Sensor Fusion UKF Highway Project Starter Code
In this project you will implement an Unscented Kalman Filter to estimate the state of multiple cars on a highway using noisy lidar and radar measurements. Passing the project requires obtaining RMSE values that are lower that the tolerance outlined in the project rubric.
The main program can be built and ran by doing the following from the project top directory.
- mkdir build
- cd build
- cmake ..
- make
- ./ukf_highway
Note that the programs that need to be written to accomplish the project are src/ukf.cpp, and src/ukf.h
The program main.cpp has already been filled out, but feel free to modify it.
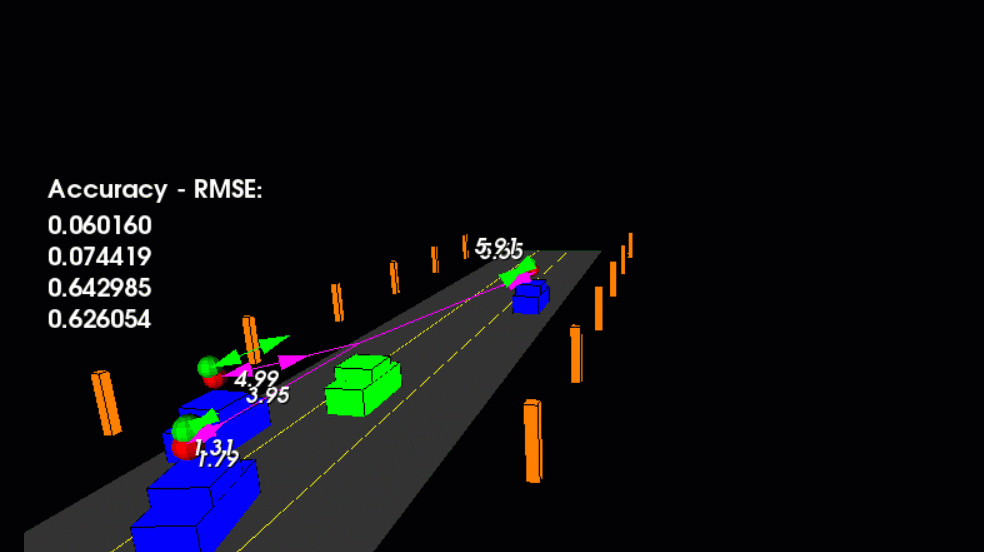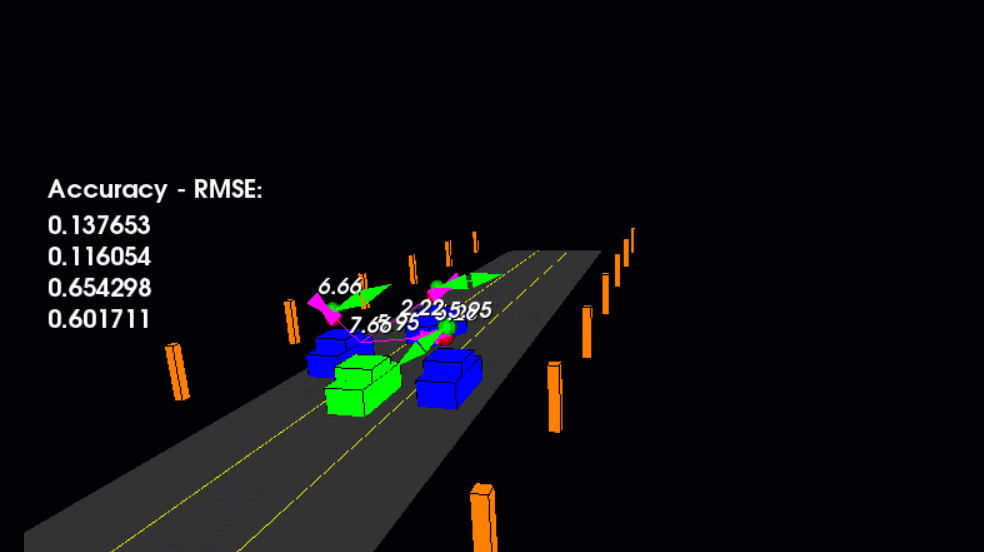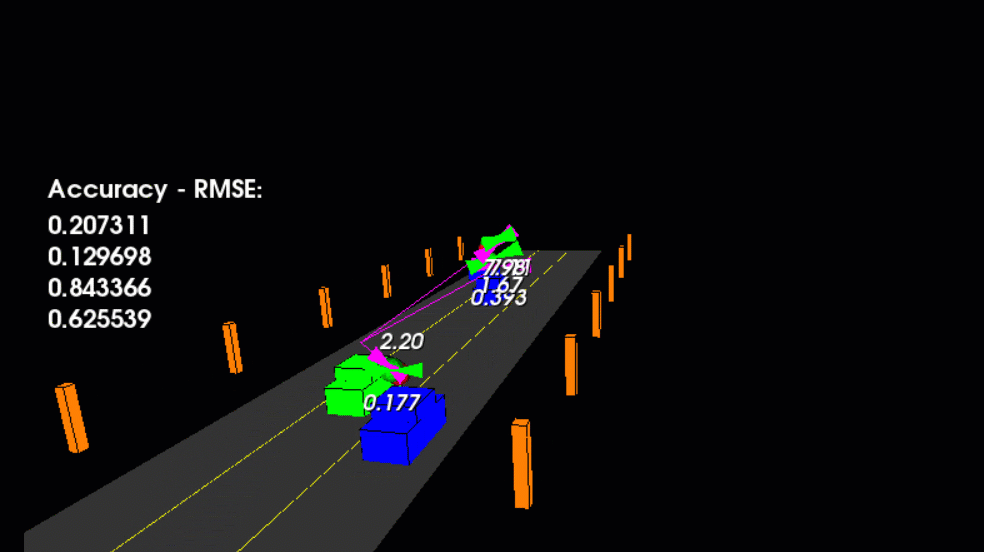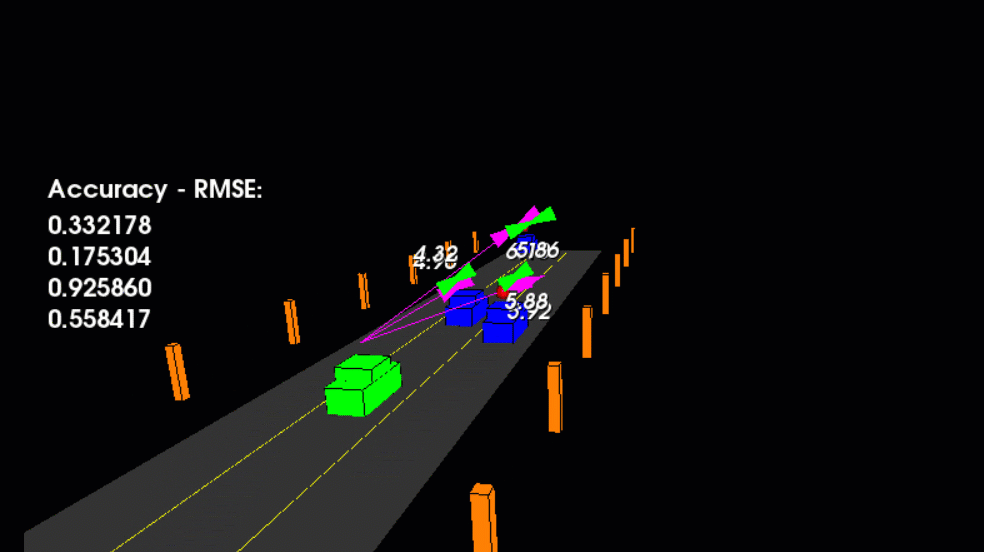
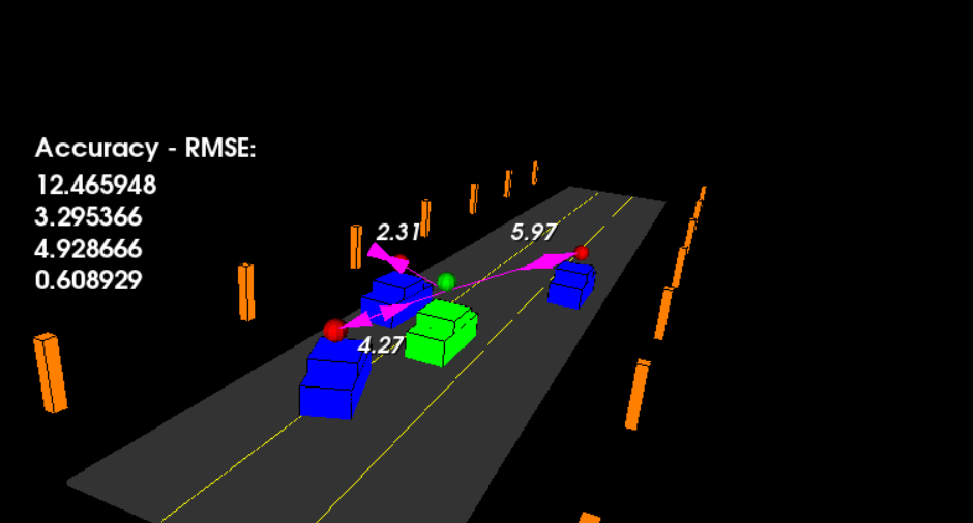
