A statistical and data mining tool for ECharts. You can use it to analyze data and then visualize the results with ECharts, or just use it to process data.
It works both in node.js and in the browser.
If you use npm, you can install it with:
npm install echarts-statOtherwise, download this tool from dist directory:
<script src='./dist/ecStat.js'></script>
<script>
var result = ecStat.clustering.hierarchicalKMeans(data, clusterNumber, false);
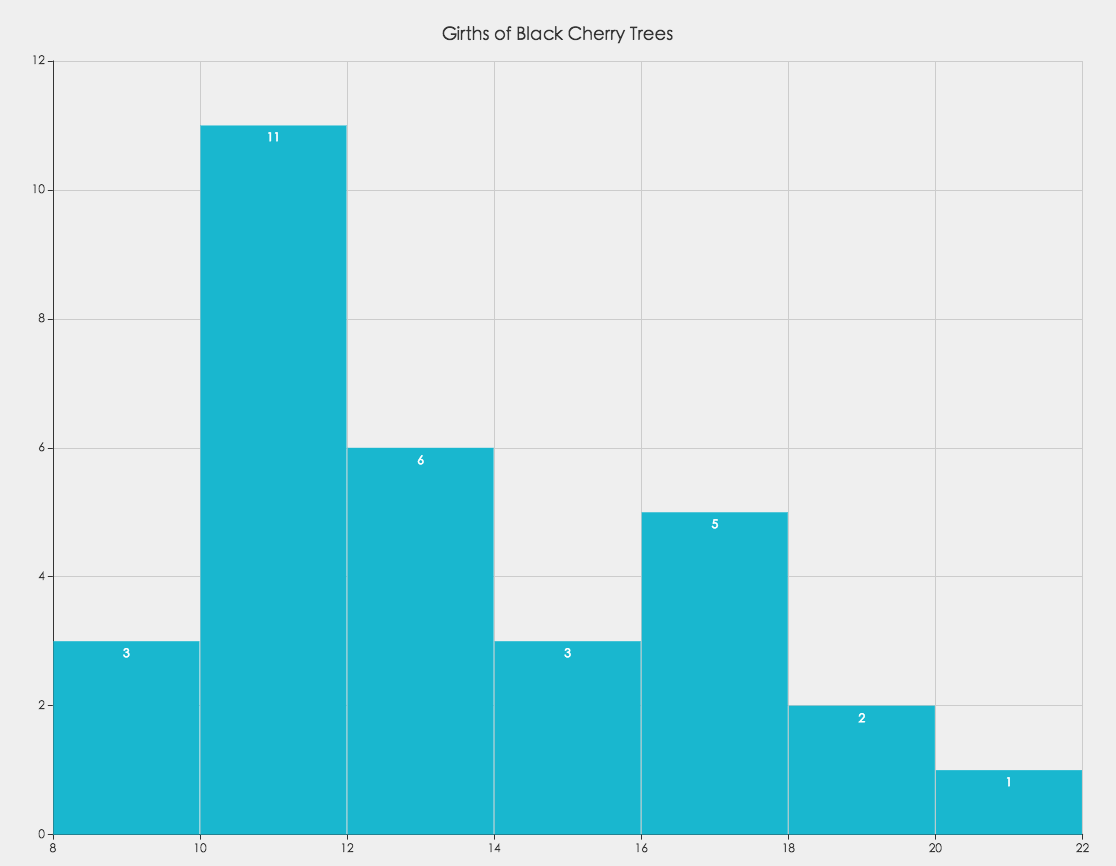
</script>A histogram is a graphical representation of the distribution of numerical data. It is an estimate of the probability distribution of a quantitative variable. It is a kind of bar graph. To construct a histogram, the first step is to "bin" the range of values - that is, divide the entire range of values into a series of intervals - and then count how many values fall into each interval. The bins are usually specified as consecutive, non-overlapping intervals of a variable. Here the bins(intervals) must be adjacent, and are of equal size.
