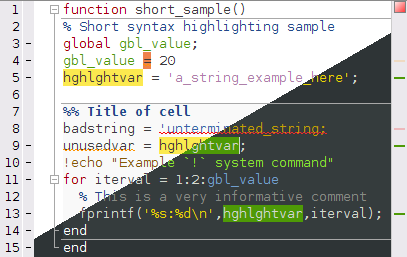
This MATLAB package makes it easy to change the color scheme (a.k.a. theme) of the MATLAB display and GUI.
You can use Schemer to import a predefined color scheme, transfer your color settings between installations, or create your own color scheme.
A collection of color schemes is available in the schemes folder. Samples of these can be seen in schemes/README.md, and browsed in the folder schemes/screenshots. This is a static subtree copy of the contents of the repository matlab-schemes.
Color schemes can be easily imported by running schemer_import at the MATLAB
command prompt, without needing any inputs. This will open a GUI to select the
file to import the color scheme from.
When importing a color scheme, most of the settings will change immediately. However, some settings will require MATLAB to be restarted:
- Variable highlighting colours
- Wavy underlines for errors
- Wavy underlines for warnings
For more details, see the documentation on the function schemer_import,
available with help schemer_import.
If you are using a personalised color scheme in MATLAB, you may wish to save it for yourself so you can re-implement it easily if you reintall MATLAB. Or you may wish to transfer your personalised color scheme from one machine to another. This section describes the steps relevant in either scenario.
On the source machine, run schemer_export to save a temporary color scheme
file, and then transfer this file to the destination machine.
When importing the new color scheme, instead of running schemer_import without
any inputs, you should run schemer_import(true). This passes a flag to tell
the function to not only import the colour preferences, but to also import your
boolean settings (such as whether to highlight the current cell/line, etc)
from the file you exported from the source installation.
Should you wish to revert to the set of colours which MATLAB ships with, you
should run schemer_import('schemes/default.prf').
This will import the MATLAB default theme from the stylesheet default.prf
which comes as part of Schemer.
To restore the out-of-the-box state for boolean settings (such as whether to
highlight the current line) in addition to the colours, run
schemer_import('schemes/default.prf', true).
You may be tempted to instead revert the colours by clicking the
Restore Default Colors buttons in the Color pane of the MATLAB preferences.
However, this will be less effective than importing the default colours through
Schemer because these buttons will not reset all the MATLAB colour preferences.
(There is no reset button for the Editor display preferences pane, nor for the
other language syntax supported by MATLAB, which is available in the Editor
Languages panel.)
When creating a color scheme to share with the rest of the world, it is recommended to ensure colours are chosen appropriately for all possible settings, even if they are not enabled.
For example, if you are creating a dark colour scheme, you may have cell highlighting disabled but it would still be ill-advised to leave the background highlight colour for cell displays as the default pale beige because other users may have this setting enabled.
If you have made a custom color scheme using the MATLAB GUI to pick the colours,
you can export the new color scheme with schemer_export.
Please note, this requires you to have visited all relevant panes of the
Preferences window at least once since MATLAB was installed, even if the
settings have not been changed from the default.
See the help for schemer_export for more details.
If you are converting a color scheme designed for another editor into a MATLAB stylesheet, you may find it easier to start with a duplicate of the template stylesheet develop/template_scheme.prf and copy the colours into this.
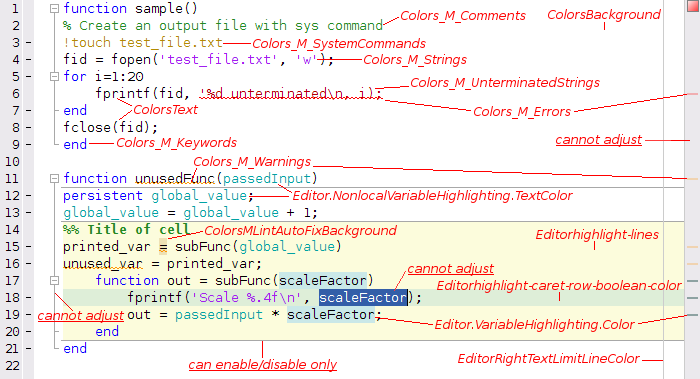
To understand which colour settings the parameter names correspond to, you can refer to the annotated screenshot, develop/annotated_default.png.
The values for each colour in the .prf stylesheet must be recorded as single
RGB integers, with each colour channel in 8-bit (0-255), R as big endian,
and a opaque alpha channel. Because the format for RGB colours in Java allows
for an alpha channel and the integers are signed, all the colours you record
in your .prf file should be negative, spanning the range
-16777216 (black, [0,0,0]) to -1 (white, [255,255,255]).
The text file for your pre-existing theme will typically specify its colous in
hexadecimal format, or in terms of R, G, B values. You will need
to convert the colours from this format into the format which MATLAB preference
files use to specify colours instead.
The Schemer package comes with a utility function
develop/color2javaRGBint.m
to help make this easier. See the color2javaRGBint documentation for more
details.
MATLAB supports syntax highlighting for several languanges in addition to its own. Currently these languages are MuPAD, TLC, VRML, C/C++, Java, VHDL, Verilog, and XML/HTML. The colours used for the syntax highlighting of all these languages can be set in the Languages subpanel of the Editor/Debugger pane in the Preferences window.
Typically, one will want to make a color scheme which has colours in these languages which match the colours of the analogous MATLAB syntax. By default, this is the behaviour which Schemer will perform.
Without specifying any inputs to schemer_export, an exported color scheme file
will contain only the colours used for MATLAB syntax highlighting and no other
languages, since it is expected that users will typically not set the colours
for any of these languages. When this is loaded with schemer_import, the missing
colours for additional languages are automatically completed based on the MATLAB
syntax.
If you do customise the colours for the additional language syntax highlighting,
you can export this by setting an appropriate flag, such as schemer_export(3).
For more details, see the schemer_export documentation.
If you are designing a color scheme and are very detail-oriented, you may like to do the following.
- Configure the colours for the MATLAB syntax first in the Preferences > Colors panel and Programming Tools subpanel, along with Editor/Debugger > Display preference pane for the Current line highlighting and Right-hand text limit.
- Export the colorscheme with
schemer_export('tmp.prf',1), excluding additional language syntax from the export. - Load the colorscheme with
schemer_import('tmp.prf'), which overwrites the syntax for the additional languages with automatically inferred colours. - Open up the panel Preferences > Editor/Debugger > Languages and inspect the quality of the colorscheme in the addition languages.
- Fix or improve any perceived issues with the colorscheme in the Languages panel.
- Export the colorscheme again, but this time with
schemer_export(3)to include the customised colours for the additional languages.
If you are particularly proud of your new color scheme (and why wouldn't you be)
and would like to to share it with the world as part of the matlab-schemer
package, this is possible!
Please head over to our daughter repository, matlab-schemes, which holds the master copy of the color schemes issued here as part of Schemer in the schemes directory.
If you fork matlab-schemes, add your .prf file and issue a pull request,
the new scheme will be reviewed and added to the repository.
This content is then mirrored here using git subtree. For more details, see
our CONTRIBUTING.md.
Please note that Schemer requires MATLAB to be run with Java support enabled.
For details on how the method was implemented, see this Undocumented Matlab article.