A simple graphing Java class for generating .dot files.
- Add Digraph.java to your project.
- Look at 'Example Usages' to see how to use the graph code.
- You need graphviz installed to generate the graph (http://www.graphviz.org/). On Ubuntu/Mint, install it with
sudo apt-get install graphviz. - After generating the graph, use
dot -Tps <filename> -o <outputfile>.pdfto generate the graph.<filename>is the name passed togenerate(), and the outputfile must end in .pdf.
- Create a new graph object with
Digraph(String name). The argument is the name of the graph. - Add a node with
addNode(String ID). The argument is the ID of the node. These need to be unique. - Link nodes with
link(String parentNodeID, String childNodeID). Make sure to create the nodes first. - Generate the graph with
generateGraph(String filename).
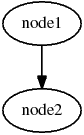
Digraph graph = new Digraph("test_Graph");
graph.addNode("node1");
graph.addNode("node2");
graph.link("node1", "node2");
graph.generate("graph.dot");The above code generates the following graph:
Add a labels to a link with
link().setLabel(String labelText).
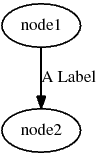
Digraph graph = new Digraph("test_Graph");
graph.addNode("node1");
graph.addNode("node2");
graph.link("node1", "node2").setLabel("A Label");
graph.generate("graph.dot");The above code generates the following graph:
You can chain
.addNode()calls, and add an optional name with.addNode(String nodeID, String nodeName). Names do not need to be unique.
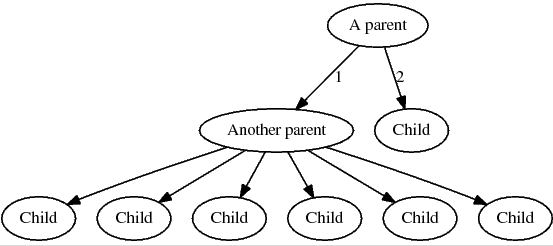
Digraph graph = new Digraph("test_Graph");
graph.addNode("parent1", "A parent")
.addNode("parent2", "Another parent")
.addNode("child1", "Child")
.addNode("child2", "Child")
.addNode("child3", "Child")
.addNode("child4", "Child")
.addNode("child5", "Child")
.addNode("child6", "Child")
.addNode("child7", "Child");
graph.link("parent1", "parent2").setLabel("1");
graph.link("parent1", "child1").setLabel("2");
graph.link("parent2", "child2");
graph.link("parent2", "child3");
graph.link("parent2", "child4");
graph.link("parent2", "child5");
graph.link("parent2", "child6");
graph.link("parent2", "child7");The above code generates the following graph:
- Only directed graphs can be constructed.
- Nodes can only have one parent.