The purpose of this assignment is to become familiar with various classification models. The dataset consists of various locations’ daily weather observations ranging from 2007 to 2019 in Australia. Given the modified version of the Kaggle competition data, the main task is to predict whether the following day will become cloudy or not. In other word, a model will be created to predicted if tomorrow will become cloudy for 10 random sample locations in Australia.
Different classification models are utilised to predict weather, such as
- Decision tree,
- Naive Bayes,
- Bagging,
- Boosting,
- Random Forecast
- Artifical Neural Network Classifier
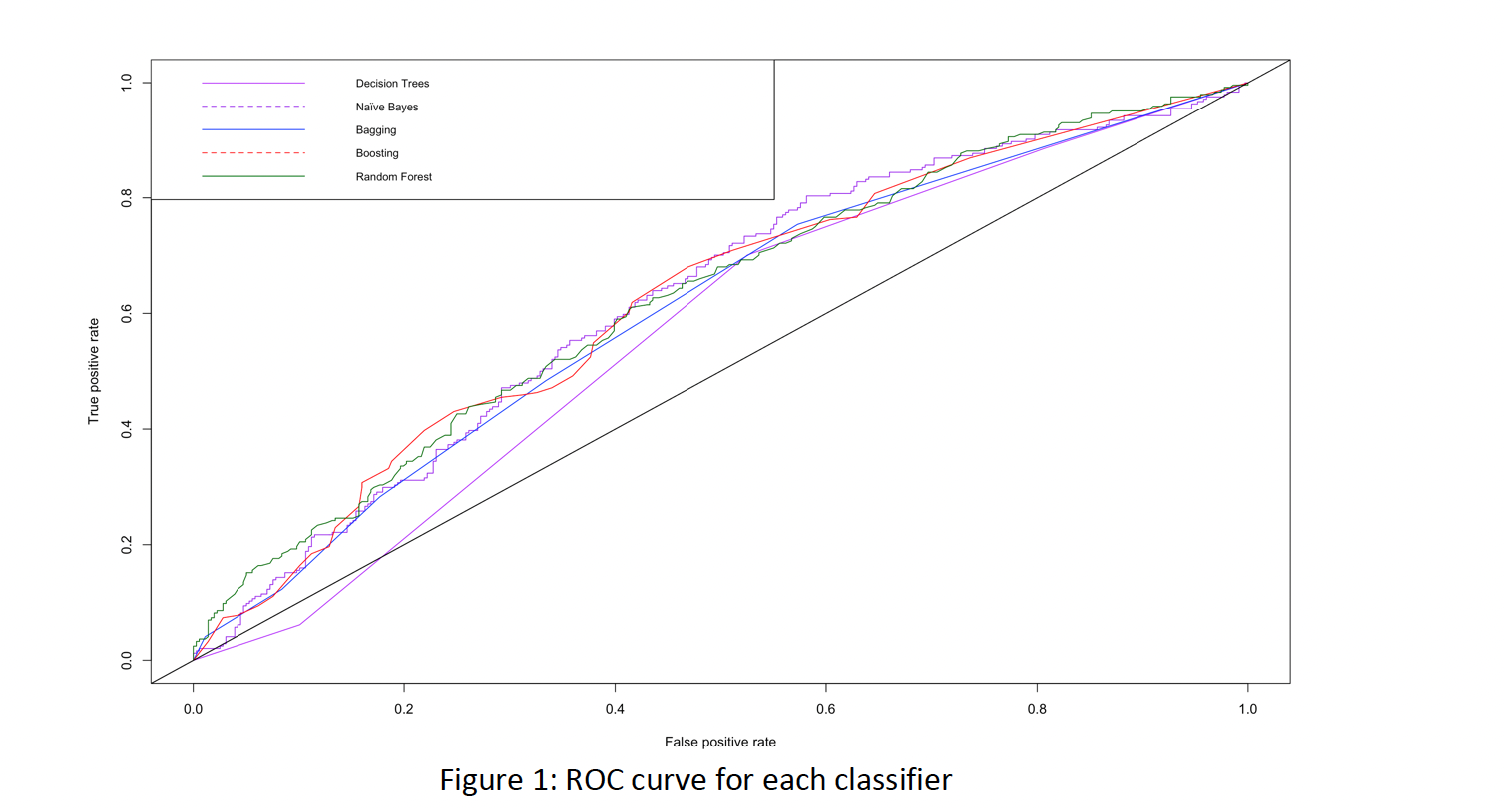
Later use ROC curve, Accuracy (%) and AUC to evaluate different classification model performance.
