This Swift library allows you to integrate the Uber Rides API into your iOS app.
- iOS 8.0+
- Xcode 10.0+
- Swift 4.2+
To install the Uber Rides SDK, you may use CocoaPods, Carthage, or add it to your project manually
pod 'UberRides', '~> 0.11'github "uber/rides-ios-sdk" ~> 0.11
To begin making calls to the Uber API, you need to register an application on the Uber Developer Site and get credentials for your app.
Then, configure your Xcode with information for the Uber SDK. Locate the Info.plist file for your application. Right-click this file and select Open As > Source Code
Add the following code snippet, replacing the placeholders within the square brackets ([]) with your app’s information from the developer dashboard. (Note: Do not include the square brackets)
<key>UberClientID</key>
<string>[ClientID]</string>
<key>UberServerToken</key>
<string>[Server Token]</string>
<key>UberDisplayName</key>
<string>[App Name]</string>
<key>LSApplicationQueriesSchemes</key>
<array>
<string>uber</string>
<string>uberauth</string>
</array>
Note: Your Server Token is used to make Price & Time estimates when your user hasn't authenticated with Uber yet. We suggest adding it in your Info.plist only if you need to get estimates before your user logs in.
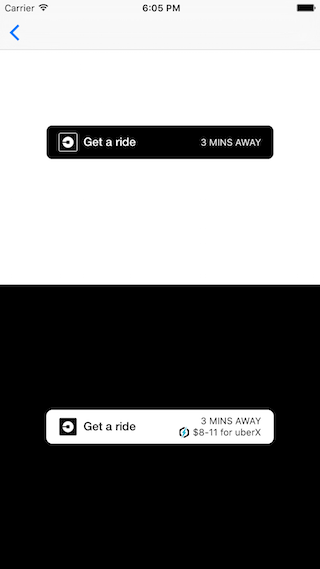
The RideRequestButton is a simple way to show price and time estimates for Uber products and can be customized to perform various actions. The button takes in RideParameters that can describe product ID, pickup location, and dropoff location. By default, the button shows no information.
To display a time estimate, set the product ID and pickup location. To display a price estimate, you need to additionally set a dropoff location.
Import the library into your project, and add a Ride Request Button to your view like you would any other UIView:
// Swift
import UberRides
let button = RideRequestButton()
view.addSubview(button)// Objective-C
@import UberRides;
UBSDKRideRequestButton *button = [[UBSDKRideRequestButton alloc] init];
[view addSubview:button];This will create a request button with default behavior, with the pickup pin set to the user’s current location. The user will need to select a product and input additional information when they are switched over to the Uber application.
The SDK provides an simple object for defining your ride requests. The RideParameters object lets you specify pickup location, dropoff location, product ID, and more. Creating RideParameters is easy using the RideParametersBuilder object.
// Swift
import UberRides
import CoreLocation
let builder = RideParametersBuilder()
let pickupLocation = CLLocation(latitude: 37.787654, longitude: -122.402760)
let dropoffLocation = CLLocation(latitude: 37.775200, longitude: -122.417587)
builder.pickupLocation = pickupLocation
builder.dropoffLocation = dropoffLocation
builder.dropoffNickname = "Somewhere"
builder.dropoffAddress = "123 Fake St."
let rideParameters = builder.build()
let button = RideRequestButton(rideParameters: rideParameters)// Objective-C
@import UberRides;
@import CoreLocation;
UBSDKRideParametersBuilder *builder = [[UBSDKRideParametersBuilder alloc] init];
CLLocation *pickupLocation = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:37.787654 longitude:-122.402760];
CLLocation *dropoffLocation = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:37.775200 longitude:-122.417587];
[builder setPickupLocation:pickupLocation];
[builder setDropoffLocation:dropoffLocation];
[builder setDropoffAddress:@"123 Fake St."];
[builder setDropoffNickname:@"Somewhere"];
UBSDKRideParameters *rideParameters = [builder build];
UBSDKRideRequestButton *button = [[UBSDKRideRequestButton alloc] initWithRideParameters:rideParameters];We suggest passing additional parameters to make the Uber experience even more seamless for your users. For example, dropoff location parameters can be used to automatically pass the user’s destination information over to the driver. With all the necessary parameters set, pressing the button will seamlessly prompt a ride request confirmation screen.