var bins = ecStat.histogram(data, binMethod);-
data-Array<number>. Data samples of numbers.var data = [8.6, 8.8, 10.5, 10.7, 10.8, 11.0, ... ];
-
binMethod-string. There are four methods to calculate the number of bins, which aresquareRoot,scott,freedmanDiaconis, andsturges. Of course, there is no "best" number of bins, and different bin sizes can reveal different features of the data.-
squareRoot- This is the default method, which is also used by Excel histograms. Returns the number of bins according to Square-root choice:var bins = ecStat.histogram(data);
-
scott- Returns the number of bins according to Scott's normal reference Rule:var bins = ecStat.histogram(data, 'scott');
-
freedmanDiaconis- Returns the number of bins according to The Freedman-Diaconis rule:var bins = ecStat.histogram(data, 'freedmanDiaconis');
-
sturges- Returns the number of bins according to Sturges' formula:var bins = ecStat.histogram(data, 'sturges');
-
bins-Object. Contain detailed messages of each bin and data used for ECharts to draw the bar chart.bins.bins-Array.<Object>. An array of bins, where each bin is an object, containing three attributes:x0-number. The lower bound of the bin (inclusive).x1-number. The upper bound of the bin (exclusive).sample-Array.<number>. Containing the associated elements from the input data.
bins.data-Array.<Array.<number>>. An array of bins data, each bins data is an array not only containing the mean value ofx0andx1, but also the length ofsample, which is the number of sample values in that bin.
When using ECharts bar chart to draw the histogram, we must notice that, setting the xAxis.scale as true.
<script src='https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.4.0/echarts.js'></script>
