Tip
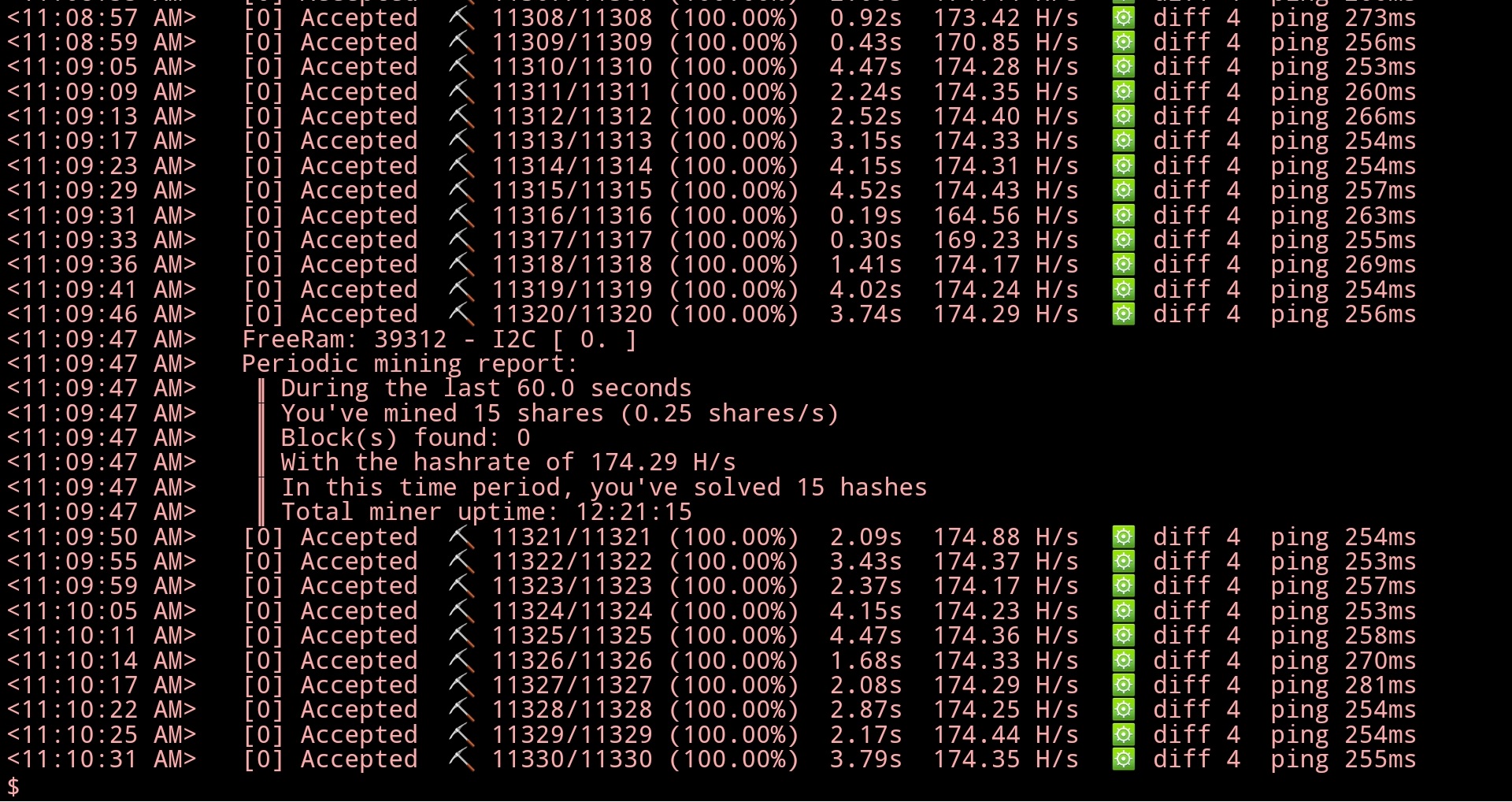
Get WARP SPEED mining firmware from DuinoI2C_ESP! Using 10 workers as benchmark. 0.82 shares/s (This DuinoCoinI2C) vs. 6 shares/s (That DuinoI2C_ESP). It is 732% faster!