Note: If you are using a RideRequestButton that deeplinks into the Uber app and you want to specify a dropoff location, you must provide a nickname or formatted address for that location. Otherwise, the pin will not display.
You can also use the RideRequestButtonDelegate to be informed of success and failure events during a button refresh.
If you don't want to use the Uber-provided button, you can also manually initiate a deeplink in a similar fashion as above:
// Swift
import UberRides
import CoreLocation
let builder = RideParametersBuilder()
// ...
let rideParameters = builder.build()
let deeplink = RequestDeeplink(rideParameters: rideParameters)
deeplink.execute()// Objective-C
@import UberRides;
@import CoreLocation;
UBSDKRideParametersBuilder *builder = [[UBSDKRideParametersBuilder alloc] init];
// ...
UBSDKRideParameters *rideParameters = [builder build];
UBSDKRequestDeeplink *deeplink = [[UBSDKRequestDeeplink alloc] initWithRideParameters:rideParameters];
[deeplink executeWithCompletion:nil];With the Ride Request deeplink, you can specify a fallback for users that don't have the Uber app installed. With a fallback, they'll get redirected to either the mobile web version of Uber, or the App Store. To do so, simply add the fallbackType parameter:
// Swift
let deeplink = RequestDeeplink(rideParameters: rideParameters, fallbackType: .mobileWeb) // Or .appStore
// Objective-C
UBSDKRequestDeeplink *requestDeeplink = [[UBSDKRequestDeeplink alloc] initWithRideParameters:rideParameters
fallbackType:UBSDKDeeplinkFallbackTypeMobileWeb];To use any of the SDK's other features, you need to have the end user authorize your application to use the Uber API.
First, open up the Uber Developer Dashboard. Go to the Authorizations tab and under App Signatures, put in your iOS application's Bundle ID.
We also need to register a Redirect URL for your application. This ensures that Uber sends users to the correct application after they log in. Make a URL in this format, and save your application: YourApplicationBundleID://oauth/consumer.
In your Xcode project, you need to register your URL scheme as well as the callback URL with the Uber SDK. Copy this into your Info.plist, replacing the relevant values:
Note: If one of the following keys already exists in your
Info.plistfile, you will have to add the values to them and not duplicate the keys.
<key>UberCallbackURIs</key>
<array>
<dict>
<key>UberCallbackURIType</key>
<string>General</string>
<key>URIString</key>
<string>[Your Bundle ID Here]://oauth/consumer</string>
</dict>
</array>
<key>CFBundleURLTypes</key>
<array>
<dict>
<key>CFBundleTypeRole</key>
<string>Editor</string>
<key>CFBundleURLSchemes</key>
<array>
<string>[Your Bundle ID Here]</string>
</array>
</dict>
</array>
You also need to modify your application's App Delegate to make calls to the RidesAppDelegate to handle URLs.
// Swift
// Add the following calls to your AppDelegate
import UberCore
@available(iOS 9, *)
func application(_ app: UIApplication, open url: URL, options: [UIApplicationOpenURLOptionsKey : Any]) -> Bool {
let handledUberURL = UberAppDelegate.shared.application(app, open: url, sourceApplication: options[UIApplicationOpenURLOptionsKey.sourceApplication] as? String, annotation: options[UIApplicationOpenURLOptionsKey.annotation] as Any)
return handledUberURL
}
func application(_ application: UIApplication, open url: URL, sourceApplication: String?, annotation: Any) -> Bool {
let handledUberURL = UberAppDelegate.shared.application(application, open: url, sourceApplication: sourceApplication, annotation: annotation)
return handledUberURL
}// Objective-C
// Add the following calls to your AppDelegate
@import UberCore;
// iOS 9+
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)app openURL:(NSURL *)url options:(NSDictionary<NSString *,id> *)options {
BOOL handledURL = [[UBSDKAppDelegate shared] application:app open:url sourceApplication:options[UIApplicationOpenURLOptionsSourceApplicationKey] annotation:options[UIApplicationOpenURLOptionsAnnotationKey]];
return handledURL;
}
// iOS 8
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application openURL:(NSURL *)url sourceApplication:(NSString *)sourceApplication annotation:(id)annotation {
BOOL handledURL = [[UBSDKAppDelegate shared] application:application open:url sourceApplication:sourceApplication annotation:annotation];
return handledURL;
}The LoginButton is a simple way to authorize your users. You initialize the button requesting certain scopes, or permissions from Uber. More about scopes. When the user taps the button, the login will be executed.
