Edit by Jan 27, 2024
HiPerGator is the University of Florida's supercomputer. Official Documents for Hipergator
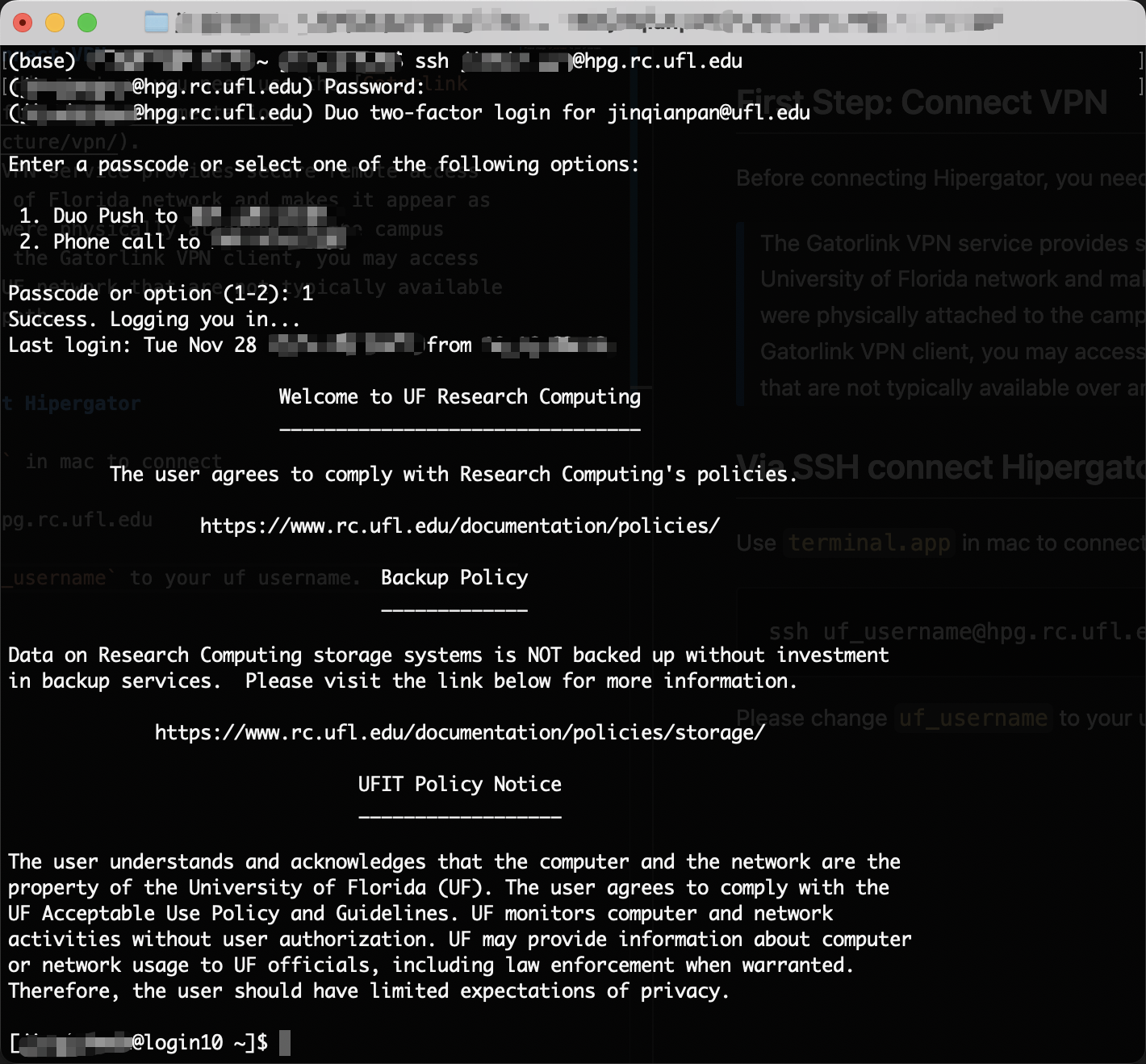
Before connecting Hipergator, you need use the Gatorlink VPN.
The Gatorlink VPN service provides secure remote access to the University of Florida network and makes it appear as if your computer were physically attached to the campus network. By using the Gatorlink VPN client, you may access resources on the UF network that are not typically available over an Internet path.
Use terminal.app in mac to connect
ssh uf_username@hpg.rc.ufl.edu
Please change uf_username to your uf username.
After typing password and select option, you are in the Hipergator.
