Jupyter Notebook Open Custom Jupyter Notebook container implementation that doesn't have any authentication
Official Jupyter Notebook: Used for Jupyter Notebook Microservice
SonarQube: Used to Build SonarQube and SonarScanner Microservice
Flask: Used to Build Driver Program
Must be on machine with kubectl configured to manage a valid existing Kubernetes cluster
Must have kube_setup/ directory from this repository copied onto the machine
Must have all of the images listed under the "Links to Deployed Docker Images" section accessible by the machine's Docker Container registry. If this program is running on GCP, this would entail pulling each of the images from the links, tagging them by adding the prefix gcr.io/<project-name>/ to the names of the images, and then pushing these containerized images using an authenticated instance of the GCloud SDK.
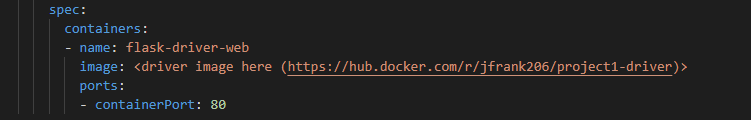
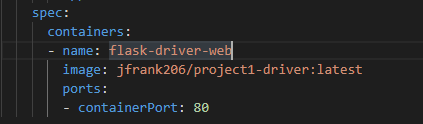
Once all of the images are in the registry, the yaml files located in the kube_setup/init_kube_objects/ directory must be configured to point to these images. Within this repository, these yaml files currently have where the images need to be defined marked with the docker hub link of the image that needs to be defined there. If these yaml files aren't properly configured, the setup of the necessary Kubernetes deployments will fail. For example, in kube_setup/init_kube_objects/flask-driver.yaml, you would need to change:
To something like this:
These changes need to occur in all of the Yaml files within the kube_setup/init_kube_objects/ directory except for kube_setup/init_kube_objects/kube-auth.yaml wherever the image: field appears within the files.
If this service is being run on the cloud, the firewall must be configured to allow incoming traffic on TCP ports 30001, 30002, 30003, 30004, and 30006. To make a rule for allowing traffic on these ports for GCP, run the following command:
gcloud compute firewall-rules create cs1660-project1-allow-public-traffic --allow tcp:30001-30006
The setup.sh file located in the kube_setup/ directory must be executable from the command line. To do this, navigate to the kube_setup/ directory and run the command:
chmod +x setup.sh
Once the preconditions are met, navigate to the kube_setup/ directory and run the command:
./setup.sh
First, this will apply all of the yaml files found in the kube_setup/init_kube_objects/ directory to the Kubernetes cluster. In addition, this will print out a url that, when navigated to in the browser, will allow the user to access the web app driver program for this service.
If this url is ever lost, it can be retrieved again by navigating to the kube_setup/ directory and running the command:
python print_url.py
Once you navigate to the web app driver, the web page will offer options to launch and disable each of the four micro-services. By clicking the link to launch a microservice, the cluster will re-scale that deployment in order to have an instance of that microservice running. The user will also be presented with a second page that has a link to go to the service they had just chosen. This link will open a new tab that will have a web UI of the microservice that was just launched. In the main menu, by clicking any of the disable microservice links, the microservice associated with the link will be rescaled back to zero, and will therefore stop being run on the cluster.
Important Note: The deployments and services that make up this system do often take some time to load. When using, please be patient for things to load!