai, Yixin Chen, Shu Liu, Jiaya Jia
AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2023 - Oral
[ SemSeg ] [ CAC ] - [ arXiv ] [ Bib ] [ 2D Part ] → soon -
Point Transformer V2: Grouped Vector Attention and Partition-based Pooling
Xiaoyang Wu, Yixing Lao, Li Jiang, Xihui Liu, Hengshuang Zhao
Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) 2022
[ Backbone ] [ PTv2 ] - [ arXiv ] [ Bib ] → [here]( -
Point Transformer
Hengshuang Zhao, Li Jiang, Jiaya Jia, Philip Torr, Vladlen Koltun
IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 2021 - Oral
[ Backbone ] [ PTv1 ] - [ arXiv ] [ Bib ] → [here](
Additionally, Pointcept integrates the following excellent work: MinkUNet, SpUNet, Stratified Transformer, Mix3d, PointContrast, ContrastiveSceneContexts, and supports the following datasets: ScanNet, ScanNet200, S3DIS, ArkitScene, Semantic KITTI, ModelNet40.
-
Mar, 2023: We released our codebase, Pointcept. Pointcept is a highly potent tool, as evidenced by its ability to significantly augment the baseline performance of SpUnet on the ScanNet validation set, resulting in an impressive mIoU score of 75.0%. Moreover, its remarkable flexibility is manifested through its expertly designed framework, which seamlessly facilitates the integration of cutting-edge methods. We welcome new work to join the Pointcept family and highly recommend reading [Quick Start](
-
Feb, 2023: MSC and CeCo accepted by CVPR 2023. MSC is a highly efficient and effective pretraining framework that facilitates cross-dataset large-scale pretraining, while CeCo is a segmentation method specifically designed for long-tail datasets. Both approaches are compatible with all existing backbone models in our codebase, and we will soon make the code available for public use.
-
Jan, 2023: CAC, oral work of AAAI 2023, has expanded its 3D result with the incorporation of Pointcept. This addition will allow CAC to serve as a pluggable segmentor within our codebase.
-
Sep, 2022: PTv2 accepted by NeurIPS 2022. It is a continuation of the Point Transformer. The proposed GVA theory can apply to most existing attention mechanisms, while Grid Pooling is also a practical addition to existing pooling methods.
-
[Installation](
-
[Data Preparation](
-
[Quick Start](
-
[Model Zoo](
-
[Citation](
-
[Acknowledgement](
-
Ubuntu: 18.04 or higher
-
CUDA: 11.3 or higher
-
PyTorch: 1.10.0 or higher
conda create -n SRX net python=3.8 -y
conda activate SRX net
conda install ninja -y
conda install pytorch==1.12.1 torchvision==0.13.1 torchaudio==0.12.1 cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch -y
conda install h5py pyyaml -c anaconda -y
conda install sharedarray tensorboard tensorboardx yapf addict einops scipy plyfile termcolor timm -c conda-forge -y
conda install pytorch-cluster pytorch-scatter pytorch-sparse -c pyg -y
pip install torch-geometric
pip install spconv-cu113
cd libs/pointops
python setup.py install
TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST="ARCH LIST" python setup.py install
TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST="7.5 8.0" python setup.py install
cd ../..pip install open3d
pip install ftfy regex tqdm
pip install git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git
pip install torch-points3d
pip uninstall SharedArray
pip install SharedArray==3.2.1
cd libs/pointops2
python setup.py install
cd ../..
conda install google-sparsehash -c bioconda
export C_INCLUDE_PATH=${CONDA_PREFIX}/include:$C_INCLUDE_PATH
export CPLUS_INCLUDE_PATH=${CONDA_PREFIX}/include:CPLUS_INCLUDE_PATH
pip install --upgrade git+https://github.com/mit-han-lab/torchsparse.git
conda install -c bioconda google-sparsehash
cd libs/pointgroup_ops
python setup.py build_ext --include-dirs=YOUR_ENV_PATH/include
python setup.py install
cd ../..The preprocessing support semantic and instance segmentation for both ScanNet20, ScanNet200 and ScanNet Data Efficient.
- Download the ScanNet v2 dataset.