Tip
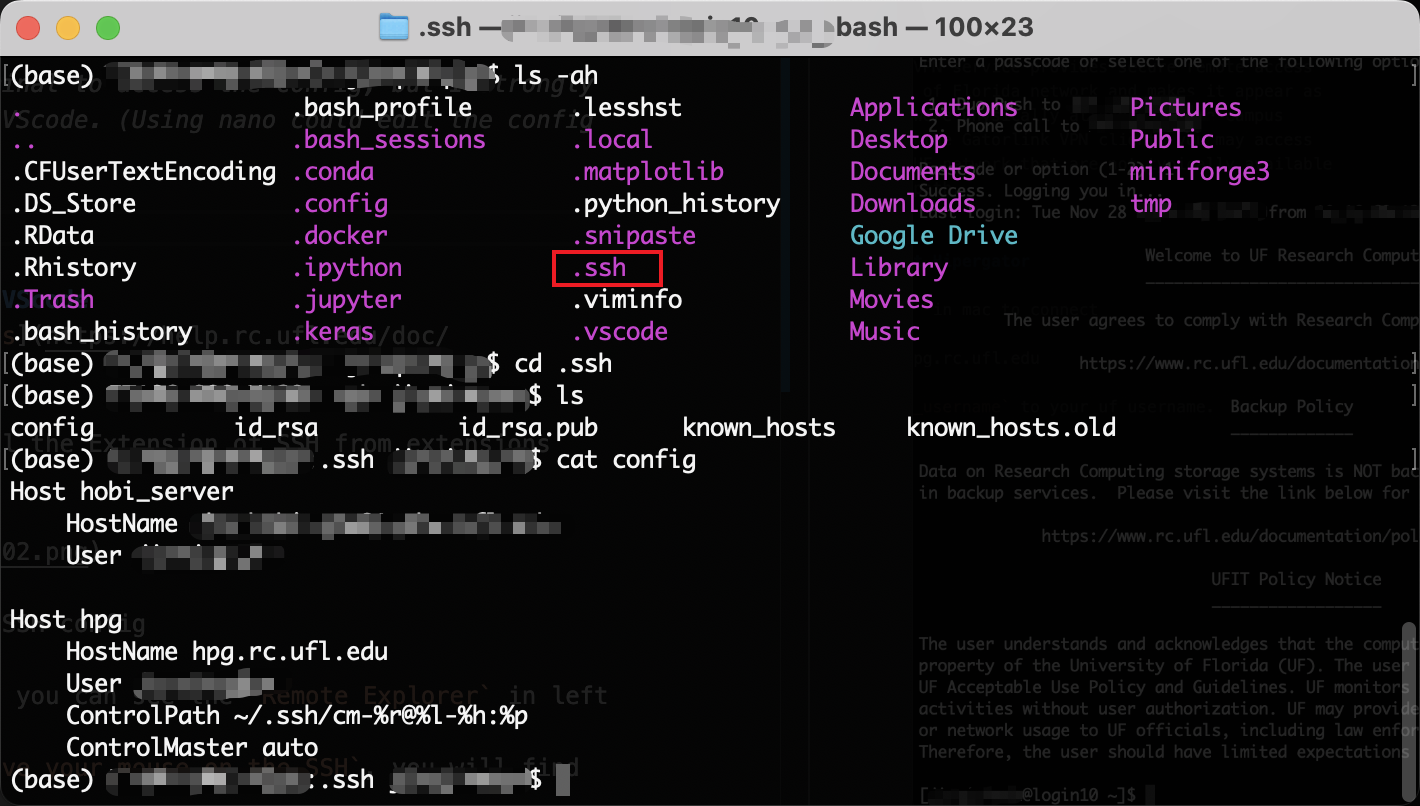
You can use terminal to access the config, but I strongly recommand to use VScode. The guide is in 0202 Set config in VScode.
Using nano could edit config file.
