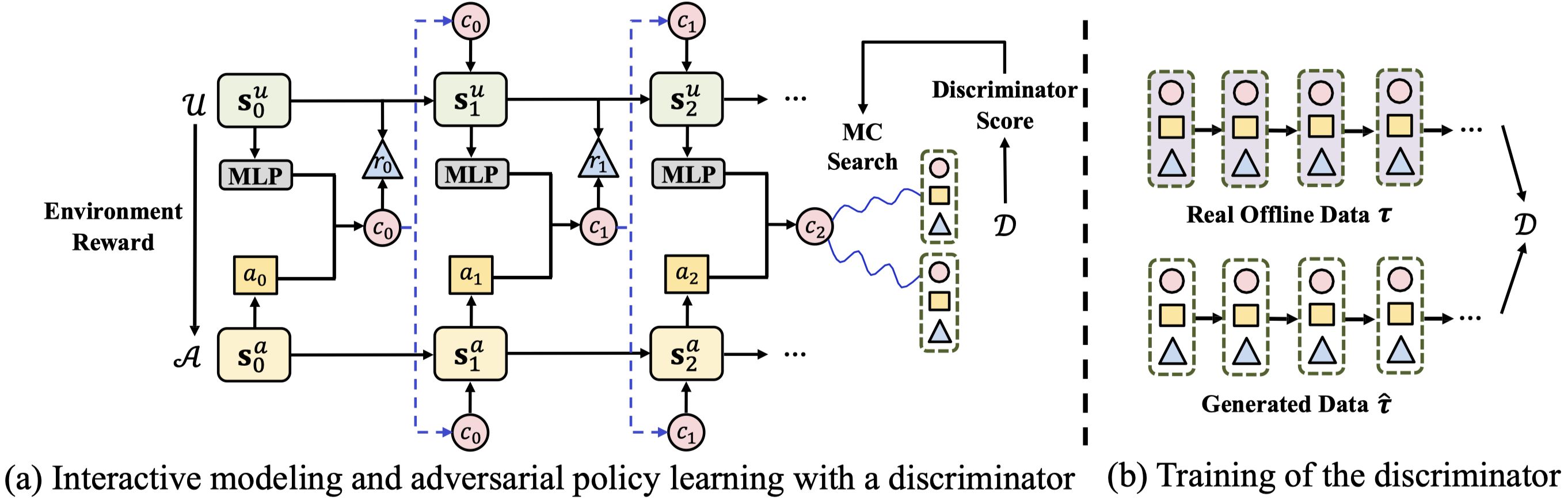
Reinforcement learning is effective in optimizing policies for recommender systems. Current solutions mostly focus on model-free approaches, which require frequent interactions with a real environment, and thus are expensive in model learning. Offline evaluation methods, such as importance sampling, can alleviate such limitations, but usually request a large amount of logged data and do not work well when the action space is large. In this work, we propose a model-based reinforcement learning solution which models the user-agent interaction for offline policy learning via a generative adversarial network. To reduce bias in the learnt policy, we use the discriminator to evaluate the quality of generated sequences and rescale the generated rewards. Our theoretical analysis and empirical evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of our solution in identifying patterns from given offline data and learning policies based on the offline and generated data.
This project is a tensorflow implementation of our work.
- Python 2.7
- Numpy 1.14.5
- Tensorflow 1.3.1
We conduct empirical evaluations on both real-world and synthetic datasets to demonstrate that our solution can effectively model the pattern of data for better recommendations, compared with state-of-the-art baselines.
-
Simulated online evaluation
We synthesize an MDP to simulate an online recommendation environment. It has 10 states and 50 items for recommendation, with a randomly initialized transition probability matrix. Under each state, an item's reward is uniformly sampled from the range of 0 to 1. During the interaction, given a recommendation list including 10 items selected from the whole item set by an agent, the simulator first samples an item proportional to its ground-truth reward under the current state as the click candidate. A Bernoulli experiment is performed on this item with the corresponding reward as the success probability; then the simulator moves to the next state according to the state transition probability. A special state is used to initialize all the sessions, which do not stop until the Bernoulli experiment fails. The immediate reward is 1 if the session continues to the next step; otherwise 0. You can begin generating simulated data by executing the following command:
python mdp.py -
Real-world offline evaluation
We use a large-scale recommendation dataset from CIKM Cup 2016 to evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed solution for offline reranking. We filtered out sessions of length 1 or longer than 40 and items that have never been clicked. We selected the top 40,000 most popular items to construct our recommendation candidate set. We randomly selected 65,284/1,718/1,820 sessions for training/validation/testing purposes, where the average length of sessions is 2.81/2.80/2.77 respectively. The percentage of recorded recommendations that lead to a purchase is 2.31%/2.46%/2.45%. The processed dataset can be downloaded here. You can begin training the IRecGAN network just by executing the following command:
python main.py
Xueying Bai*, Jian Guan*, Hongning Wang. Model-Based Reinforcement Learning with Adversarial Training for Online Recommendation. Published in the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2019), Vancouver, Canada. Here is the preprint paper and poster.
Contact info: j-guan19@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn (Welcome any suggestions or questions.)