- Run preprocessing code for raw ScanNet as follows:
python SRX net/datasets/preprocessing/scannet/preprocess_scannet.py --dataset_root ${RAW_SCANNET_DIR} --output_root ${PROCESSED_SCANNET_DIR}- (Optional) Download ScanNet Data Efficient files:
python download-scannet.py --data_efficient -o ${RAW_SCANNET_DIR}
cd ${RAW_SCANNET_DIR}/tasks
unzip limited-annotation-points.zip
unzip limited-bboxes.zip
unzip limited-reconstruction-scenes.zip
cp -r ${RAW_SCANNET_DIR}/tasks ${PROCESSED_SCANNET_DIR}- Link processed dataset to codebase:
mkdir data
ln -s ${RAW_SCANNET_DIR} ${CODEBASE_DIR}/data/scannet- Download S3DIS data by filling this Google form. Download the
Stanford3dDataset_v1.2.zipfile and unzip it. - Run preprocessing code for S3DIS as follows:
python SRX net/datasets/preprocessing/s3dis/preprocess_s3dis.py --dataset_root ${S3DIS_DIR} --output_root ${PROCESSED_S3DIS_DIR}
python SRX net/datasets/preprocessing/s3dis/preprocess_s3dis.py --dataset_root ${S3DIS_DIR} --output_root ${PROCESSED_S3DIS_DIR} --align_angle
python SRX net/datasets/preprocessing/s3dis/preprocess_s3dis.py --dataset_root ${S3DIS_DIR} --output_root ${PROCESSED_S3DIS_DIR} --raw_root ${RAW_S3DIS_DIR} --parse_normal
python SRX net/datasets/preprocessing/s3dis/preprocess_s3dis.py --dataset_root ${S3DIS_DIR} --output_root ${PROCESSED_S3DIS_DIR} --raw_root ${RAW_S3DIS_DIR} --align_angle --parse_normal
- Link processed dataset to codebase.
mkdir data
ln -s ${RAW_S3DIS_DIR} ${CODEBASE_DIR}/data/s3dis- Download [Semantic KITTI](http://www.semantic-kitti.org/dataset.html
- Link dataset to codebase.
mkdir -p data
ln -s ${SEMANTIC_KITTI_DIR} ${CODEBASE_DIR}/data/semantic_kitti- Download modelnet40_normal_resampled.zip and unzip
- Link dataset to codebase.
mkdir -p data
ln -s ${MODELNET_DIR} ${CODEBASE_DIR}/data/modelnet40_normal_resampledTrain from scratch. The training processing is based on configs in configs folder.
The training script will generate an experiment folder in exp folder and backup essential code in the experiment folder.
Training config, log, tensorboard and checkpoints will also be saved into the experiment folder during the training process.
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=${CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES}
sh scripts/train.sh -p ${INTERPRETER_PATH} -g ${NUM_GPU} -d ${DATASET_NAME} -c ${CONFIG_NAME} -n ${EXP_NAME}
export PYTHONPATH=./
python tools/train.py --config-file ${CONFIG_PATH} --num-gpus ${NUM_GPU} --options save_path=${SAVE_PATH}For example:
sh scripts/train.sh -p python -d scannet -c semseg-ptv2m2-0-base -n semseg-ptv2m2-0-base
export PYTHONPATH=./
python tools/train.py --config-file configs/scannet/semseg-pt-v2m2-0-base.py --options save_path=exp/scannet/semseg-ptv2m2-0-baseResume training from checkpoint. If the training process is interrupted by accident, the following script can resume training from a given checkpoint.
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=${CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES}
sh scripts/train.sh -p ${INTERPRETER_PATH} -g ${NUM_GPU} -d ${DATASET_NAME} -c ${CONFIG_NAME} -n ${EXP_NAME} -r true
export PYTHONPATH=./
python tools/train.py --config-file ${CONFIG_PATH} --num-gpus ${NUM_GPU} --options save_path=${SAVE_PATH} resume=True weight=${CHECKPOINT_PATH}The validation during training only evaluate model on point clouds after grid sampling (voxelization) and testing is needed to achieve a precise evaluation result. Our testing code support TTA (test time augmentation) testing. (Currently only support testing on a single GPU, I might add support to multi-gpus testing in the future version.)
sh scripts/test.sh -p ${INTERPRETER_PATH} -d ${DATASET_NAME} -n ${EXP_NAME} -w ${CHECKPOINT_NAME}
export PYTHONPATH=./
python tools/test.py --config-file ${CONFIG_PATH} --options save_path=${SAVE_PATH} weight=${CHECKPOINT_PATH}For example:
sh scripts/test.sh -p python -d scannet -n semseg-ptv2m2-0-base -w model_best
export PYTHONPATH=./
python tools/test.py --config-file configs/scannet/semseg-pt-v2m2-0-base.py --options save_path=exp/scannet/semseg-ptv2m2-0-base weight=exp/scannet/semseg-ptv2m2-0-base/models/model_best.pthOffset is the separator of point clouds in batch data, and it is similar to the concept of Batch in PyG.
