Speaker Count Estimation using Deep Neural Networks
Estimating the number of concurrent speakers from single channel mixtures is a very challenging task that is a mandatory first step to address any realistic “cocktail-party” scenario. It has various audio-based applications such as blind source separation, speaker diarisation, and audio surveillance. Building upon powerful machine learning methodology and the possibility to generate large amounts of learning data, Deep Neural Network (DNN) architectures are well suited to directly estimate speaker counts.
Publication
Accepted for ICASSP 2018
- Title: Classification vs. Regression in Supervised Learning for Single Channel Speaker Count Estimation
- Authors: Fabian-Robert Stöter, Soumitro Chakrabarty, Bernd Edler, Emanuël A. P. Habets
- Preprint: arXiv 1712.04555
Model
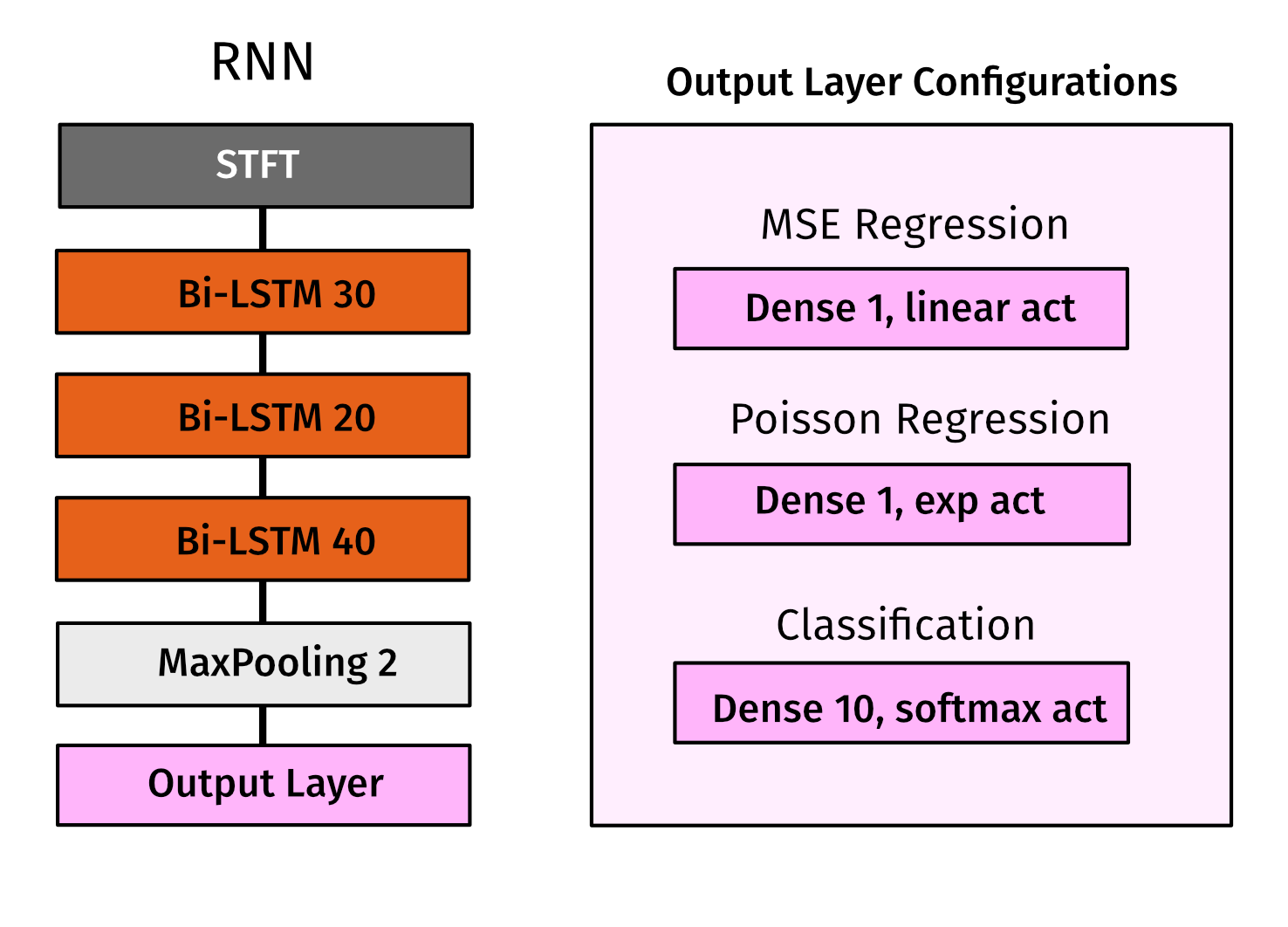
In this work a recurrent neural network was trained to generate speaker count estimates for 0 to 10 speakers. The model uses three Bi-LSTM layers inspired by a model for singing voice separation by Leglaive15.
Demos
A demo video is provided on the accompanying website.
Usage
This repository provides the keras model to be used from Python to infer count estimates. The preprocessing dependes on librosa and scikit-learn. Not that the provided model is trained on 16 kHz samples of 5 seconds duration.
Docker
Docker makes it easy to reproduce the results and install all requirements. If you have docker installed, run the following steps to predict a count from the provided test sample.