This project design to mine Duino-Coin using an Esp8266/Esp32 as a master and Arduino as a slave.
Using the I2C communication to connect all the boards and make a scalable communication between the master and the slaves.
Visit youtube for video of How to Make the DuinoCoinI2C Mining Rig
Watch Programming ESP-01 video
DuinoCoinI2C Version 4.3
All Slaves have the same code and should select the I2C Address automatically if #define I2CS_FIND_ADDR is set to true
Arduino shall use DuinoCoin_RPI_Tiny_Slave sketch
RP2040 support dual core dual I2C. Dual core is counted as 2 workers
RP2040 shall use DuinoCoin_RPI_Pico_DualCore
Set the value below to 8 and false in the ESP and RP2040 sketch
// ESP
#define REPEATED_WIRE_SEND_COUNT 8 // 1 for AVR, 8 for RP2040
// RP2040
#define CRC8_EN falseATTiny85 is tested to be working. You may try other ATTiny chip (modification maybe needed)
ATTiny shall use DuinoCoin_ATTiny_Slave
- ArduinoUniqueID (Handle the chip ID)
- StreamJoin (StreamString for AVR)
The I2C Address on the Arduino is automatically updated when the board starts, if an Address already exists on the I2C bus the code finds another Address to use (with I2CS_FIND_ADDR enabled).
However, depending on vendor, some cloned Arduino have a pretty bad random number generator. It causes it to either wait too long or clashes with each other during address assignment. So this feature is strongly NOT RECOMMENDED
Instead use manual address assignment, change the value on the define for each device (RECOMMENDED)
#define DEV_INDEX 0 // increment 1 per device
#define I2CS_START_ADDRESS 1The master requests the job on the DuinoCoin server and sends the work to the slave (Arduino).
After the job is done, the slave sends back the response to the master (Esp8266/Esp32) and then sends back to the DuinoCoin server.
- ArduinoJson (Request Pool Version 2.6)
- ESPAsyncWebServer (ESPAsyncWebServer)
- ESPAsyncTCP (ESP8266)
- AsyncTCP (ESP32)
The code supports 10 clients and can be changed on the define:
#define CLIENTS 10
Note: Community reported share rate will not improve beyond 5 slaves
Optional. AsyncWebServer allow user to get Master status, print pool info or force switch to specific pool.
Connect to the Master via local IP address. Example address: 192.168.0.2
| Link | Description |
|---|---|
| http://192.168.0.2/ | show Serial monitor |
| http://192.168.0.2/heap | show free memory |
| http://192.168.0.2/clients | show connected slaves |
| http://192.168.0.2/printPool | print Pool address and port |
| http://192.168.0.2/updatePool | force refresh pool address |
| http://192.168.0.2/set?host=123.123.123.123&port=123 | force pool address to 123.123.123.123 and port to 123 |
| http://192.168.0.2/printMOTD | print pool message |
Optional. AsyncWebServer allow user to get periodic mining report via any Internet browser. e.g. Chrome/Firefox/Safari/etc
Upload data folder by using corresponding data upload tool
https://github.com/esp8266/arduino-esp8266fs-plugin
https://github.com/me-no-dev/arduino-esp32fs-plugin
Connect to the Master via local IP address. Example address: 192.168.0.2
Change reporting interval by modifying #define REPORT_INTERVAL 60000
Connect the pins of the Esp01, Esp8266 or Esp32 on the Arduino like the table/images below, use a Logic Level Converter to connect between the ESP and Arduino.