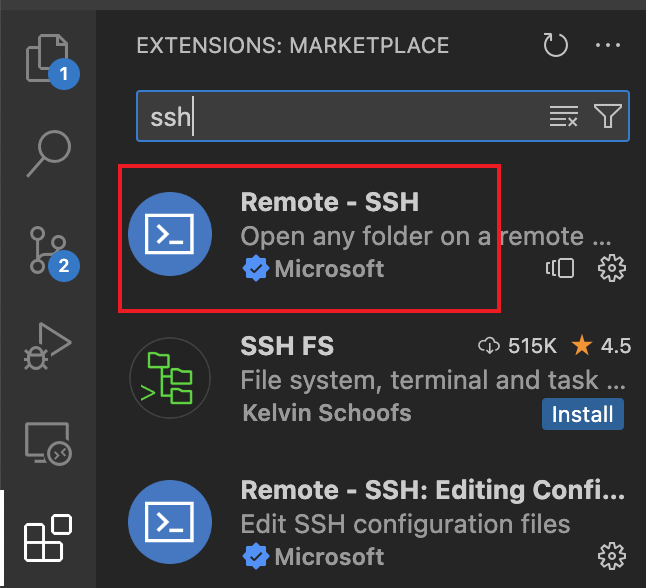
Step1: Install the Extension of SSH from extensions store.
Step2: Setup SSH config
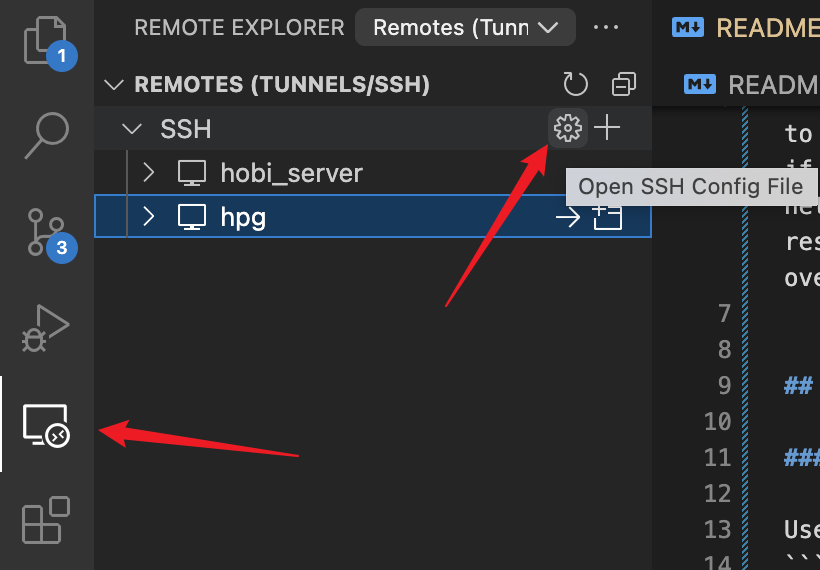
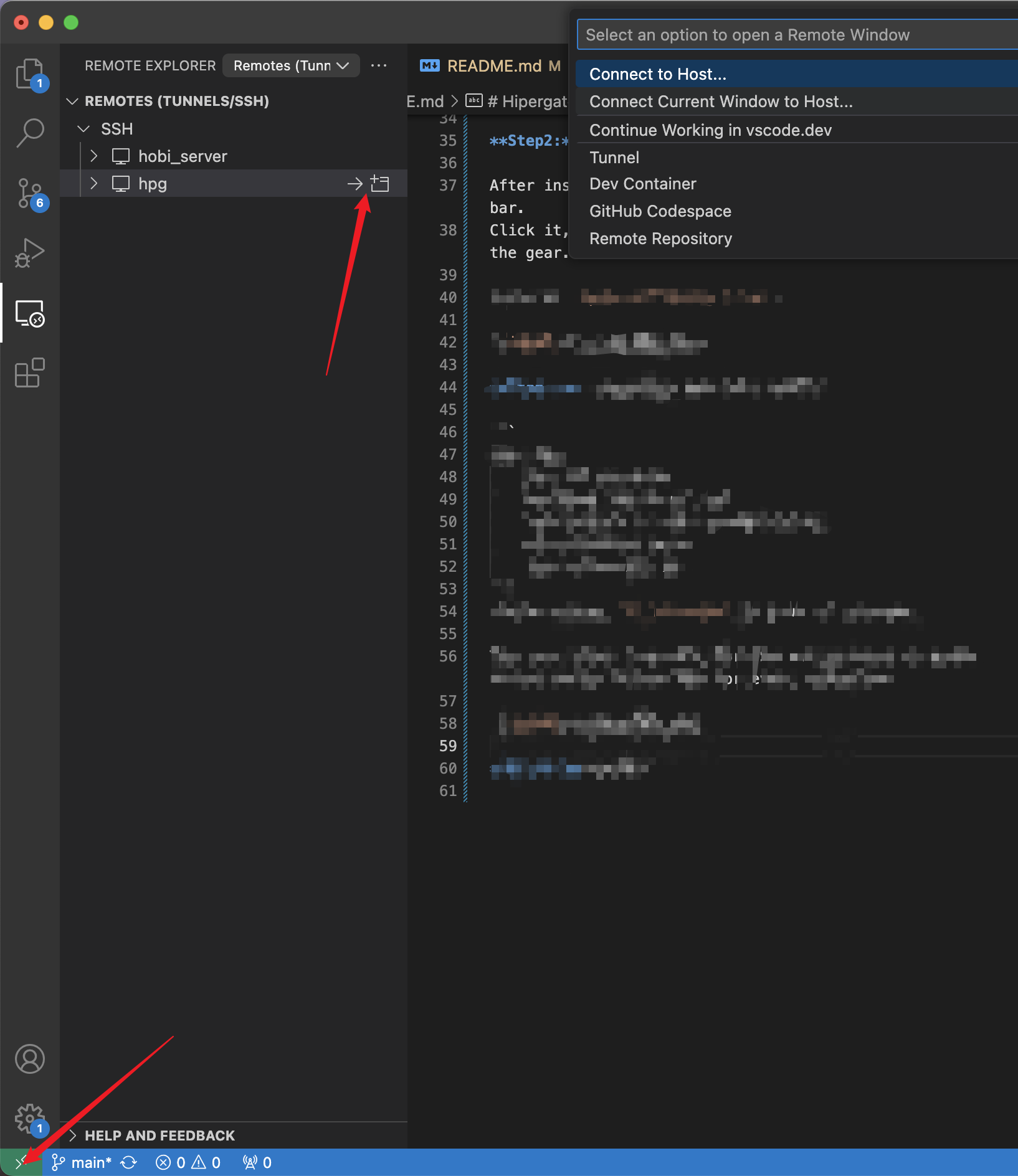
After installing, you can see the Remote Explorer in left bar.
Click it, and move your mouse on the SSH, you will find the gear.
Click to Open SSH Config File.
Step3: Copy&Paste and edit config
Official Documents for SSH Multiplexing
Host hpg
User uf_username
HostName hpg.rc.ufl.edu
ControlPath ~/.ssh/cm-%r@%l-%h:%p
ControlMaster auto
ControlPersist 8h
Please change uf_username to your uf username.
The last three line help for SSH Multiplexing to avoid having to go through MFA for every connection.
There are two ways in VScode. You can see two arrows in the image006.
Now you can type ssh hpg in the terminal to connect.
Official Documents for Storage
The storage has be divided in 4 part: home storage, blue storage, orange storage, and red storage.
Generally, we use home storage, blue storage, and orange storage.
Home Storage: When you log in, the first thing that appears in front of you is home storage.
It is permissible to keep
software builds, conda environments, text documents, and valuable scripts in $HOMEas it is somewhat protected by daily snapshots.
Blue Storage: This part is responsible for reading and writing. Under the condition that the data can be placed, we will put the data required for code running in this area.
Orange Storage: Data storage area (if our data can't be put in the blue storage, we will also put the data here).
Important
Run Efficiency: Home Storage > Blue Storage > Orange Storage
Storage Space: Orange Storage >> Blue Storage >> Home Storage
Path
cd /blue
cd /orange
Checking Quotas and Managing Space
home_quota
blue_quota
orange_quota
Important
We cannot store our data directly in storages. We need first check what group we are. And then store the data in that group.
slurmInfo -h
This code would display resource usage for your group.
We have three ways to get the computational recourses: srun, slurm, and OOD.
-
srunandslurmare working on terminal. -
OODis working on Jupyter.
Because connection to VScode is easy to edit our code and VScode also includes terminal, most time, we would use VScode.