- Build the docker image:
docker build -t countnet . - Predict from example:
docker run -i countnet python predict_audio.py examples/5_speakers.wav
Manual Installation
Make sure you have Python 3.6, libsndfile and libhdf5 installed on your system (e.g. through Anaconda). To install the requirements run
pip install -r requirements.txt
You can now run the command line script and process wav files
python predict_audio.py examples/5_speakers.wav
Reproduce Paper Results using the LibriCount Dataset
The full test dataset is available for download on Zenodo.
LibriCount10 0dB Dataset
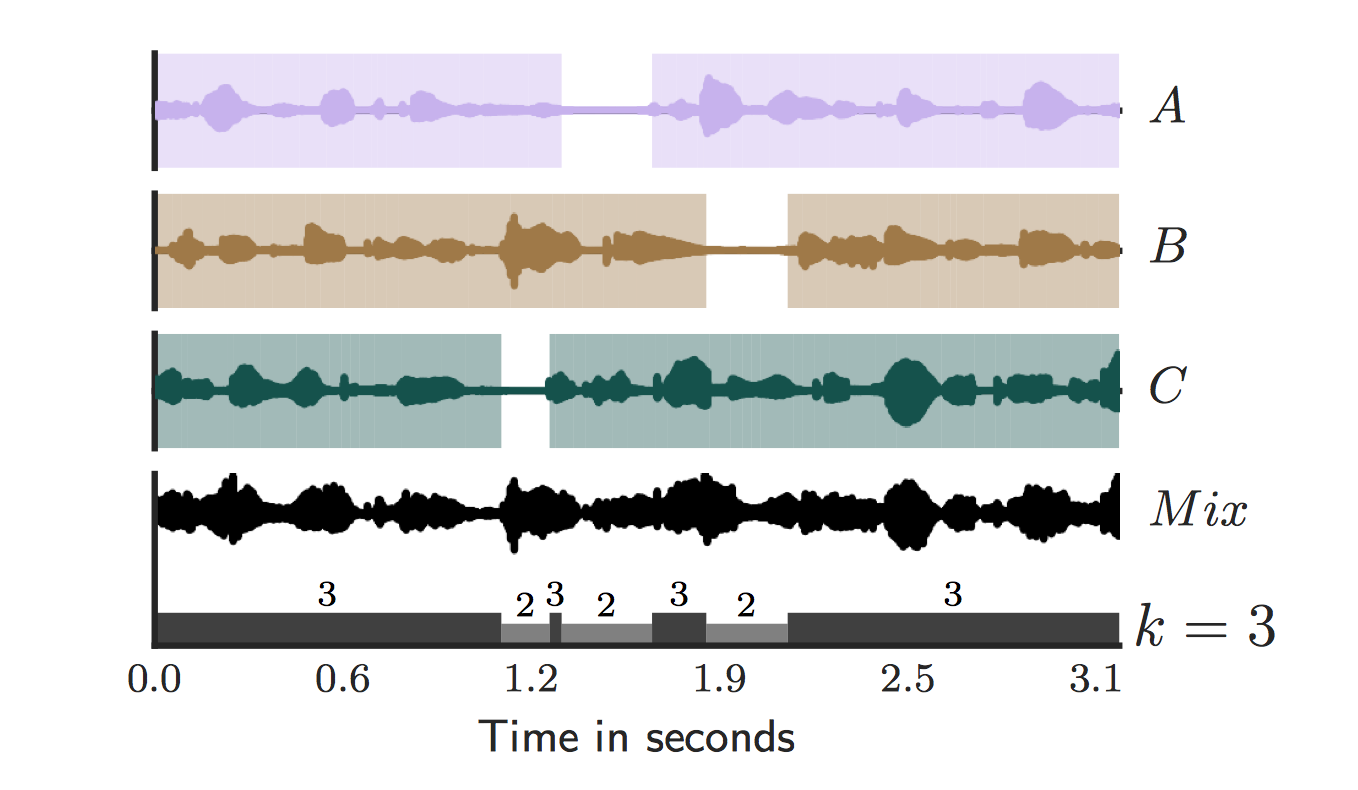
The dataset contains a simulated cocktail party environment of [0..10] speakers, mixed with 0dB SNR from random utterances of different speakers from the LibriSpeech CleanTest dataset.
For each recording we provide the ground truth number of speakers within the file name, where k in, k_uniquefile.wav is the maximum number of concurrent speakers with the 5 seconds of recording.
All recordings are of 5s durations. For each unique recording, we provide the audio wave file (16bits, 16kHz, mono) and an annotation json file with the same name as the recording.
Metadata
In the annotation file we provide information about the speakers sex, their unique speaker_id, and vocal activity within the mixture recording in samples. Note that these were automatically generated using a voice activity detection method.
In the following example a speaker count of 3 speakers is the ground truth.
[
{
"sex": "F",
"activity": [[0, 51076], [51396, 55400], [56681, 80000]],
"speaker_id": 1221
},
{
"sex": "F",
"activity": [[0, 51877], [56201, 80000]],
"speaker_id": 3570
},
{
"sex": "M",
"activity": [[0, 15681], [16161, 68213], [73498, 80000]],
"speaker_id": 5105
}
]License
MIT