Created by Raffael Bienz. As a final project for a DAS in Data Science at FHNW. Supervisor: Marco Willi
The example data was kindly provided by the Kanton of Aargau.
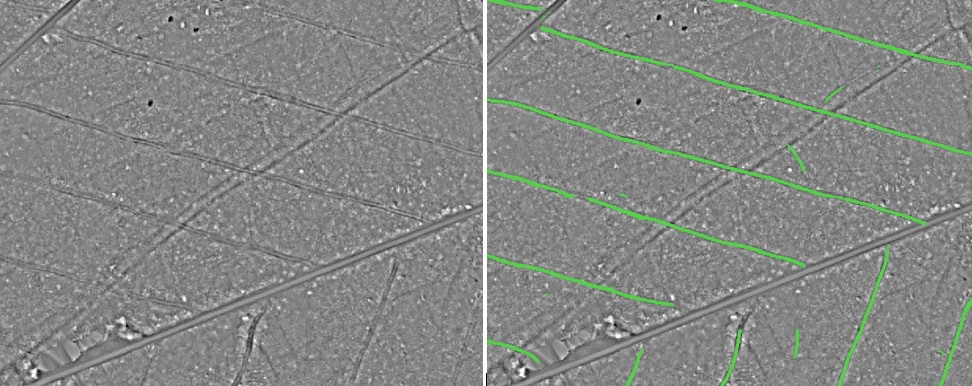
In this repository an algorithm is provided to automatically detect skid roads/trails in lidar data. The algorithm was specifically trained for skid roads/trails (Feinerschliessung), whereas forest roads (Waldstrassen) are not detected by this method.
Two datasets are required for the algorithm to work:
- Ground structure dataset of the area of interest (tif, with a 0.5 m resolution). Calculated based on Lidar data. For the method see: https://github.com/RaffiBienz/dtmanalyzer
- Forest delineation of the area of interest (polygons as shapefile).
Example datasets are provided in this repository.
A combination of R and Python are used. R is used for geoprocessing tasks during pre- and postprocessing and for vectorizing the segmentation masks. Python is used for the semantic segmentation of the ground structure data. The segmentation model is based on a U-Net architecture and was trained with 800 75x75 m windows of the ground structure dataset and the associated ground truth masks. For the vectorization of the segmentation masks a region growing algorithm was developed.
The segmentation model achieved a F1-Score of 0.6 on the validation dataset (Recall: 0.64, Precision: 0.57).
git clone https://github.com/RaffiBienz/skidroad_finder.git
Download the pretrained model from the following link and put in a folder named "model": https://drive.google.com/file/d/1-19k1sK8yHX16nlxd5rZcjLhEjcobTg0
Install Anaconda (https://docs.anaconda.com/anaconda/install/index.html)
Open Anaconda Prompt, change the directory to the root folder and type:
conda create -y -n skidroad_finder python==3.8
conda activate skidroad_finder
pip install -r ./src/requirements.txt
- Install R (https://www.r-project.org/) and add the path to Rscript to your PATH environment variable.
- Required packages: rgdal, rgeos, raster, imager, doParallel, foreach, sp (see requirements.R). These packages are automatically installed when main.R is run.
- If desired, open config.R and set configurations. If the main.R Script is run from RStudio, add the path to the python or the conda environment in config.R (Typically: C:/Users/USERNAME/.conda/envs/skidroad_finder/python.exe). If the main.R Script is run from the conda command prompt (this is the recommended method), just leave the default value "python".
Execute main.R from the root folder.
Rscript ./src/main.R
Interim results per forest delineation element are saved in the wd folder. The final products over the whole area of interest are saved in the results folder. The final segmentation mask is saved as raster dataset (tif). The vectorized segmentation mask is saved as a shapefile (shp). Use a GIS to visualize the results.
Alternatively to the above setup, you can also use the Dockerfile provided. Open a command prompt, cd into the root folder and execute:
docker build -t skidroad_finder .
docker run -v ${PWD}/wd:/skidroad_finder/wd -v ${PWD}/results:/skidroad_finder/results skidroad_finder
This starts a docker container which automatically executes the calculations and shuts down the container when it is finished. You then can find the model outputs in the results folder.
Final Result: