A terminal program that uses DRNN to detect the wake word "activate" from input audio stream. The program was written in Keras with TensorFlow backend and trained on Google Colab T4 GPU. I used FFmpeg to format the audio files.
See resources for the blogs and code fragments that assisted me in making this project. In the model directory, general_model.h5 was trained on 4000 audio samples from speakers with varied accents and tones. However, maybe it's due to my accent or weird background noises, the general model was not accurate enough for me. Therefore, I recorded, formatted, and synthesized my own training data and further trained the general model for my own use. The end result my_model.h5 was deployed with real_time_detection.py and I evaluated qualitatively and quantitatively. Check out the video below for qualitative demo and the performance section for quantitative measures.
Watch the Result (not cherry picked)
All audio files are in 16 bit mono wav format. Directory input/sample_raw_input contains folders positive (audios of "activate"), negative (audios of not "activate"), and background (background audios). In preprocess_data.ipynb, I randomly selected positive/negative samples and layered them onto the background files to synthesize training samples.
I recorded ~15 audio files of myself saying "activate" and ~50 audio files of myself saying some common English words. For the background files, I got them off from here. I performed the same preprocessing operations on them and formatted the audio files with the FFmpeg software. With the pipeline in preprocess_data.ipynb, I synthesized 360 training samples and 90 test samples.
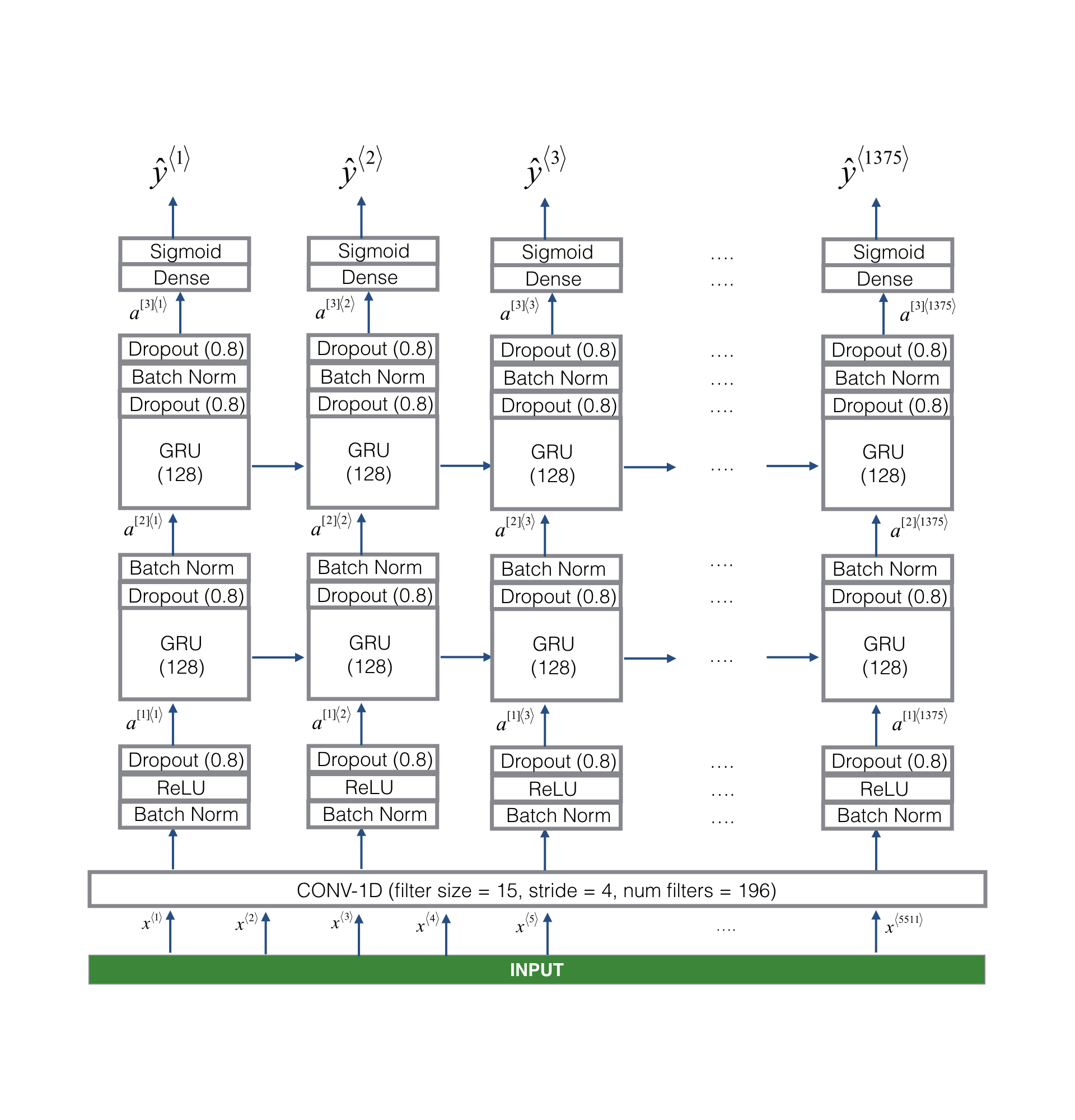
The model first encodes 5511 timesteps of audio into 1375 timesteps for low-level feature extraction and reducing the amount of data for later layers, this step is critical for running real-time audio detection on limited computing power. Then,the processed timesteps are fed into 2 uni-directional (online detection) GRU layers for extracting high-level audio features and infer whether the wake word has been detected. Lastly, the GRU outputs are connected with a time distributed dense layer and signmoid for the classification.
Note: batch normalization was used after each layer (both conv and GRU). I also heavily used dropout layers (0.8) to combat overfitting.
As mentioned on the top of this file, the general model did not perform well for me. No matter what threshold I use, the program did not feel robust if I ever want to actually employ it. Therefore, I recorded my own datasets and used my own training data to further train the general model. Finally, I evaluated both models with my custome F1 score function (since Keras took it away for some reason) on my own test data. As expected, general_model.h5 achieved an average of ~0.28 and my_model.h5 achieved ~0.85. Needless to say, my own model worked very well for myself (demo).
Requirements in info/requirements.txt.
- Make 3 directories called positives, negatives, and backgrounds
- Record a number of audio files for each
- Format all audios to 16 bits mono wav files with FFmpeg (or any websites)
- Zip all directories together and synthesize the audio files with
preprocess_data.ipynb
Follow the code/comments in wake_word_detection.ipynb for training your own model.
Since this project is a terminal program, simply run python real-time-detection.py (all command line inputs have default values). Read the file's argparse (top of file) to use a different model, change audio stream time, etc.
README.md - self measure_surrounding.py - script for logging and averaging the volume of surrounding preprocess_data.ipynb - colab notebook for playing with audio files and producing data (audio synthesis) wake_word_detection.ipynb - colab notebook for building model, training model and comparing model performances real-time-detection.py - script for trying out the model through terminal (audio stream) assets - images and videos for this markdown info - contains the model summary and requirements for running this program input - contains input sample data and my own data output - the mp4 file of my video demo model - contains the trained general model and further trained model for myself
- pydub
- CS230 slides
- Blog on trigger word recognition
- Coursera sequence models specialization (the skeleton code for this project)
- Background wav files