main.cpp is using highway.h to create a straight 3 lane highway environment with 3 traffic cars and the main ego car at the center.
The viewer scene is centered around the ego car and the coordinate system is relative to the ego car as well. The ego car is green while the
other traffic cars are blue. The traffic cars will be accelerating and altering their steering to change lanes. Each of the traffic car's has
it's own UKF object generated for it, and will update each indidual one during every time step.
The red spheres above cars represent the (x,y) lidar detection and the purple lines show the radar measurements with the velocity magnitude along the detected angle. The Z axis is not taken into account for tracking, so you are only tracking along the X/Y axis.
- cmake >= 3.5
- All OSes: click here for installation instructions
- make >= 4.1 (Linux, Mac), 3.81 (Windows)
- Linux: make is installed by default on most Linux distros
- Mac: install Xcode command line tools to get make
- Windows: Click here for installation instructions
- gcc/g++ >= 5.4
- Linux: gcc / g++ is installed by default on most Linux distros
- Mac: same deal as make - install Xcode command line tools
- Windows: recommend using MinGW
- PCL 1.2
UKF implementation follows the concept shown in the class. After implementation, some parameters had to be tuned to order to fulfill the rubric requirement of not crossing the RMSE threshhold. In order for the RMSE goes down faster, we needed a faster convergence of P_, which we achieve by setting a higher initial value.
Since it was mostly the velocity RMSE which could not hold the required threshhold, we set P_(2,2) to a higher initial value(e.g. 50).
For P_ of px and py, we can use a much lower value then 1 for laser, because the std deviation of laser for position is very low.
