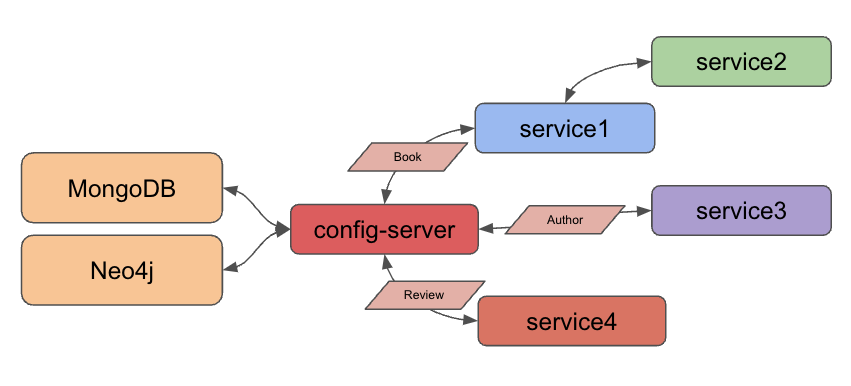
In this installment of the project, we are implementing Spring Cloud Config for all services that connect to a database. Service1 and service3 connect to MongoDB for book and author data, and service4 connects to Neo4j for book review data.
This project is part of a series for creating microservices. In this repository, we use the following technologies:
-
Spring Boot
-
Java
-
REST services
-
Lombok
-
Spring Data
-
MongoDB document database
-
loaded with Book/Author domain data
-
-
Docker and docker compose
-
Neo4j AuraDB free tier
-
load with Book/Author/Review domain data
-
-
Spring Cloud Config
For the domain, we loaded a publicly-available UCSD Book Graph dataset that provides books and related information.
We have 4 services in this repository: service1, service2, service3, and service4. Responsibilities of each service are outlined below, followed by the changes to execution.
-
Service1: backend service hosting the REST api for book data (MongoDB)
-
Service2: client REST service for calling service1 and returning books
-
Service3: backend service hosting the REST api for author data (MongoDB)
-
Service4: backend service hosting the REST api for review data (Neo4j)
Services 1, 2, and 3 have been packaged into Docker containers, and we are using Docker Compose to run and manage the services together. With all services running in Docker containers, there were a few configuration changes needed, but the applications can communicate and pass data as before. Service4 is currently run locally, but will be containerized and added to our Docker Compose setup later.
We also have a few supporting folders explained below.
-
Config-server: application code to set up the config server for service1, service3, and service4 to reference for MongoDB or Neo4j database credentials
-
Data-neo4j: folder that includes steps and script for loading data set on books, authors, and reviews to Neo4j.
-
Docker-mongodb: folder containing steps and data for starting and loading books and authors data to MongoDB Docker container.
-
Microservices-java-config: holds sample YAML files containing MongoDB or Neo4j database credentials.
Note: Notes how to use the config yaml file are in the readme that folder.
There are a variety of reasons businesses and users might choose to develop applications in a microservices architecture. Some potential reasons are listed below.
-
Scalability
-
Functionality independence (separating grouped features, often for reliability)
-
Maintenance simplicity (changes only affect pieces, and less likely to impact whole)
-
Shift resource load (from large instance running single monolith application, to many smaller instances hosting/coordinating microservices)
To reproduce the Docker compose portion of this example, please follow the steps.
-
Clone this repository
-
Build each service’s (1, 2, and 3) Docker container (note: if not on arm64 silicon chip, will need to update image names in compose file, as well).
-
Execute Docker compose with
docker-compose up -d. -
Test backing service (books): Open a command line window and execute
curl localhost:8081/db/books. -
Test client service: Open a command line window and execute
curl localhost:8080/goodreads/books. -
Test backing service (authors): Open a command line window and execute
curl localhost:8082/db/authors. -
See the results of books or authors appear :)
Separately, we can test the config service and related services with additional steps.
-
Create a free Neo4j AuraDB instance.
-
Load the data using the steps in the
data-neo4jfolder. -
Start the config-server project from an IDE or command line.
-
Test the config server: Open a command line window and execute
curl localhost:8888/neo4j-client/defaultorcurl localhost:8888/mongo-client/default. -
Start the
service1application from an IDE or command line. -
Test backing service (books): Open a command line window and execute
curl localhost:8081/db/books. -
Start the
service3application from an IDE or command line. -
Test backing service (authors): Open a command line window and execute
curl localhost:8082/db/authors. -
Start the
service4application from an IDE or command line. -
Test review backing service: Open a command line window and execute
curl localhost:8083/neo/reviewsorcurl localhost:8083/neo/reviews/178186. -
See the results of reviews appear :)
== Content
-
Blog post: Microservices Level 8
-
-
Level1 - Sending a string message from one Spring Boot app to another
-
Level2 - Retrieving prepopulated Book data from one Spring Boot app to another
-
Level3 - Storing Book data in MongoDB and retrieving all stored books
-
Level4 - Adding new service for author data
-
Level5 - Adding Docker compose to manage services as containers
-
Level6 - Adding new service for review data (in Neo4j)
-
Level7 - Adding Spring Cloud Config for Neo4j database credentials