<script src='./dist/ecStat.js'></script>
<script>
var bins = ecStat.histogram(data);
var option = {
...
xAxis: [{
type: 'value',
// this must be set as true, otherwise barWidth and bins width can not corresponding on
scale: true
}],
...
}
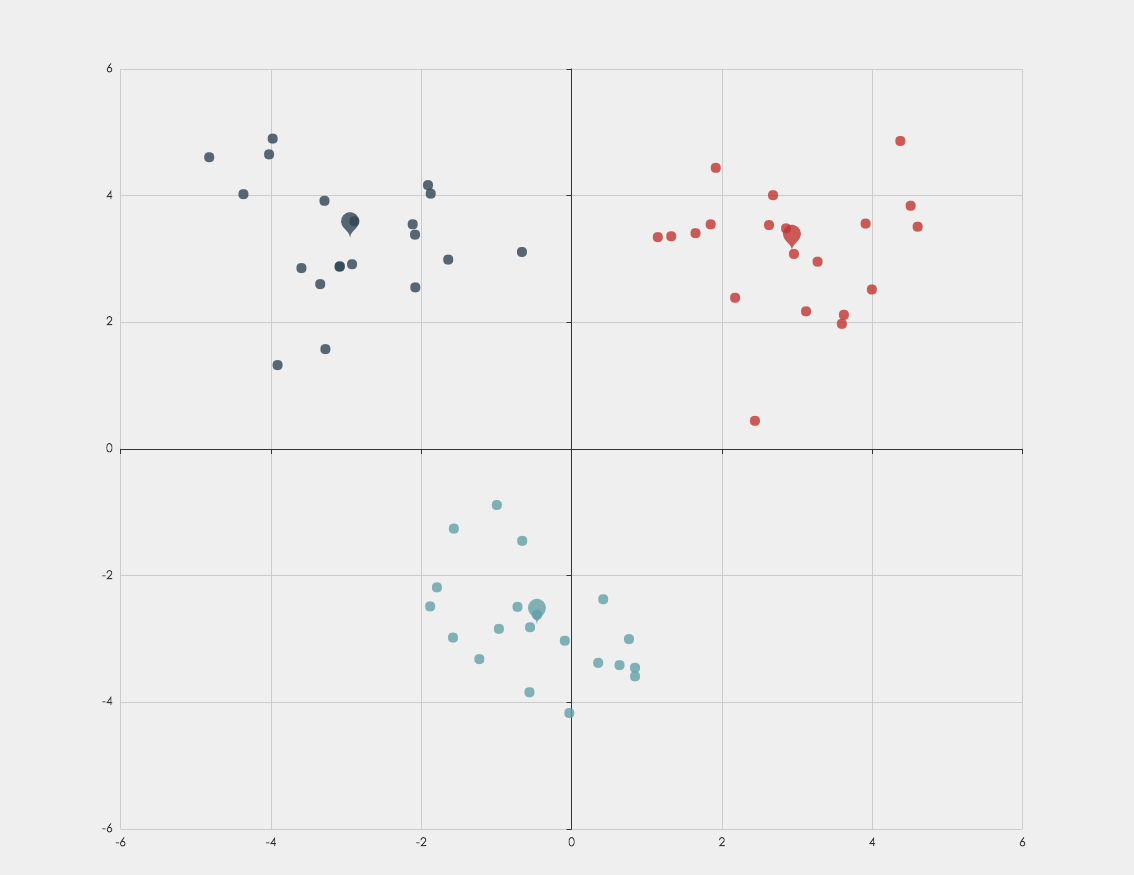
</script>Clustering can divide the original data set into multiple data clusters with different characteristics. And through ECharts, you can visualize the results of clustering, or visualize the process of clustering.
var result = ecStat.clustering.hierarchicalKMeans(data, clusterNumber, stepByStep);
-
data-two-dimensional Numeric Array. Each data point can have more than two numeric attributes in the original data set. In the following example,data[0]is calleddata pointanddata[0][1]is one of the numeric attributes ofdata[0].var data = [ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10], [11, 12, 13, 14, 15], ... ];