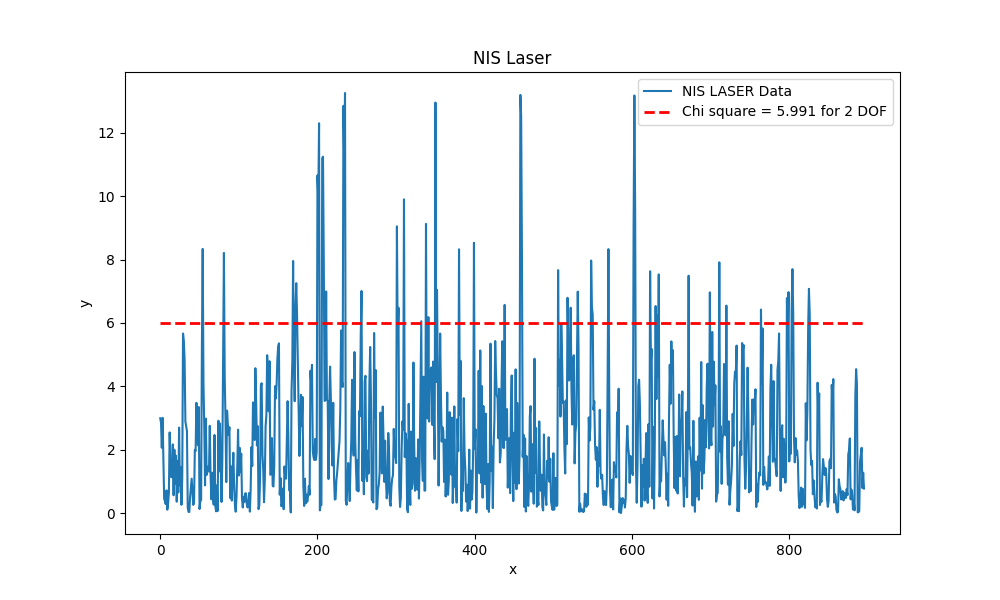
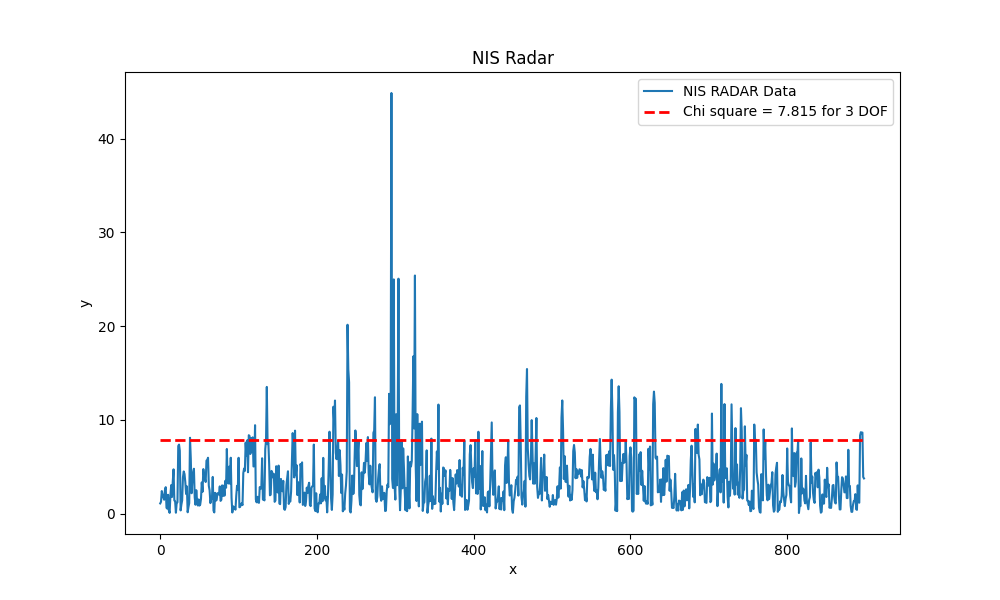
Using plot.py, we can plot the nis plot for laser and radar in order to check our filter for consistency. With our iteratively tuned process noise we get the following nis graphs:
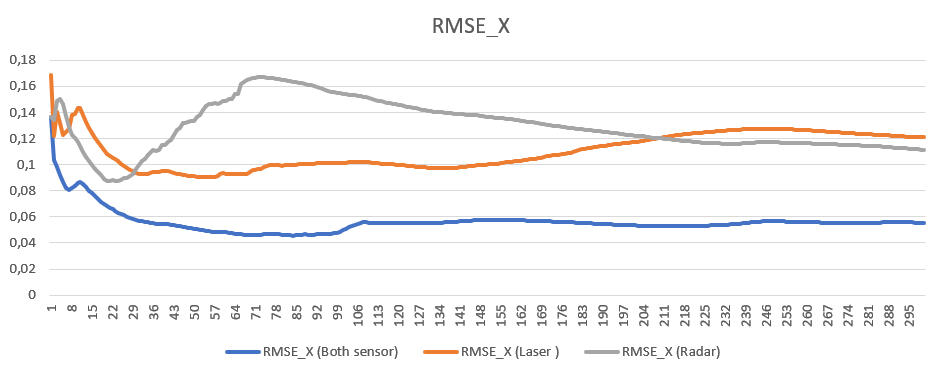
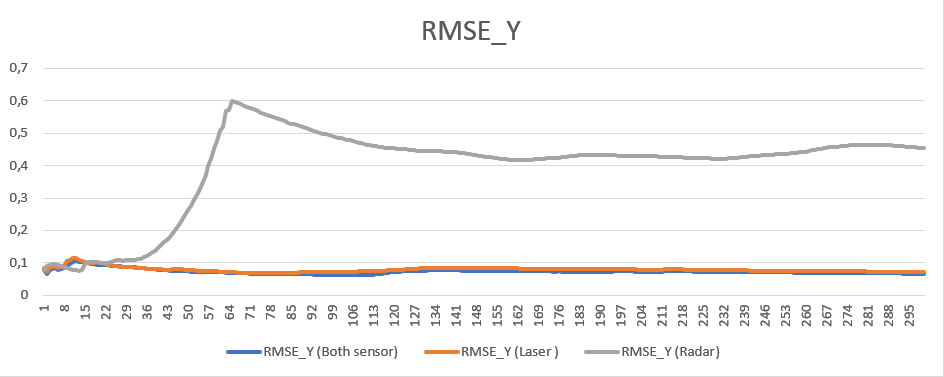
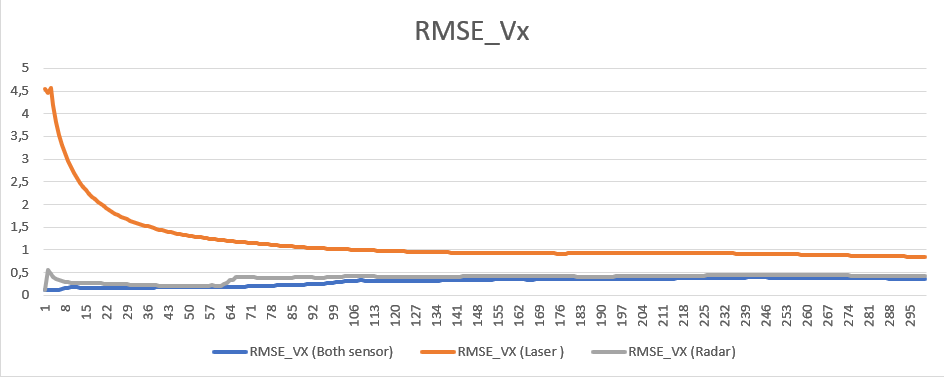
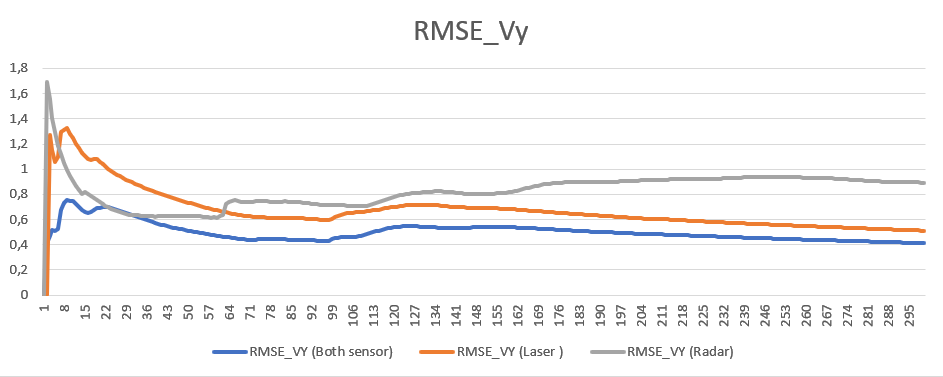
Finally, we take a look at the comparison of sensor fusion rmse results vs single sensor:
We can observe a single lidar sensor has better RMSE values compared to single radar regarding position, whereas radar sensor deliver better velocity RMSE results especially in x direction.
The main takeaway from the graphs though, is that multiple sensor always provide better results. Even in the case of e.g. position where radar has a much higher stddeviation then lidar, the combined measurement still provide lower RMSE.