A visual illustration of batch and offset is as follows:
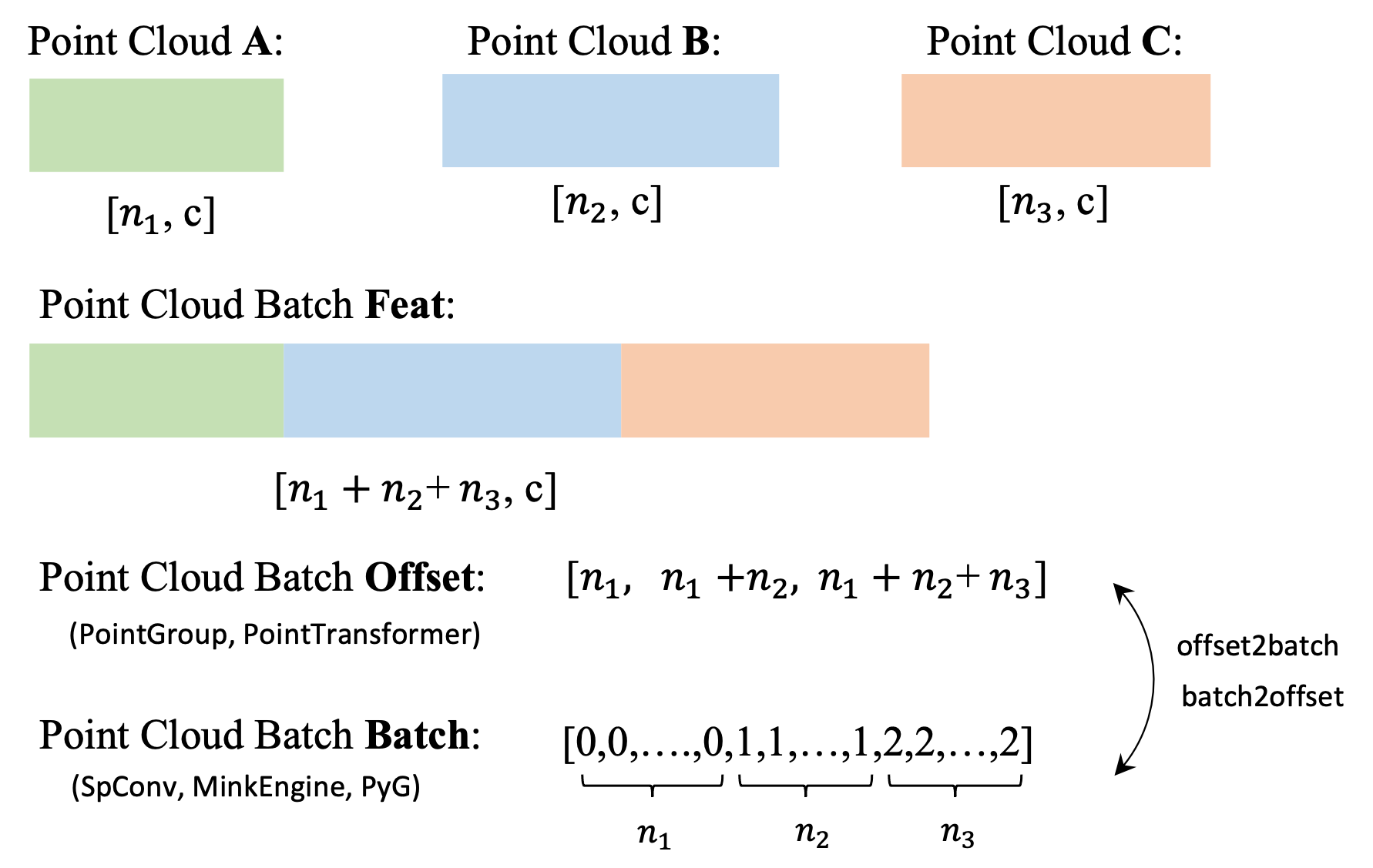
Pointcept provides SparseUNet implemented by SpConv and MinkowskiEngine. The SpConv version is recommended since SpConv is easy to install and faster than MinkowskiEngine. Meanwhile, SpConv is also widely applied in outdoor perception.