-
clusterNumer-number. The number of clusters generated -
stepByStep-boolean. Control whether doing the clustering step by step
-
result-Object. Including the centroids, clusterAssment, and pointsInCluster. For Example:result.centroids = [ [-0.460, -2.778], [2.934, 3.128], ... ]; // indicate which cluster each data point belonging to, and the distance to cluster centroids result.clusterAssment = [ [1, 0.145], [2, 0.680], [0, 1.022], ... ]; // concrete data point in each cluster result.pointsInCluster = [ [ [0.335, -3.376], [-0.994, -0.884], ... ], ... ];
You can not only do cluster analysis through this interface, but also use ECharts to visualize the results.
Note: the clustering algorithm can handle multiple numeric attributes, but for the convenience of visualization, two numeric attributes are chosen here as an example.
<script src='https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.4.0/echarts.js'></script>
<script src='./dist/ecStat.js'></script>
<script>
var clusterNumber = 3;
var result = ecStat.clustering.hierarchicalKMeans(data, clusterNumber, false);
</script><script src='https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.4.0/echarts.js'></script>
<script src='./dist/ecStat.js'></script>
<script>
var clusterNumber = 6;
var result = ecStat.clustering.hierarchicalKMeans(data, clusterNumber, true);
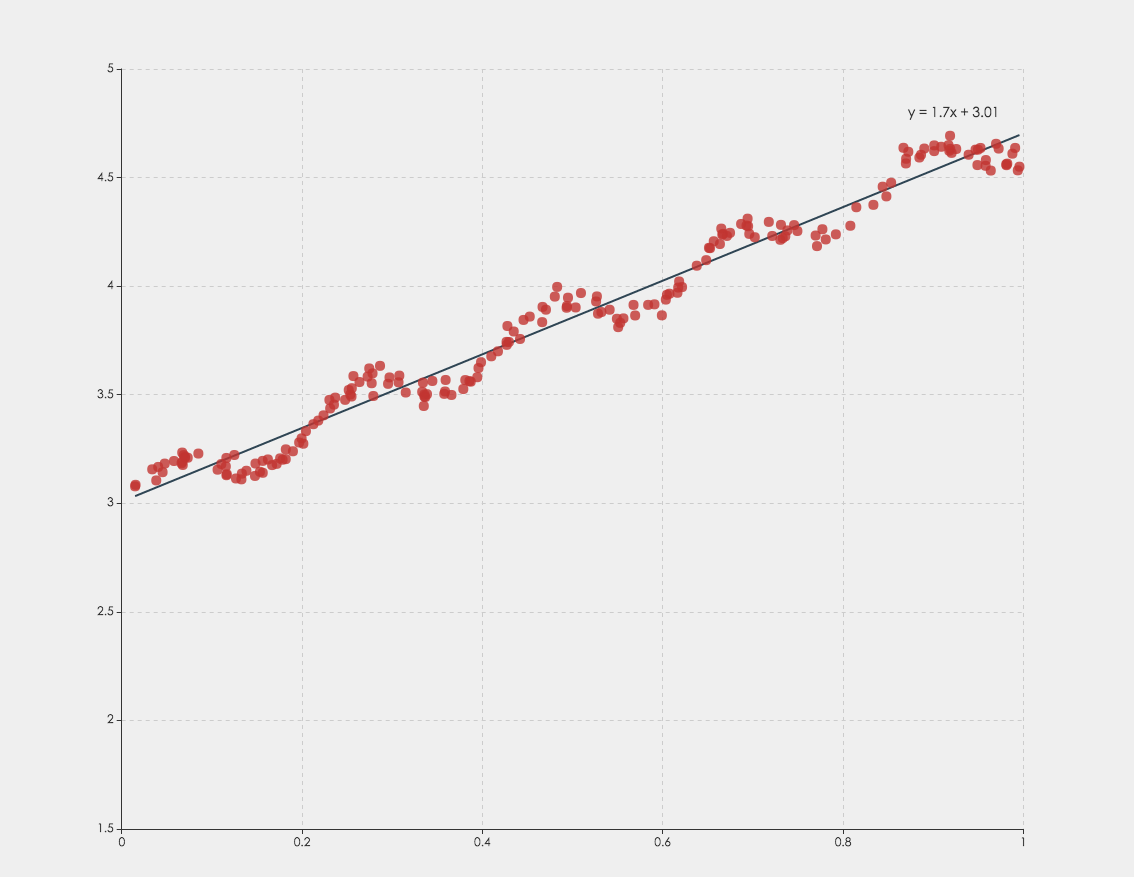
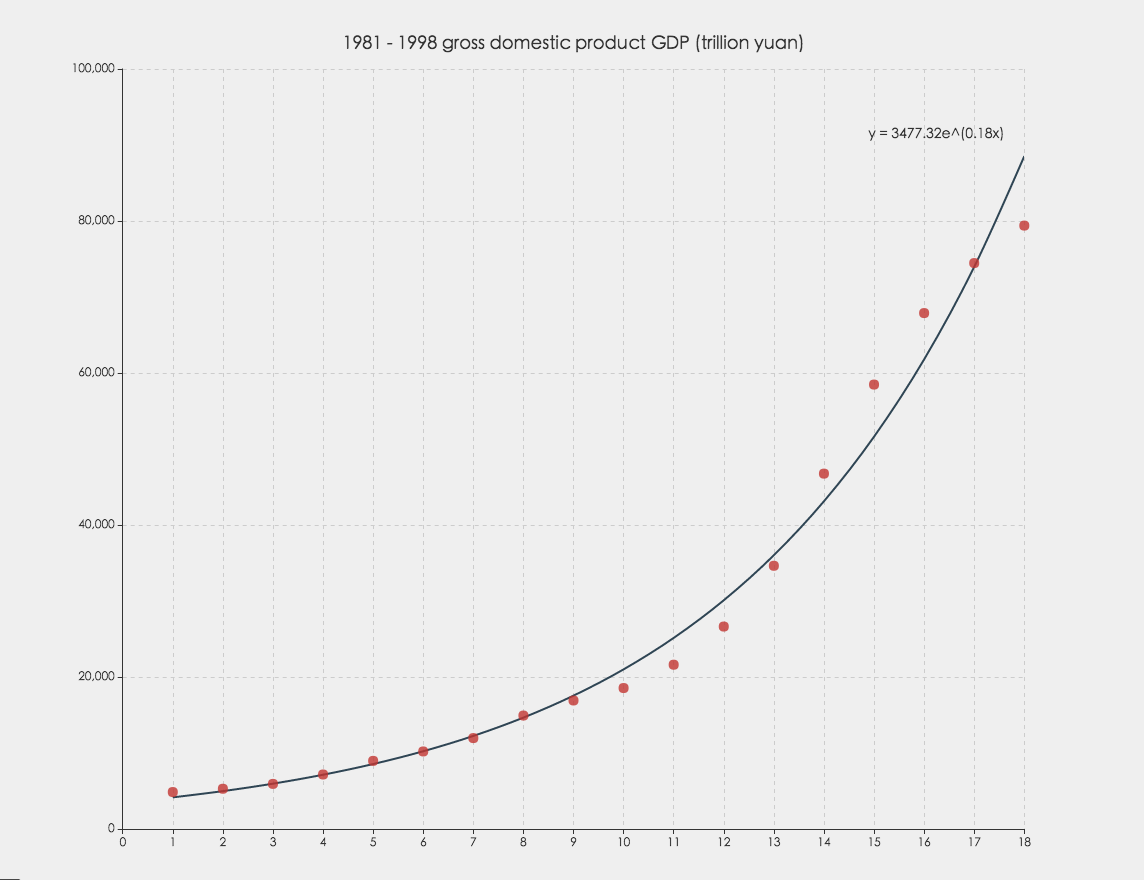
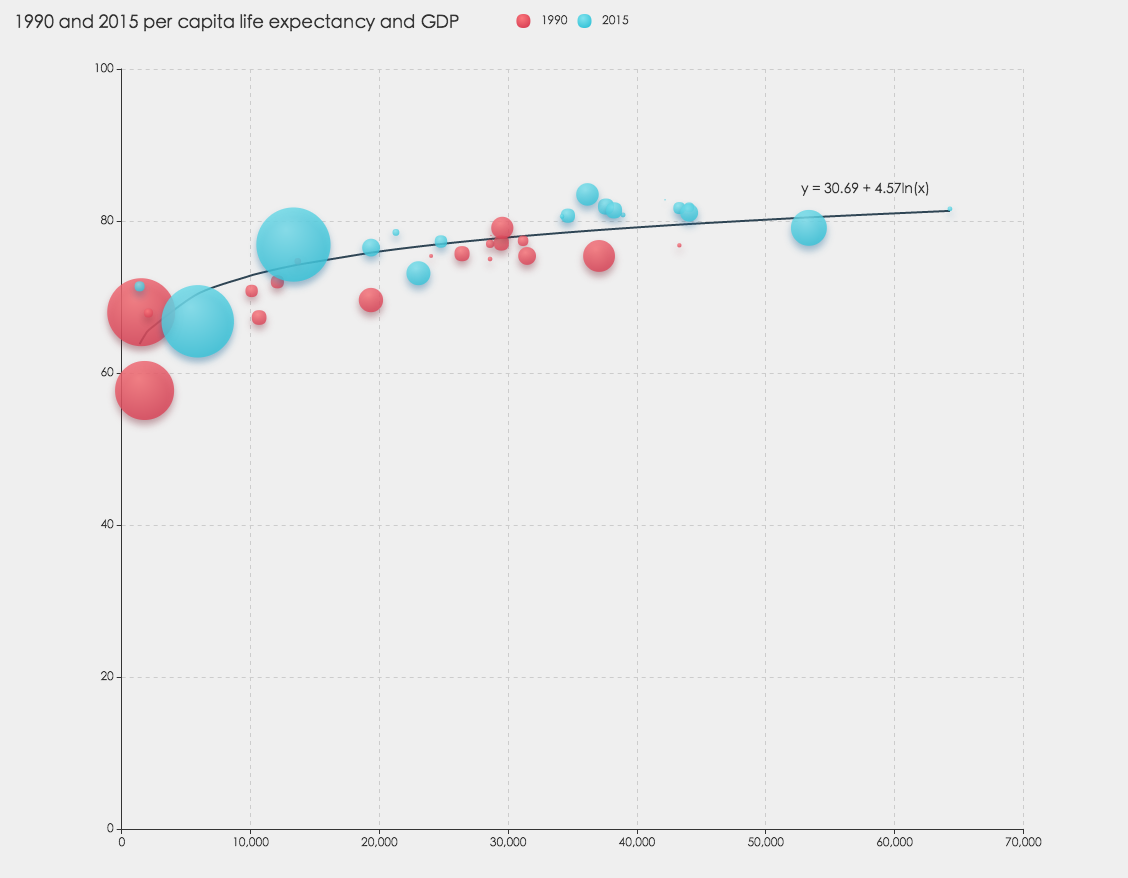
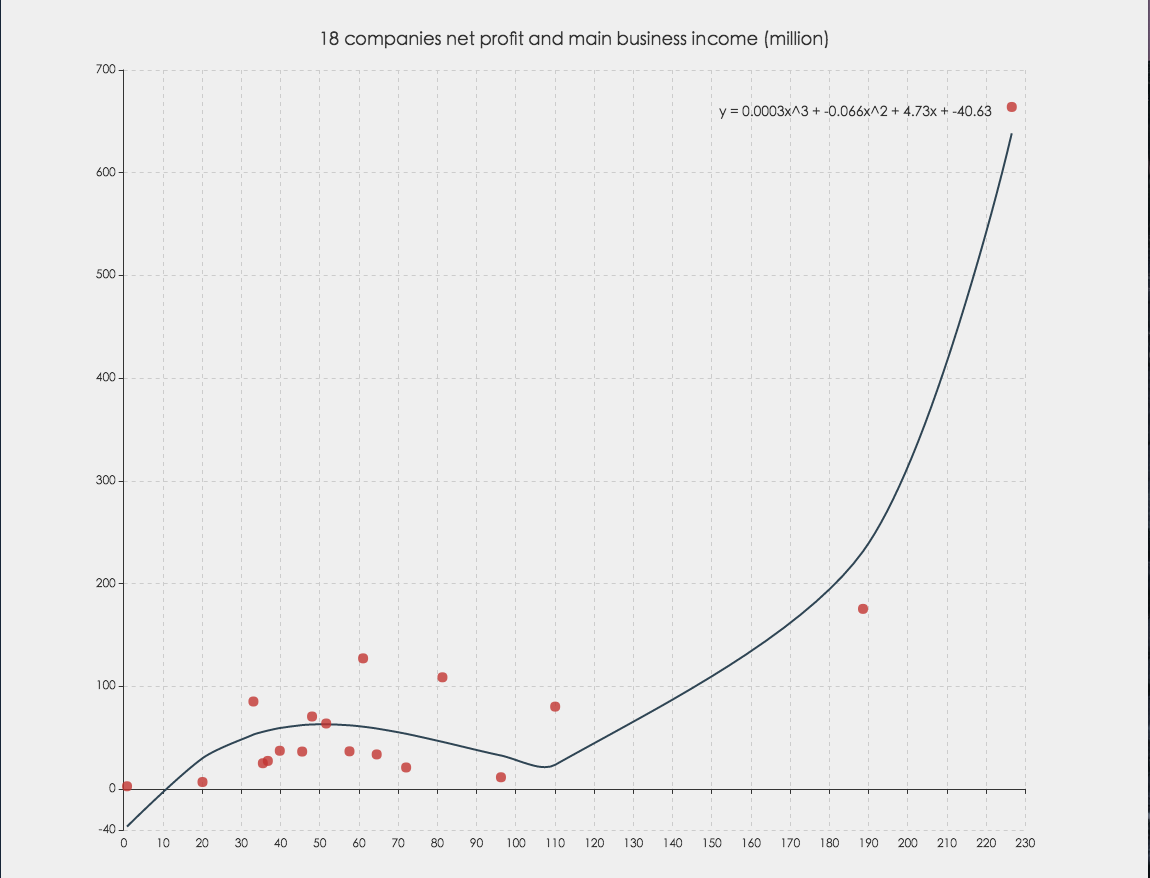
</script>Regression algorithm can according to the value of the dependent and independent variables of the data set, fitting out a curve to reflect their trends. The regression algorithm here only supports two numeric attributes.