| ESP8266 | ESP32 | Logic Level Converter | Arduino | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3V | 3.3V | <---> | 5V | |
| GND | GND | <---> | GND | |
SCL |
D1 (GPIO5) | GPIO22 | <---> | A5 |
SDA |
D2 (GPIO4) | GPIO21 | <---> | A4 |
ESP01
| ESP01 | Logic Level Converter | Arduino | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3V | <---> | 5V | |
| GND | <---> | GND | |
SCL |
GPIO2 | <---> | A5 |
SDA |
GPIO0 | <---> | A4 |
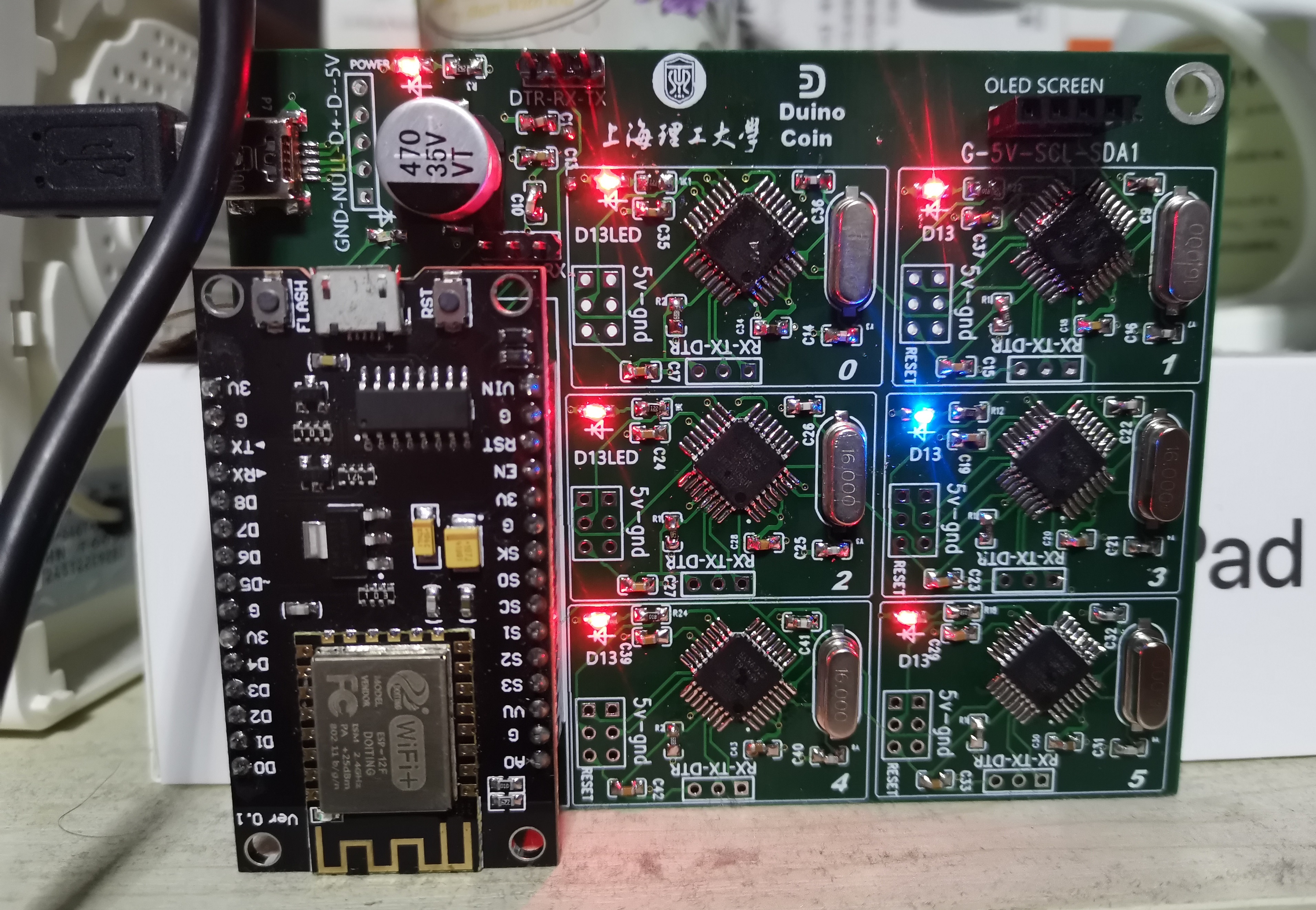
ericddm shared this amazing pcb!
Do you like this project? Please star this project on GitHub!