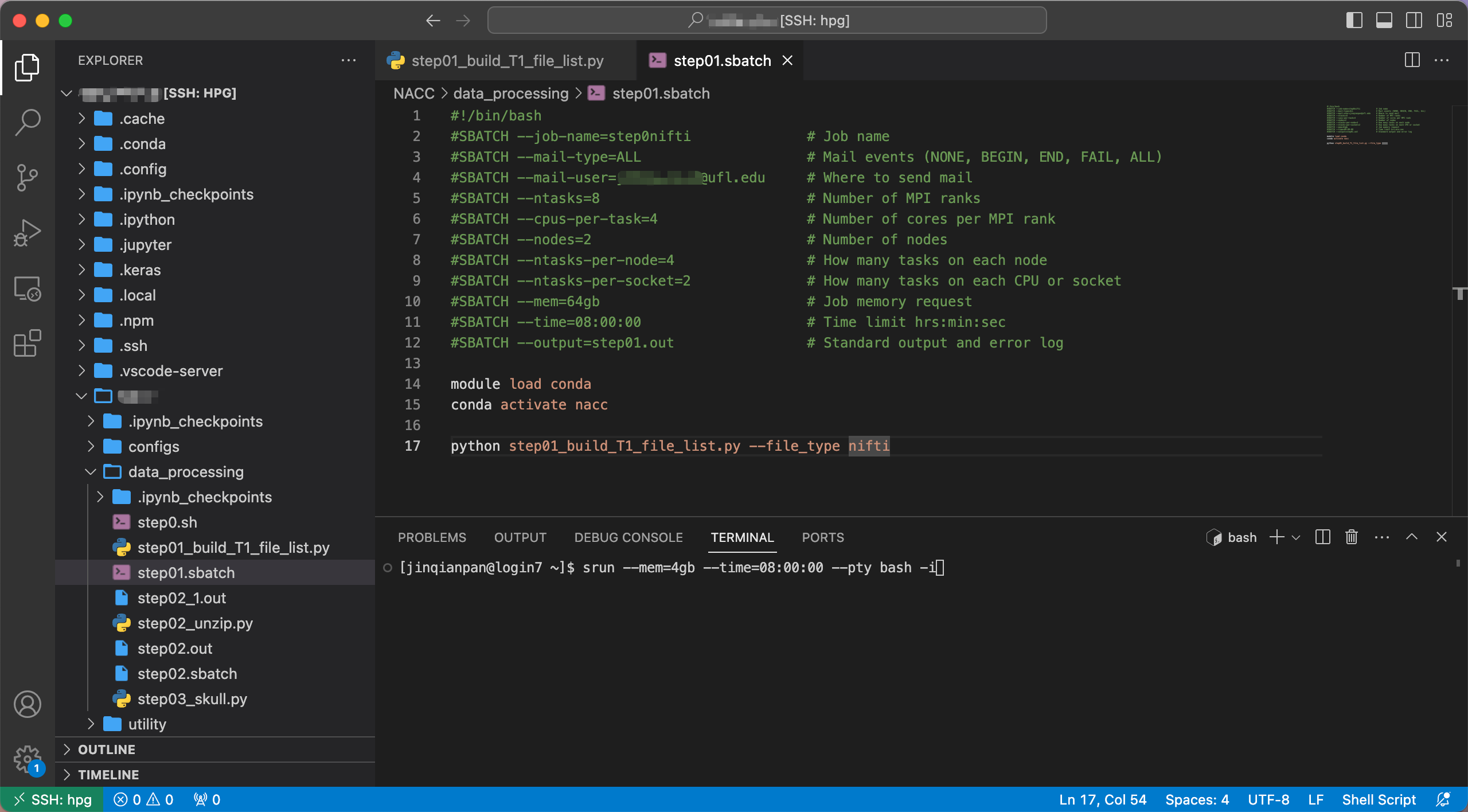
SRUN:
For the srun, you can just open the terminal from VScode and type the resourses you want. The Hipergator will allocate resources to you in your setting time (Shows in the bottom of image009). For more detail, please read the Official Documents for Srun.
This method is only suitable for debugging code. When debugging the code, you need to run slurm to complete the running of the code.
SLRUM:
For the slurm, you need to create a sbatch file first (the suffix is .sbatch). And enter the instructions you need resources into this file, then get the environment and run the python code. Just like what I show in the top and left of Image009. For more detail, please read the Official Documents for SLURM.
Tip
- module purge: clear all imported software environments.
- module load: load the environments you want.
module purge
module load cuda/12.2.0 intel/2020 openmpi/4.1.5 vasp/6.4.1
You can use https://ood.rc.ufl.edu/ to run the code on Jupyter Notebook/Lab.
The Hipergator has already a number of module for us. For more detail, please read the Official Documents for Module.
For loading these module:
module load env
However, we always want to build our own conda environment. Official Documents for Conda Environment
For running GPU in feature, we need to install
mamba install cudatoolkit=11.3 pytorch=1.12.1=gpu_cuda* -c pytorch
Before creating the environment, we need to load conda.
module load conda
Create the environment, change the name of the env and python version.
mamba create -n name python=3.9
And then you can use any command line of conda and pip.
Tip
Everytime you want use conda, you need to load it first:
module load conda
conda activate myenv
Warning
Still need time to figure out how to create the personal kernel.
