Inhibitory Recurrent Neural Networks for Cognitive
So far only for RT version
Xiaohe Xue
This project trys to implementate the Perceptual Decision Making Task in the paper Training excitatory-inhibitory recurrent neural networks for cognitive tasks: A simple and flexible framework
Python 3
Tensorflow 2.0
python main.py
-a, --action, test/train
-tv, --task_version, rt/fd
--init_state_trainable, set if init sate trainable
-e_num, --epoch_num, num of epochs for training
-e_size, --epoch_size, default=1000, num of trails in one epoch for training
--model_date, None/string(%Y%m%d-%H%M%S, the path of checkpoint coreesponding to the date when it is saved)
In the RT task, the choice targets were displayed for a variable interval before the onset of the motion stimulus. The duration of this prestimulus interval was randomly selected from an exponential distribution (mean 700 msec). This randomization served to discourage anticipation of the onset of the motion stimulus. We found that randomization of the prestimulus interval in this fashion was essential for training on the RT task. When the onset of the stimulus was predictable, RT was faster than in these experiments and varied less across the range of coherences. Once the motion stimulus began, the monkey was free to indicate its choice at any time. When the computer detected a break in fixation, the random dots were extinguished. If the monkey made a saccade to either choice target, the trial was scored as correct or incorrect. Breaks in fixation that were not associated with an immediate saccade to a choice target were rare and are not included in our data set.
- Response of neurons in the lateral intraparietal area during a combined visual discrimination reaction time task.J. D. Roitman & M. N. Shadlen, JNS 2002. http://www.jneurosci.org/content/22/21/9475.abstract
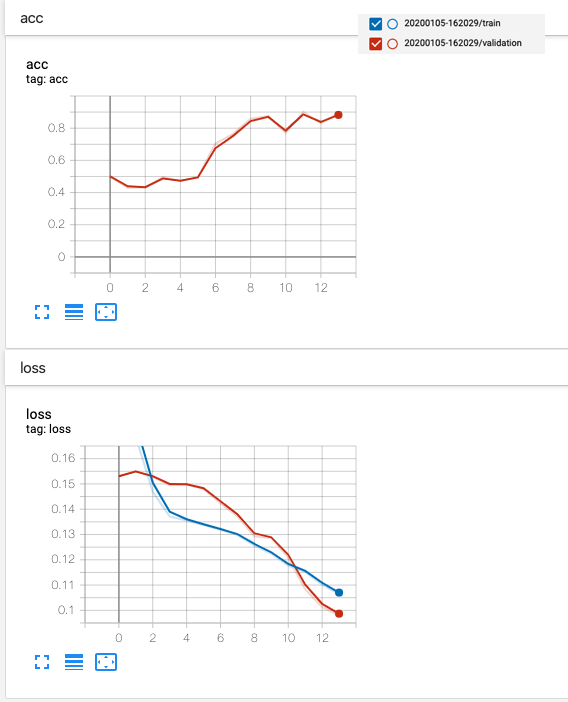
- Loss and accuracy during training
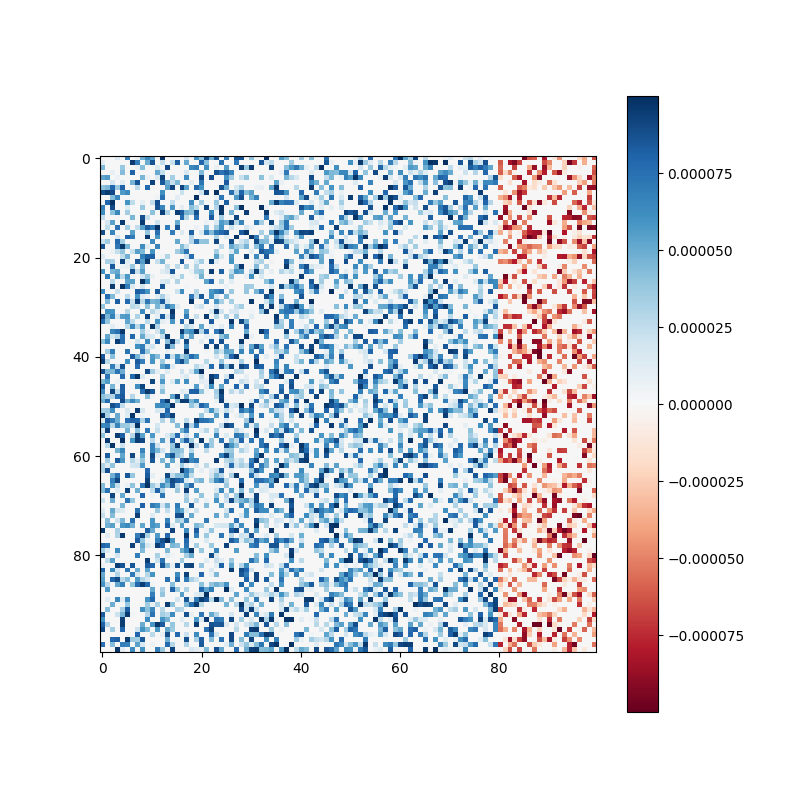
- W_rec matrix
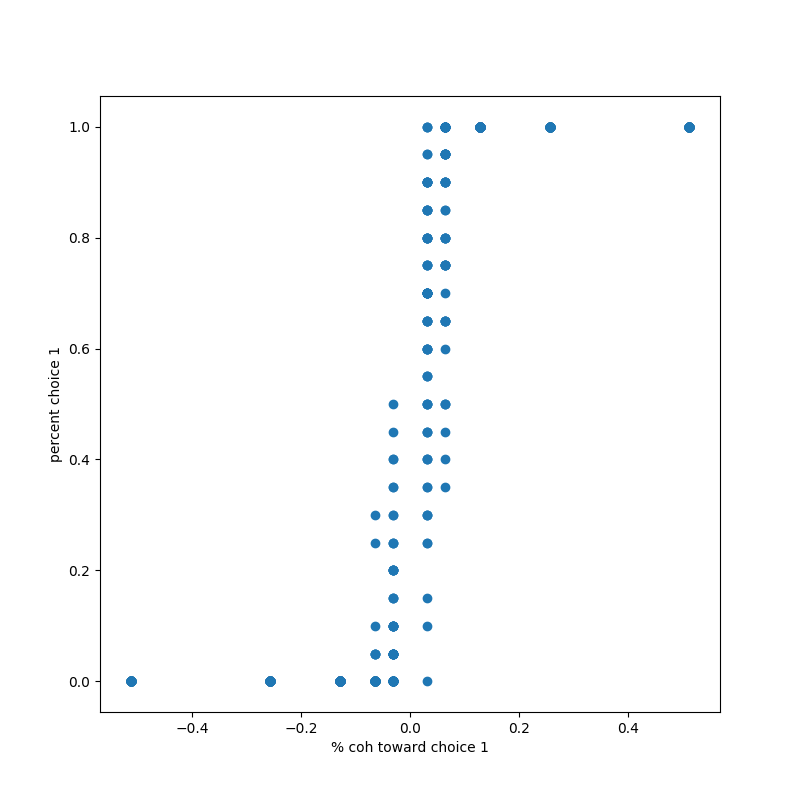
- The plot showing the percentage of trials on which the network chose choice 1 as a function of the signed coherence, which fits the Psychometric function in the paper.
- Extract reaction time