A Cypress plugin specifically created for SDK's that integrate
with Auth0! Cypress-Auth0-Simulator will simulate an auth0 server, running on localhost, so you
don't have to create fake Auth0 accounts while developing or running tests that require authentication!
Features:
- No interaction with real Auth0 servers making any token request completely free!
- Supports multiple SDK's that integrate with Auth0!
- Create individual users for each test, each with a unique set of claims, permissions or scopes!
- Can be run in CI/CD pipelines!
- Works with the latest Cypress and Auth0 SDK versions!
- cypress-auth0-simulator uses a package called @simulacrum/auth0-simulator, which will start a GraphQL interface/web server (by default on localhost:4000), ready to accept mutations.
- An Auth0 simulated server is created with all the normal Auth0 endpoints (by default on localhost:4400).
- In each Cypress test, a user can be registered through the use of the
cy.given()command. - The application under test uses those user credentials to request a token from the simulated Auth0 server, which is then used to put the application in an authenticated state.
npm install cypress-auth0-simulator --devThis plugin supports the following javascript sdks that interface with auth0:
To set the correct SDK, you need to set the AUTH0_SDK environment variable inside your cypress.config.ts or through
any of the usual cypress environmental variables options.
in the cypress.config.ts file
// integrations/cypress/cypress.config.ts
export default defineConfig({
env: {
// This is the SDK used to communicate with Auth0, can be either 'auth0-js', 'auth0-vue', 'auth0-react' or 'nextjs-auth0'
AUTH0_SDK: 'auth0-js',
}
});or with the use of an .env file (
examples: auth0-vue, auth0-react, nextjs-auth0
or create-react-app)
# .env.auth0-react
AUTH0_SDK="auth0-js"// cypress/support/e2e.ts or in your cypress/support/commands.ts
import 'cypress-auth0-simulator/commands';We need to register an encrypt cypress task.
// cypress.config.ts
import { encrypt } from 'cypress-auth0-simulator';
export default defineConfig({
e2e: {
setupNodeEvents(on) {
on('task', { encrypt });
},
},
});// cypress.config.ts
export default defineConfig({
e2e: {
setupNodeEvents(on) {
const { encrypt } = require('cypress-auth0-simulator');
on('task', { encrypt });
},
},
});An example of all the possible environment variables can be found in the cypress.config.ts file.
// cypress.config.ts
export default defineConfig({
env: {
// This is the SDK used to communicate with Auth0, can be either 'auth0-js', 'auth0-vue', 'auth0-react' or 'nextjs-auth0'
AUTH0_SDK: 'auth0-js',
// This is the port of the simulated Auth0 server to which the Auth0 SDK will connect
AUTH0_SIMULATOR_PORT: 4400,
// The intended consumer of the token
AUTH0_AUDIENCE: 'https://your-audience/',
// The Client ID of the Auth0 application
AUTH0_CLIENT_ID: '67c25b266aa911ee8c990242ac120002',
// The type of authentication flow used by the Auth0 SDK
AUTH0_CONNECTION: 'Username-Password-Authentication',
// The default scope for the Auth0 user
AUTH0_SCOPE: 'openid profile email offline_access',
// This is the secret used to sign the JWT tokens
AUTH0_CLIENT_SECRET: '',
// This is the secret used to encrypt the session cookie
AUTH0_COOKIE_SECRET: '',
// This is the name of the session cookie used by the Cypress tests
AUTH0_SESSION_COOKIE_NAME: 'appSession',
}
});These same variables can also be set through the use of env files: (
examples: auth0-react, nextjs-auth0 create-react-app)
# /integrations/cypress/.env.auth0-react
AUTH0_SDK="auth0-react"
AUTH0_SIMULATOR_PORT=4400
AUTH0_AUDIENCE="https://your-audience/"
AUTH0_CONNECTION="Username-Password-Authentication"
AUTH0_SCOPE="openid profile email offline_access"
AUTH0_CLIENT_ID="67c25b266aa911ee8c990242ac120002"
AUTH0_CLIENT_SECRET='YOUR_AUTH0_CLIENT_SECRET'
AUTH0_COOKIE_SECRET='6d0598f28f62a9aee14929ef46c7c8befdc0150d870ec462fa45629511fd2a46'NOTE: Make sure that the SDK you're using is pointing to the same values as you're passing in the Cypress env when running in Cypress!