You can try the method from Official document for Jupyter.
But the hipergator provides several kernels for Jupyter. For now, I just choose the kernel most similar to the personal kernel, and install the package in it.
Warning
Before coding in the VScode, please request resource first!
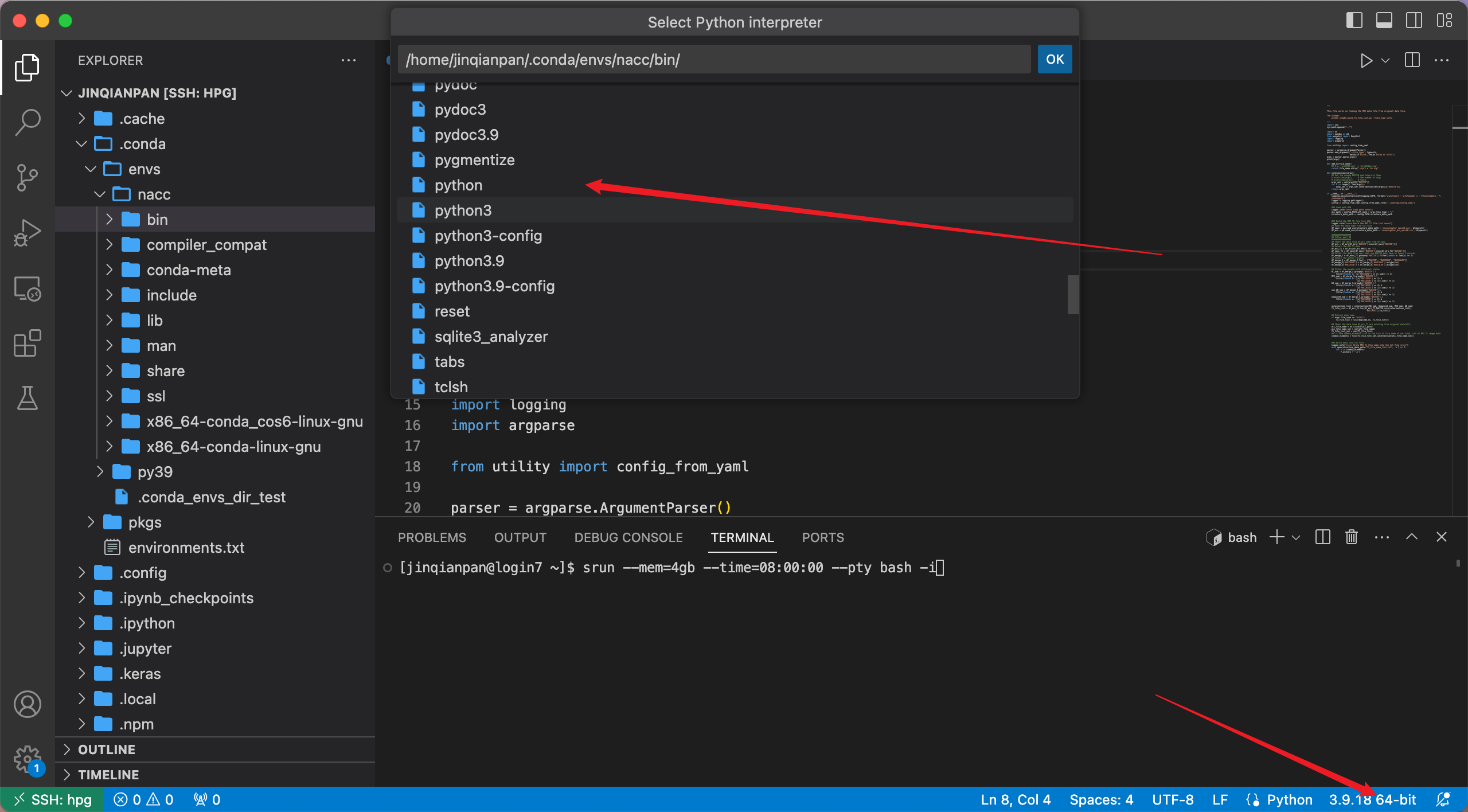
After getting resource and create a python file, we first set python interpreter.
First click the interpreter in the right bottom of VScode, just like image010.
And paste the path below. (Remamber change the UF_username and env_name)
/home/UF_username/.conda/envs/env_name/bin/
Caution
Although VScode could also open Jupyter file and find kernel use before method, the resource which we request COULD NOT use in this Jupyter. If you want to use Jupyter, PLEASE go to OOD!