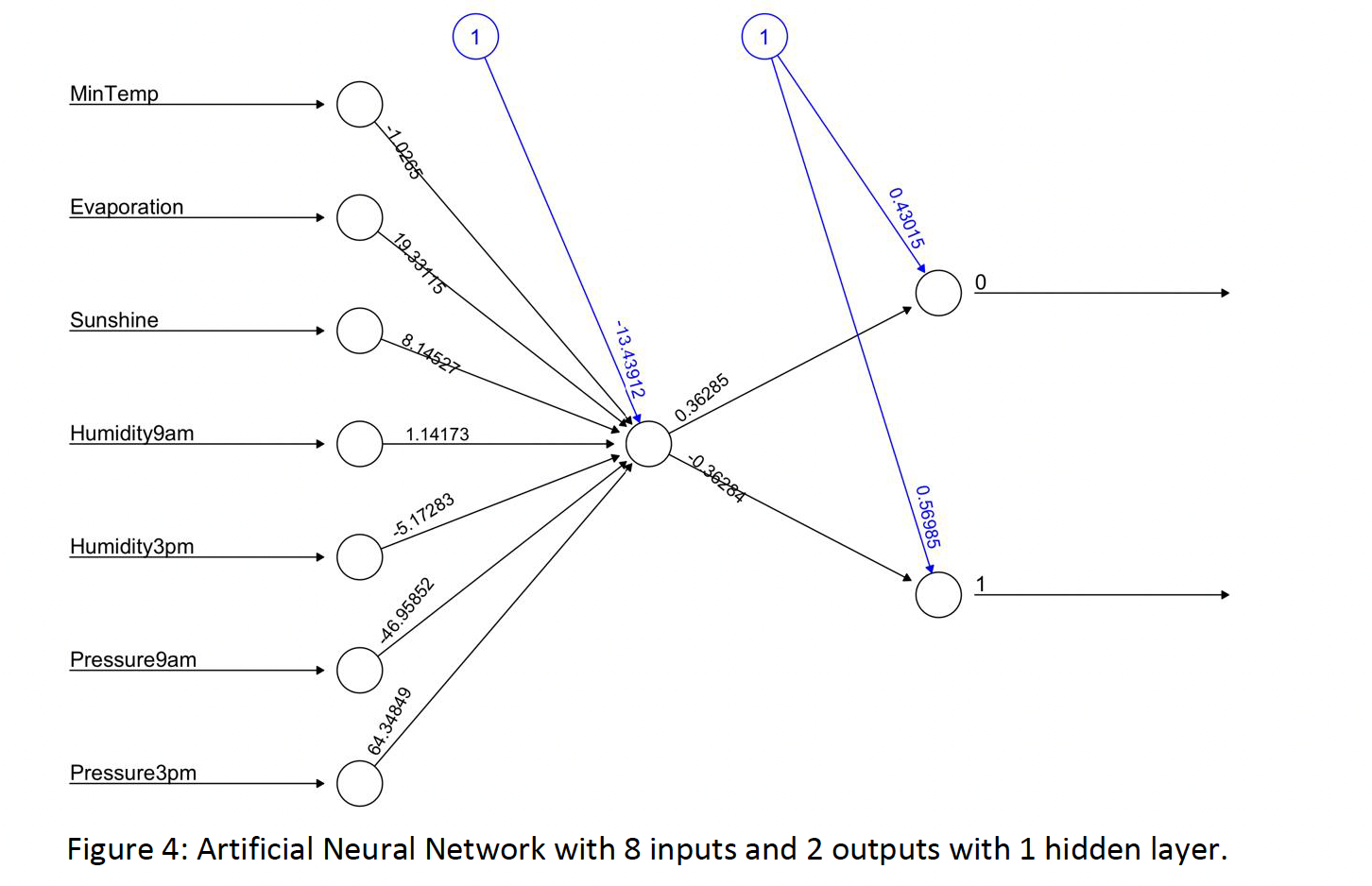
In conclusion, given the modified version of Kaggle data, to predict if tomorrow will be cloudy, after applying multiple classification techniques, it is worthy to notice that there are a few significantly domain attributes such as Sunshine, Mintemp, Pressure9am, Pressure3pm and Humidity3pm. As a result, it is easy to use these 5 top attributes to build a simple classifier by partitioning the dataset via ‘best’ attribute that can easily help partition the data. Moreover, the boosting techniques can provide the highest accuracy for prediction for cloudy day compared with other 4 techniques including Decision Tree, Random Forest, Bagging and Naïve Bayes. To improve the classification performance, cross-validation is applied, but unfortunately it seems that accuracy has not improved due to potential problems such as poor quality of data set. In the end, after combing all insight from previous section, then Artificial Neural Network model is created with 7 inputs, 1 hidden layer and 2 outputs, the accuracy is about 61%.
- R language
- IDE