// Auth0-Vue SDK example
export const auth0 = createAuth0({
domain: 'https://localhost:4400',
clientId: '67c25b266aa911ee8c990242ac120002',
authorizationParams: {
audience: 'https://your-audience/',
scope: 'openid profile email offline_access',
},
});The Auth0 SDK's require a https connection to work. This can easily be setup by using mkcert to create a self-signed certificate for your localhost.
A running example with setting up mkcert instruction can be found here at @simulacrum/ui
Cypress recommends using start-server-and-test to ensure the test process exits and any servers are shut down.
Make sure to follow the following convention for creating your own start command with Auth0-Cypress
npx start-server-and-test <first command> <first resource> <second command> <second resource> <test command>As example:
# This will start the server and test commands in parallel
npx start-server-and-test \
# This will start the application server that will be tested against in Cypress
'npm run start:server' http://localhost:3000 \
# This will start the Auth0 simulator GraphQL server
'npm run start:auth0' http://localhost:4000 \ ##
# This will start the Cypress tests
cypress openSee the scripts section in package.json for various examples on the use of integrating
withstart-server-and-test command.
The following commands are now available in your test suite:
An example of these commands in use can be found in the login.spec.ts file.
createSimulation creates the fake auth0 server with your configuration
describe('tests requiring auth', () => {
it('should access restricted resource', () => {
cy.createSimulation(); // Will use the default configuration set in cypress.config.ts
// OR
cy.createSimulation({ options }); // Will use the options passed in to start the simulated Auth0 server
});
})given creates a fake user that can be used to log into the fake auth0 server.
describe('tests requiring auth', () => {
it('should access restricted resource', () => {
cy
.createSimulation({ options })
.given() // with no arguments a random user is created
.login();
});
})describe('tests requiring auth', () => {
it('should access restricted resource', () => {
cy
.createSimulation()
.given({ email: 'bob@gmail.com' }) // fixed fields
.login();
});
})Depending on the SDK that has been configured, a token will be requested through the use of getTokenSilently(). Which will set the token in the local storage of the browser.
Call login and logout in your test. For example:
describe('log in', () => {
it('should get token without signing in', () => {
cy
.createSimulation({ options })
.visit("/")
.contains("Log out").should('not.exist')
.given()
.login()
.visit("/")
.contains("Log out")
.logout();
});
});cy.logout will destroy the simulation and do any clean up between tests like removing cookies.
cy.logout();When running my app in Cypress, the login is successful but the app is not logged in or it redirects me to the login page:
Make VERY sure that the Auth0 env variable values you're using, are the EXACT same as the variables you're passing into Cypress.
https://github.com/bahmutov/start-server-and-test#use-http-get-requests
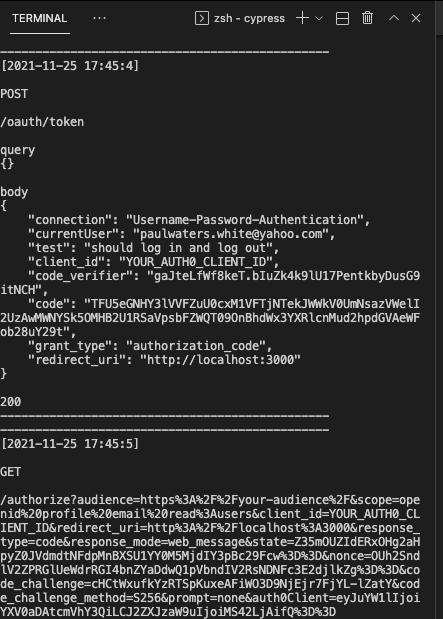
It is possible to hook up express middleware to log each endpoint that is called and any associated querystring or POST
data by simply adding the debug: true option when calling createSimulation:
describe('debug auth0 server', () => {
it("should log in and log out", () => {
cy.createSimulation({ debug: true })
});
});