You can optionally set a LoginButtonDelegate to receive notifications for login/logout success.
// Swift
import UberCore
let scopes: [UberScope] = [.profile, .places, .request]
let loginManager = LoginManager(loginType: .native)
let loginButton = LoginButton(frame: CGRect.zero, scopes: scopes, loginManager: loginManager)
loginButton.presentingViewController = self
loginButton.delegate = self
view.addSubview(loginButton)
// Mark: LoginButtonDelegate
func loginButton(_ button: LoginButton, didLogoutWithSuccess success: Bool) {
// success is true if logout succeeded, false otherwise
}
func loginButton(_ button: LoginButton, didCompleteLoginWithToken accessToken: AccessToken?, error: NSError?) {
if let _ = accessToken {
// AccessToken Saved
} else if let error = error {
// An error occured
}
}// Objective-C
@import UberCore;
NSArray<UBSDKScope *> *scopes = @[UBSDKScope.profile, UBSDKScope.places, UBSDKScope.request];
UBSDKLoginManager *loginManager = [[UBSDKLoginManager alloc] initWithLoginType:UBSDKLoginTypeNative];
UBSDKLoginButton *loginButton = [[UBSDKLoginButton alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectZero scopes:scopes loginManager:loginManager];
loginButton.presentingViewController = self;
[loginButton sizeToFit];
loginButton.delegate = self;
[self.view addSubview:loginButton];
#pragma mark - UBSDKLoginButtonDelegate
- (void)loginButton:(UBSDKLoginButton *)button didLogoutWithSuccess:(BOOL)success {
// success is true if logout succeeded, false otherwise
}
- (void)loginButton:(UBSDKLoginButton *)button didCompleteLoginWithToken:(UBSDKAccessToken *)accessToken error:(NSError *)error {
if (accessToken) {
// UBSDKAccessToken saved
} else if (error) {
// An error occured
}
}If you want to provide a more custom experience in your app, there are a few classes to familiarize yourself with. Read the sections below and you’ll be requesting rides in no time!
The SDK exposes all the endpoints available in the Uber Developers documentation. Some endpoints can be authenticated with a server token, but for most endpoints, you will require a bearer token. A bearer token can be retrieved via implicit grant, authorization code grant, or SSO. To authorize privileged scopes, you must use authorization code grant or SSO.
Read the full API documentation at CocoaDocs
The RidesClient is your source to access all the endpoints available in the Uber Rides API. With just your server token, you can get a list of Uber products as well as price and time estimates.
// Swift example
let ridesClient = RidesClient()
let pickupLocation = CLLocation(latitude: 37.787654, longitude: -122.402760)
ridesClient.fetchProducts(pickupLocation: pickupLocation, completion:{ products, response in
if let error = response.error {
// Handle error
return
}
for product in products {
// Use product
}
})// Objective-C example
UBSDKRidesClient *ridesClient = [[UBSDKRidesClient alloc] init];
CLLocation *pickupLocation = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude: 37.787654 longitude: -122.402760];
[ridesClient fetchProductsWithPickupLocation: pickupLocation completion:^(NSArray<UBSDKProduct *> * _Nullable products, UBSDKResponse *response) {
if (response.error) {
// Handle error
return;
}
for (UBSDKProduct *product in products) {
// Use product
}
}];To get access to more informative endpoints, you need to have the end user authorize your application to access their Uber data.