- SpConv (recommend)
The SpConv version SparseUNet in the codebase was fully rewrite from Li Jiang's code, example running script is as follows:
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-base -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet200 -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-base -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d s3dis -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-base -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d s3dis -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-cn-base -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-cn-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 2 -d semantic-kitti -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-base -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 2 -d modelnet40 -c cls-spunet-v1m1-0-base -n cls-spunet-v1m1-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-la20 -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-la20
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-la50 -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-la50
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-la100 -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-la100
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-la200 -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-la200
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-lr1 -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-lr1
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-lr5 -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-lr5
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-lr10 -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-lr10
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-lr20 -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-2-efficient-lr20
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-enable-profiler -n semseg-spunet-v1m1-0-enable-profiler- MinkowskiEngine
The MinkowskiEngine version SparseUNet in the codebase was modified from original MinkowskiEngine repo, and example running script is as follows:
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-minkunet34c-0-base -n semseg-minkunet34c-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet200 -c semseg-minkunet34c-0-base -n semseg-minkunet34c-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d s3dis -c semseg-minkunet34c-0-base -n semseg-minkunet34c-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 2 -d semantic-kitti -c semseg-minkunet34c-0-base -n semseg-minkunet34c-0-base- PTv2 mode2 (recommend)
The original PTv2 was trained on 4 * RTX a6000 (48G memory). Even enabling AMP, the memory cost of the original PTv2 is slightly larger than 24G. Considering GPUs with 24G memory are much more accessible, I tuned the PTv2 on the latest Pointcept and made it runnable on 4 * RTX 3090 machines.
PTv2 Mode2 enables AMP and disables Position Encoding Multiplier & Grouped Linear. During our further research, we found that precise coordinates are not necessary for point cloud understanding (Replacing precise coordinates with grid coordinates doesn't influence the performance. Also, SparseUNet is an example). As for Grouped Linear, my implementation of Grouped Linear seems to cost more memory than the Linear layer provided by PyTorch. Benefiting from the codebase and better parameter tuning, we also relieve the overfitting problem. The reproducing performance is even better than the results reported in our paper.
Example running script is as follows:
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-pt-v2m2-0-base -n semseg-pt-v2m2-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-pt-v2m2-1-benchmark-submit -n semseg-pt-v2m2-1-benchmark-submit
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet200 -c semseg-pt-v2m2-0-base -n semseg-pt-v2m2-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d s3dis -c semseg-pt-v2m2-0-base -n semseg-pt-v2m2-0-base- PTv2 mode1
PTv2 mode1 is the original PTv2 we reported in our paper, example running script is as follows:
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-pt-v2m1-0-base -n semseg-pt-v2m1-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet200 -c semseg-pt-v2m1-0-base -n semseg-pt-v2m1-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d s3dis -c semseg-pt-v2m1-0-base -n semseg-pt-v2m1-0-base- PTv1
The original PTv1 is also available in our Pointcept codebase. I haven't run PTv1 for a long time, but I have ensured that the example running script works well.
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-pt-v1-0-base -n semseg-pt-v1-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet200 -c semseg-pt-v1-0-base -n semseg-pt-v1-0-base
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d s3dis -c semseg-pt-v1-0-base -n semseg-pt-v1-0-base- Uncomment `
- Refer Optional Installation to install dependence.
- Training with the following example running scripts:
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-st-v1m2-0-refined -n semseg-st-v1m2-0-refined
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet -c semseg-st-v1m1-0-origin -n semseg-st-v1m1-0-origin
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d scannet200 -c semseg-st-v1m2-0-refined -n semseg-st-v1m2-0-refined
sh scripts/train.sh -g 4 -d s3dis -c semseg-st-v1m2-0-refined -n semseg-st-v1m2-0-refinedI did not tune the parameters for Stratified Transformer and just ensured it could run.
SPVCNN is baseline model of SPVNAS, it is also a practical baseline for outdoor dataset.
sh scripts/train.sh -g 2 -d semantic-kitti -c semseg-spvcnn-v1m1-0-base -n semseg-spvcnn-v1m1-0-baseIf you find Pointcept useful to your research, please cite our work:
@misc{pointcept2023,
title={Pointcept: A Codebase for Point Cloud Perception Research},
author={Pointcept Contributors},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/Pointcept/Pointcept}},
year={2023}
}
Pointcept is designed by Xiaoyang, named by Yixing and the logo is created by Yuechen. It is derived from Hengshuang's Semseg and inspirited by several repos, e.g., MinkowskiEngine, pointnet2, mmcv, and Detectron2.