var myRegression = ecStat.regression(regressionType, data, order);
-
regressionType-string. There are four types of regression, whice arelinear,exponential,logarithmic,polynomial -
data-two-dimensional Numeric Array. Each data object should have two numeric attributes in the original data set. For Example:var data = [ [1, 2], [3, 5], ... ];
-
order-number. The order of polynomial. If you choose other types of regression, you can ignore it
-
myRegression-Object. Including points, parameter, and expression. For Example:myRegression.points = [ [1, 2], [3, 4], ... ]; // this is the parameter of linear regression, for other types, it shoule be a little different myRegression.parameter = { gradient: 1.695, intercept: 3.008 }; myRegression.expression = 'y = 1.7x + 3.01';
You can not only do regression analysis through this interface, you can also use ECharts to visualize the results.
<script src='https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.4.0/echarts.js'></script>
<script src='./dist/ecStat.js'></script>
<script>
var myRegression = ecStat.regression('linear', data);
</script><script src='https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.4.0/echarts.js'></script>
<script src='./dist/ecStat.js'></script>
<script>
var myRegression = ecStat.regression('exponential', data);
</script><script src='https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.4.0/echarts.js'></script>
<script src='./dist/ecStat.js'></script>
<script>
var myRegression = ecStat.regression('logarithmic', data);
</script><script src='https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.4.0/echarts.js'></script>
<script src='./dist/ecStat.js'></script>
<script>
var myRegression = ecStat.regression('polynomial', data, 3);
</script>This interface provides basic summary statistical services.
var sampleDeviation = ecStat.statistics.deviation(dataList);
dataList:Array.<number>
sampleDeviation:number. Return the deviation of the numeric array dataList. If the dataList is empty or the length less than 2, return 0.
var varianceValue = ecStat.statistics.sampleVariance(dataList);
dataList:Array.<number>
varianceValue:number. Return the variance of the numeric array dataList. If the dataList is empty or the length less than 2, return 0.
var quantileValue = ecStat.statistics.quantile(dataList, p);
dataList:Array.<number>. Sorted array of numbers.p:number. where 0 =< p <= 1. For example, the first quartile at p = 0.25, the seconed quartile at p = 0.5(same as the median), and the third quartile at p = 0.75.
quantileValue:number. Return the p-quantile of the sorted array of numbers. If p <= 0 or the length of dataList less than 2, return the first element of the sorted array; if p >= 1, return the last element of the sorted array; If dataList is empty, return 0.
var maxValue = ecStat.statistics.max(dataList);
dataList:Array.<number>
maxValue:number. The maximum value of the dataList.
var minValue = ecStat.statistics.min(dataList);
dataList:Array.<number>
minValue:number. The minimum value of the dataList.
var meanValue = ecStat.statistics.mean(dataList);
dataList:Array.<number>
meanValue:number. The average of the dataList.
var medianValue = ecStat.statistics.median(dataList);
dataList:Array.<number>. Sorted array of numbers
medianValue:number. The median of the dataList.
var sumValue = ecStat.statistics.sum(dataList);
dataList:Array.<number>
sumValue:number. The sum of the dataList.