The easiest form of authorization is using the .native login type. It allows you to request Privileged scopes and, if your user is logged into the Uber app, it doesn't require your user to enter a username and password. It requires the user to have the native Uber application on their device.
Native authentication can occur either through the main Uber rides app or through the Uber Eats app. You can also fallback from one app to another, so that for example if the user does not have the UberEats app installed on their device, you can instead authenticate through the main Uber rides app:
// Swift
let loginManager = LoginManager(loginType: .native, productFlowPriority: [UberAuthenticationProductFlow(.eats), UberAuthenticationProductFlow(.rides)])// Objective-C
UBSDKUberAuthenticationProductFlow *eatsProduct = [[UBSDKUberAuthenticationProductFlow alloc] init:UberProductTypeEats];
UBSDKUberAuthenticationProductFlow *ridesProduct = [[UBSDKUberAuthenticationProductFlow alloc] init:UberProductTypeRides];
UBSDKLoginManager *loginManager = [[UBSDKLoginManager alloc] initWithLoginType:loginType productFlowPriority:@[ eatsProduct, ridesProduct ]];The LoginManager defaults to using the Native login type using the main Uber rides app, so you can simply instantiate a LoginManager and call login() with your requested scopes.
// Swift
let loginManager = LoginManager()
loginManager.login(requestedScopes:[.request], presentingViewController: self, completion: { accessToken, error in
// Completion block. If accessToken is non-nil, you’re good to go
// Otherwise, error.code corresponds to the RidesAuthenticationErrorType that occured
})// Objective-C
UBSDKLoginManager *loginManager = [[UBSDKLoginManager alloc] init];
[loginManager loginWithRequestedScopes:@[ UBSDKScope.request ] presentingViewController: self completion: ^(UBSDKAccessToken * _Nullable accessToken, NSError * _Nullable error) {
// Completion block. If accessToken is non-nil, you're good to go
// Otherwise, error.code corresponds to the RidesAuthenticationErrorType that occured
}];Note: The presentingViewController parameter is optional, but if provided, will attempt to intelligently fallback to another login method. Otherwise, it will redirect the user to the App store to download the Uber app.
| Auth Method | Token Type | Allowed Scopes |
|---|---|---|
| None | Server | None (can access products and estimates) |
| Implicit Grant | Bearer | General |
| Authorization Code Grant | Bearer | Privileged and General |
| SSO | Bearer | Privileged and General |
If your app allows users to authorize via your own customized logic, you will need to create an AccessToken manually and save it in the keychain using the TokenManager.
// Swift
let accessTokenString = "access_token_string"
let token = AccessToken(tokenString: accessTokenString)
if TokenManager.save(accessToken: token) {
// Success
} else {
// Unable to save
}// Objective-C
NSString *accessTokenString = @"access_token_string";
UBSDKAccessToken *token = [[UBSDKAccessToken alloc] initWithTokenString: accessTokenString];
if ([UBSDKTokenManager saveWithAccessToken: token]) {
// Success
} else {
// Unable to save
}The TokenManager can also be used to fetch and delete AccessTokens
// Swift
TokenManger.fetchToken()
TokenManager.deleteToken()// Objective-C
[UBSDKTokenManager fetchToken];
[UBSDKTokenManager deleteToken];Uber developers actively monitor the Uber Tag on StackOverflow. If you need help installing or using the library, you can ask a question there. Make sure to tag your question with uber-api and ios!
For full documentation about our API, visit our Developer Site.
We ❤️ contributions. Found a bug or looking for a new feature? Open an issue and we'll respond as fast as we can. Or, better yet, implement it yourself and open a pull request! We ask that you include tests to show the bug was fixed or the feature works as expected.
Note: All contributors also need to fill out the Uber Contributor License Agreement before we can merge in any of your changes.
Please open any pull requests against the develop branch.
The Uber Rides iOS SDK is released under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more details.